
- Aug. 6, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 136-147.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20223039
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
DONG Hongchun1,ZHANG Zhilan1,WANG Ning3,TANG Dandan1,QIU Zihui1,SHU Jie1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-24
Published:2023-06-05
Online:2023-03-14
Contact:
SHU Jie
E-mail:shujie@suda.edu.cn
CLC Number:
DONG Hongchun,ZHANG Zhilan,WANG Ning,TANG Dandan,QIU Zihui,SHU Jie. The Improved Solid-state NMR Quantitative Method on the Bases of Multiple-cross Polarization Technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 136-147.

Fig. 1
(a) The pulse sequence of MLGCP-1 method with the following phase cycles: Ф1 = y, -y; Ф2 = x; Ф3 = -y, y; Ф4 = x, x, -x, -x, y, y, -y, -y; Ф5 = - y, y, y, -y, x, -x, -x, x; Ф6 = y, -y, - y, y, -x, x, x, -x; Ф7 = -y; Ф8 = y; ФRec= x, -x, -x, x, y, -y, -y, y; (b) multiCP pulse sequence with following phase cycles: Ф1 = y, -y; Ф2 = x; Ф3 = -y, y; Ф4 = x, x, -x, -x, y, y, -y, -y; Ф5= -y, y, y, -y, x, -x, -x, x; Ф6 = y, -y, -y, y, -x, x, x, -x; ФRec = x, -x, -x, x, y, -y, -y, y

Table 1
TCH and T 1 ρ Hvalues of L-alanine and L-valine measured under ramp-CP and LGCP conditions
| Sample | Carbons | T1,H/ms | ramp-CP | LGCP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCH/ms | TCH/ms | ||||||
| L-alanine | 1 | 977.1 | 0.170 | 1.7 | 0.387 | 12.8 | |
| 2 | 0.042 | 0.174 | |||||
| 3 | 0.360 | 0.331 | |||||
| L-valine | 4 | 718.5 | 0.174 | 2.5 | 0.414 | 24.3 | |
| 5 | 0.036 | 0.157 | |||||
| 6 | 0.033 | 0.120 | |||||
| 7 | 0.290 | 0.240 | |||||
| 8 | 0.154 | 0.374 | |||||

Fig. 3
The cross polarization 1H→13C dynamic curves of CH3, CH and CO groups in L-alanine by using the schemes of (a) ramp-CP, (b) LGCP, (c) multiCP and (d) MLGCP-1; The percentage errors of L-alanine were calculated according to the normalized peak integrals, by using the schemes of (e) ramp-CP, (f) LGCP, (g) multiCP and (h) MLGCP-1. The red background highlights the regions with percentage errors less than 5%
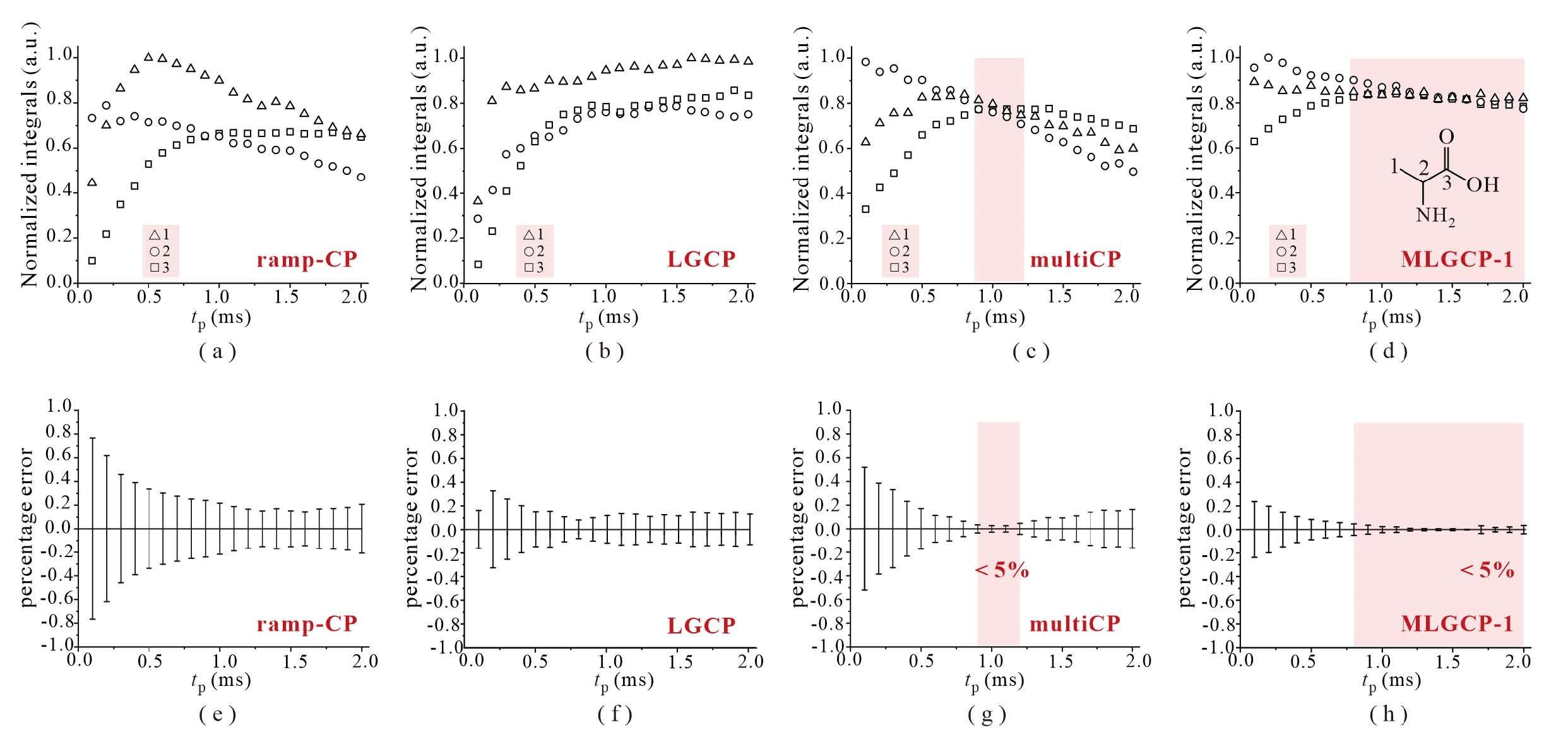
Fig. 4
