引言
从实验采集信号属性及提取信息的不同,核磁共振波谱技术可以大致分为傅里叶核磁共振(Fourier NMR)与拉普拉斯核磁共振(Laplace NMR)两大类[1].Fourier NMR可获取化学位移信息,是解析分子结构的强大工具[2];而Laplace NMR可提供扩散系数或弛豫时间的信息,从中人们可分析分子的化学结构、物理环境,得到分子动力学及构象、相互作用等信息[3,4].例如,扩散排序谱(DOSY,diffusion ordered spectroscopy)或者扩散NMR(Diffusion NMR)[5⇓⇓-8]即属于Laplace NMR,利用该技术可对混合物进行虚拟分离,从而解析出样品中不同的分子成分[9],或利用分子扩散系数分析其物理环境、分子大小、聚合程度等等[10].而测量横向或纵向弛豫时间的实验也同样属于Laplace NMR,在材料化学领域,研究者常通过对弛豫参数的分析获取物质成分或多孔材料的孔径大小分布信息[11⇓-13];在结构生物学领域,弛豫参数的测量可有助于研究者们了解蛋白质等大生物分子的构象、相互作用及动力学信息[14].
在Fourier NMR中所采集的自由感应衰减(FID,free induction decay)信号是具有振荡与衰减的复指数信号,一个极简化的信号模型如(1)式所示:
式中t是演化时间,
而在Laplace NMR中所采集的是仅有衰减的无振荡指数信号,一个极简化的信号模型如(2)式所示:
式中b是实验中的演化量,在DOSY实验中b是与梯度场强度有关的变量[15],而对于弛豫实验而言b是演化时间变量;
傅里叶变换为酉变换,时域与频域之间的相互变换均有唯一的结果.而与之不同的是,拉普拉斯变换并不具有良好的反变换形式,即,实验采集信号
1 Laplace NMR数据反演问题的不适定性
Laplace NMR数据反演问题存在着较强的不适定性[16],即可能存在无穷多个解,或者解对于输入数据的微小变化是高度敏感的.在数学中,一个适定问题应该有唯一的解,并且在输入数据的扰动下解仍然保持稳定,而不适定性问题需要额外的信息或约束条件来确保唯一性和稳定性.
在Laplace NMR数据处理时,有两大类处理方案,一类涉及参数定量问题,而另一类则是参数定性分析.无论是定量或定性分析问题,均面临不适定性的挑战,下面我们将分别举例说明.
1.1 参数定量问题的多解性
尽管扩散过程和弛豫过程具有不同的物理本质,但在核磁共振实验中获取的实验信号具有相似的数学描述,即信号将经由指数衰减趋于平衡.在扩散系数或弛豫时间参数分布已知的情况下,其对应实验中可采集到的衰减信号可以通过一个前向的物理模型进行仿真.上一节(2)式是一个简化的单指数模型,而一个更一般的表达形式为:
(3)式中,衰减参数σ由扩散系数或弛豫时间决定(比如在横向弛豫实验中
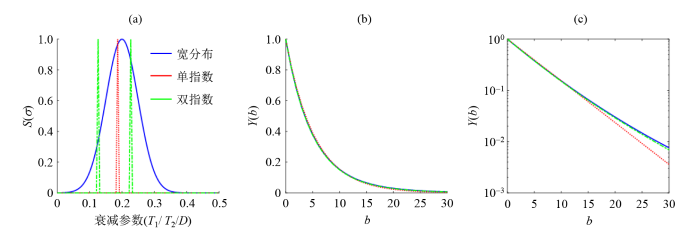
在图1中给出一个例子.图1(a)中展示了三种
图1
图1
(a) 不同衰减参数分布情况,及其对应的实验仿真信号 (b) 