The cross polarization 1H→13C dynamic curves of the five groups in L-valine by using the schemes of (a) ramp-CP, (b) LGCP, (c) multiCP and (d) MLGCP-1; The percentage errors of L-valine were calculated according to the normalized peak integrals, by using the schemes of (e) ramp-CP, (f) LGCP, (g) multiCP and (h) MLGCP-1. The red background highlights the regions with percentage errors less than 5%


Fig. 5
The two-dimensional projection diagrams of normalized integrals of (a) CO, (b) CH, (c) CH3 in L-alanine using MLGCP-1 method, the normalized integrals was modulated by the experimental parameters tp and td. (d) The two-dimensional projection of the percentage errors under corresponding experimental parameters. multiCP method was employed for comparison. The corresponding diagrams were plotted in (e)~(h)

Fig. 6
The two-dimensional projection diagrams of normalized integrals of (a) CO, (b) CH, (c) CH3 in L-alanine using MLGCP-1 method. The normalized integrals was modulated by the experimental parameters tp and n. (d) The two-dimensional projection of the percentage errors under corresponding experimental parameters. multiCP method was employed for comparison. The corresponding diagrams were plotted in (e)~(h)


Fig. 7
The impact of TCH difference in L-valine on the quantified range of tp. (a) MLGCP-1 percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 8%; (b) MLGCP-1 percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 76%; (c) MLGCP-1 percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 89%; (d) multiCP percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 8%; (e) multiCP percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 76%; (f) multiCP percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 89%. TCH values were measured under ramp-CP condition
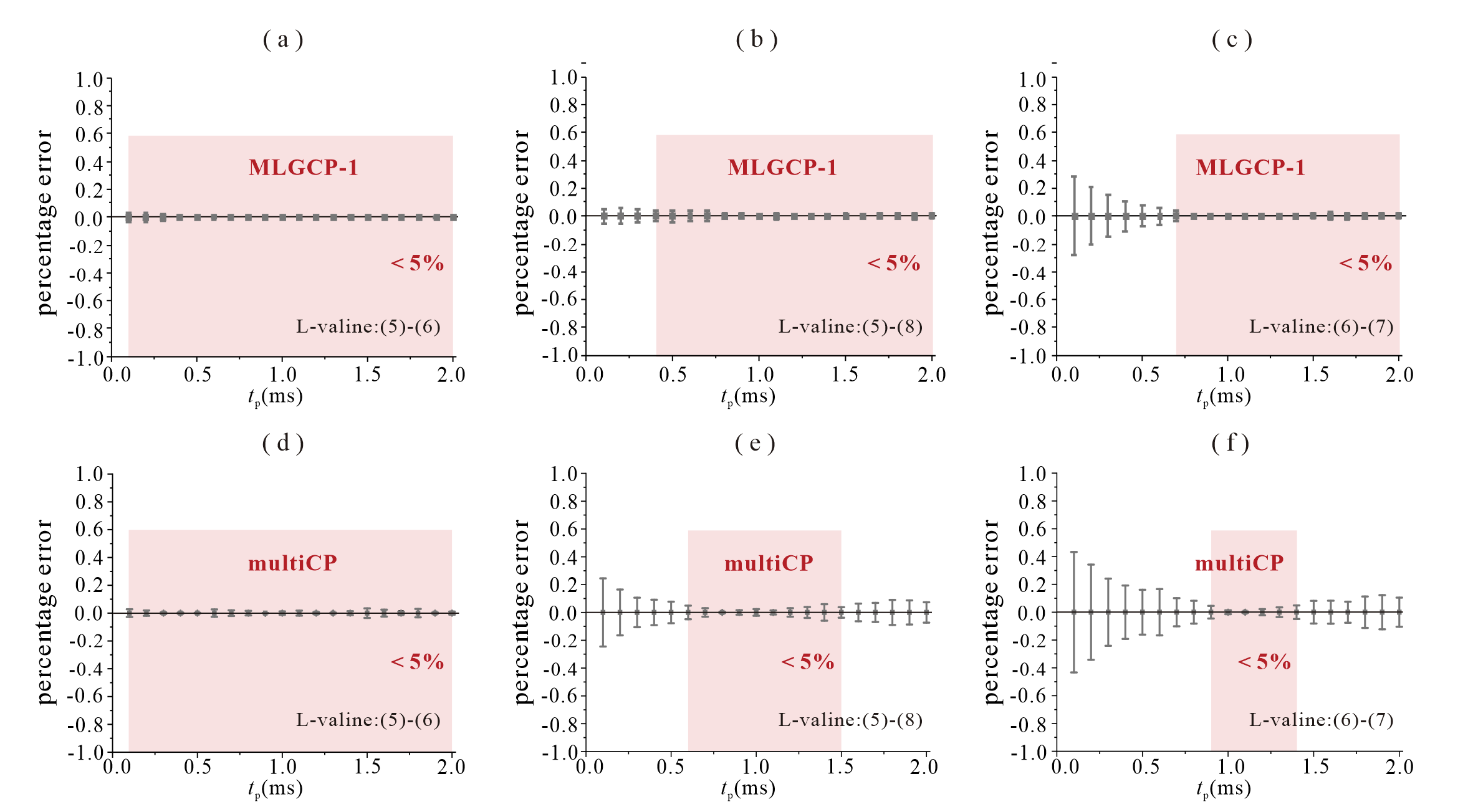
Table 2
The percentage errors of multiCP and MLGCP-1 results measuring from three L-alanine/L-valine mixtures with different component contents
| 样品组分 | tp/ms | MLGCP-1百分误差/% | multiCP百分误差/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/5 | 2/6 | 3/6 | 2/5 | 2/6 | 3/6 | |||
| 1:3 | 0.5 | 1.29 | 0.94 | 14.4 | 4.54 | 4.40 | 18.2 | |
| 1.0 | 1.80 | 4.57 | 4.53 | 0.85 | 8.35 | 10.2 | ||
| 1.5 | 4.91 | 3.88 | 4.05 | 0.22 | 12.5 | 28.5 | ||
| 2.0 | 3.63 | 1.27 | 10.1 | 0.58 | 18.7 | 51.0 | ||
| 1:1 | 0.5 | 1.24 | 1.84 | 9.67 | 0.49 | 1.31 | 20.1 | |
| 1.0 | 1.33 | 1.40 | 3.16 | 1.14 | 2.14 | 3.96 | ||
| 1.5 | 1.09 | 1.13 | 3.54 | 0.83 | 2.63 | 12.7 | ||
| 2.0 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 4.40 | 3.71 | 0.70 | 23.1 | ||
| 3:1 | 0.5 | 0.72 | 2.09 | 6.99 | 2.31 | 0.46 | 11.9 | |
| 1.0 | 2.14 | 1.76 | 2.34 | 0.68 | 4.99 | 4.09 | ||
| 1.5 | 0.06 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 0.72 | 7.29 | 9.63 | ||
| 2.0 | 0.92 | 1.48 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 9.98 | 14.2 | ||
| [1] | KOMOROSKI R A. High resolution NMR spectroscopy of synthetic polymers in bulk[M]. Florida: VCH. 1986. |
| [2] | MEHRING M. Principles of high resolution NMR in solids[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. 1983. |
| [3] | DUER M J. Introduction to solid state NMR spectroscopy[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Science. 2004. |
| [4] |
MAO J D, CAO X Y, OLK D C, et al. Advanced solid-state NMR spectroscopy of natural organic matter[J]. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc, 2017, 100: 17-51.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.11.003 |
| [5] |
ZHANG L L, CHEN Q, HANSEN E W. Morphology and phase characteristics of high-density polyethylene probed by NMR spin diffusion and second moment analysis[J]. Macromol Chem Phys, 2005, 206(2): 246-257.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3935 |
| [6] |
ZHANG L L, LIU Z, CHEN Q, et al. Quantitative determination of phase content in multiphase polymers by combining spin-diffusion and CP-MAS NMR[J]. Macromolecules, 2007, 40(15): 5411-5419.
doi: 10.1021/ma0707786 |
| [7] |
LIU H W, ZHOU X Y, CHEN Q, et al. Accurate quantitative and maximum cross polarization via multiple ramped contacts[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2017, 679: 233-236.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2017.05.009 |
| [8] |
SHU W F, ZHANG S M. Relaxation compensated and intensity recovered dynamics of cross polarization in the frame of reciprocity relation[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2011, 511(4-6): 424-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2011.06.037 |
| [9] |
HOU G J, DING S W, ZHANG L M, et al. Breaking the T-1 constraint for quantitative measurement in magic angle spinning solid-state NMR Spectroscopy[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132(16): 5538-5539.
doi: 10.1021/ja909550f |
| [10] |
HOU G J, DENG F, DING S W, et al. Quantitative cross-polarization NMR spectroscopy in uniformly C-13-labeled solids[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2006, 421(4-6): 356-360.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2006.01.105 |
| [11] |
GU J L, ZHANG T T, ZHAO H P, et al. Time-saving and highly applicable quantitative method based on solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance techniques[J]. Chem J Chin Univ, 2018, 39(3): 463-469.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v39.2 |
|
顾佳丽, 张田田, 赵辉鹏, 等. 耗时短、通用性强的固体核磁共振交叉极化定量检测方法[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(3): 463-469.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v39.2 |
|
| [12] |
SHU J, CHEN Q, ZHANG S M. Quantification of cross polarization with relaxation compensated reciprocity relation in NMR[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2008, 462(1-3): 125-128.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2008.07.026 |
| [13] |
JOHNSON R L, SCHMIDT-ROHR K. Quantitative solid-state C-13 NMR with signal enhancement by multiple cross polarization[J]. J Magn Reson, 2014, 239: 44-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2013.11.009 |
| [14] |
DUAN P, SCHMIDT-ROHR K. Composite-pulse and partially dipolar dephased multiCP for improved quantitative solid-state C-13 NMR[J]. J Magn Reson, 2017, 285: 68-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2017.10.010 |
| [15] |
HOU G J, DENG F, YE C H, et al. Towards uniform enhancement in solid-state cross polarization magic angle spinning NMR: A scheme incorporating cross polarization with rotational resonance[J]. J Chem Phys, 2006, 124(23): 234512.
doi: 10.1063/1.2206787 |
| [16] | GERSTEIN B C, DYBOWSKI C R. Transient techniques in NMR of solids: An introduction to theory and practice[M]. San Diego: Academic Press. 1985. |
| [17] |
ZHANG S M, WU X L, MEHRING M. Successive polarization under mismatched Hartmann-Hahn condition[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 1990, 166(1): 92-94.
doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(90)87056-W |
| [18] |
RAYA J, PERRONE B, HIRSCHINGER J. Chemical shift powder spectra enhanced by multiple-contact cross-polarization under slow magic-angle spinning[J]. J Magn Reson, 2013, 227: 93-102.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.12.006 pmid: 23314257 |
| [19] |
RAYA J, HIRSCHINGER J. Sensitivity enhancement by multiple-contact cross-polarization under magic-angle spinning[J]. J Magn Reson, 2017, 281: 253-271.
doi: S1090-7807(17)30167-2 pmid: 28662486 |
| [20] |
BERNARDINELLI O D, LIMA M A, REZENDE C A, et al. Quantitative C-13 MultiCP solid-state NMR as a tool for evaluation of cellulose crystallinity index measured directly inside sugarcane biomass[J]. Biotechnol Biofuels, 2015, 8(110): 1-11.
doi: 10.1186/s13068-014-0179-6 |
| [21] |
SAIDI F, TAULELLE F, MARTINEAU C. Quantitative C-13 solid-state NMR spectra by multiple-contact cross-polarization for drug delivery: From active principles to excipients and drug carriers[J]. J Pharm Sci, 2016, 105(8): 2397-2401.
doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2016.05.025 |
| [22] |
DUARTE R M B O, DUAN P, MAO J D, et al. Exploring water-soluble organic aerosols structures in urban atmosphere using advanced solid-state C-13 NMR spectroscopy[J]. Atmos Environ, 2020, 230: 117503.
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117503 |
| [23] |
CHU W Y, CAO X Y, SCHMIDT-ROHR K, et al. Investigation into the effect of heteroatom content on kerogen structure using advanced C-13 solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Energ Fuels, 2019, 33(2): 645-653.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b01909 |
| [24] |
ZHANG Y L, LI L J, YAO S H, et al. Distinct changes in composition of soil organic matter with length of cropping time in subsoils of a Phaeozem and Chernozem[J]. Eur J Soil Sci, 2018, 69(5): 868-878.
doi: 10.1111/ejss.2018.69.issue-5 |
| [25] |
WANG X Y, HAN X X, YOU Y L, et al. Molecular characterization of Dachengzi oil shale kerogen by multidimensional solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Fuel, 2021, 303(6): 121215.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121215 |
| [26] |
ZHANG Z L, WANG N, TANG D D, et al. Experimental set-up and application research of solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance Multiple-CP technique[J]. Chem J Chin Univ, 2021, 42(3): 784-793.
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200698 |
|
张志兰, 王宁, 唐丹丹, 等. 固体核磁共振Multiple-CP定量技术的参数优化与应用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 784-793.
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200698 |
|
| [27] |
GOLDBURG W I, LEE M. Nuclear magnetic resonance line narrowing by a rotating RF field[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1963, 11(6): 255-258.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.11.255 |
| [28] | LEE M, GOLDBURG W I. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance line narrowing by a Rotating RF field[J]. Phys Rev, 1965, 140(4a): 1261-1271. |
| [29] |
PEERSEN O B, SMITH S O. Rotational resonance NMR of biological membranes[J]. Concepts Magn Reson, 1993, 5(4): 303-317.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0534 |
| [30] |
BENNETT A E, RIENSTRA C M, AUGER M, et al. Heteronuclear decoupling in rotating solids[J]. J Chem Phys, 1995, 103(16): 6951-6958.
doi: 10.1063/1.470372 |
| [31] |
MORCOMBE C R, ZILM K W. Chemical shift referencing in MAS solid state NMR[J]. J Magn Reson, 2003, 162(2): 479-486.
pmid: 12810033 |
| [32] |
LADIZHANSKY V, VEGA S. Polarization transfer dynamics in Lee-Goldburg cross polarization nuclear magnetic resonance experiments on rotating solids[J]. J Chem Phys, 2000, 112(16): 7158-7168.
doi: 10.1063/1.481281 |
| [33] |
FU R, HU J, CROSS T. Towards quantitative measurements in solid-state CPMAS NMR: A Lee-Goldburg frequency modulated cross-polarization scheme[J]. J Magn Reson, 2004, 168(1): 8-17.
pmid: 15082244 |
| [34] |
JOHNSON R, SCHMIDT K. Quantitative solid-state 13C NMR with signal enhancement by multiple cross polarization[J]. J Magn Reson, 2014, 239: 44-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2013.11.009 |
| [1] | Wen-jie YANG,Jun HUANG. Analysis of Local Structure, Acidic Property and Activity of Solid Acids by Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 460-473. |
| [2] | Zi-chun WANG,Jun HUANG,Yi-jiao JIANG. Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy Studies of Enhanced Acidity of Silica-Aluminas Based on Penta-Coordinated Aluminum Species [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 552-570. |
| [3] | Chao-wei SHI,Pan SHI,Chang-lin TIAN. NMR Studies of Large Protein Dynamics Using Unnatural Amino Acids [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 523-532. |
| [4] | WEI Ling, ZHANG Shan-min. Suppressing Background 13C NMR Signal From the Probe Head by Phase Incremented Pulses [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 123-130. |
| [5] | LIANG Li-xin, DENG Feng, HOU Guang-jin. Quantitative Cross Polarization Magic-Angle Spinning NMR Spectroscopy in Solids [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 1-15. |
| [6] | SUN Yi, CHEN Yan-ke, LI Jian-ping, ZHAO Yong-xiang, YANG Jun. Efficiency of Double Cross Polarization in Magic-Angle Spinning Solid-State NMR Studies on Membrane Proteins [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2017, 34(3): 257-265. |
| [7] | ZHAN You-yang, XUE Rong, ZHU Yun-long, LI Xiao-jing, PEI Feng-kui, FENG Jiang-hua. A Biocompatible Gadolinium-Based Amino Acid Copolymer Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2016, 33(4): 635-645. |
| [8] | HUANG Jing, TANG Hui-Ru. Measurement of Spin Relaxation Times for Studying the Molecular Dynamics of Solid Metabolites [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2012, 29(4): 605-620. |
| [9] | WANG Zhe, FENG Yu-Ping, Liu-Lin-Yuan, SHAN Lu, ZHAO Yu-Fen. Natural Abundance N-Phosphoryl Amino Acids Studied by 15N NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2009, 26(4): 512-517. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lei, YANG Guang, CHEN Qun. Influence of CP time on Intermolecular Cross Polarization in the Composite of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) and Fullerene [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2005, 22(3): 245-251. |
| [11] | MEI Hu, ZHOU Peng, QIN Ren-Hui, ZHOU Yuan, LIANG Gui-Zhao, ZENG Hui, TIAN Fei-Fei, LI Zhi-Liang. Calculation of 13C Chemical Shifts of Amino Acids Using Atomic Electronegativity Interaction Vector [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2005, 22(2): 163-172. |
| [12] | LIU Li-Jun, ZHONG Bo-Hua, MIAO Zhen-Chun. An NMR Study of Thymopoietin [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2005, 22(2): 201-207. |
| [13] | YU Zhi-li, GAO Li-mei, LIU Zong-ying, LI Yan-ping, YANG Peng. AN IMPROVED METHOD FOR CALCULATING 17O NMR CHEMICAL SHIFT OF HYDROXYL GROUP IN CARBOXYLIC ACIDS [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2003, 20(4): 415-419. |
| [14] | SHAO Wei-yan, ZHONG Shi-zhou, HU Xiao-peng, CAI Ji-wen. NMR STUDIES OF COMPLEXES [Co(TREN)(AMINO ACIDATO-N, O)]X2·nH2O IN S OLUTION [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2002, 19(2): 149-157. |
| [15] | LI Zhiliang, ZHOU Liping, XIA Zhining, LIU Yan, ZHANG Mengjun, PENG Haijiao, LIU Shushen, YU Banmei. ON VADE CHARACTERIZATION AND 13C NMR SIMULATION FOR AMINO BASES [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2000, 17(4): 309-315. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 283
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 206
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||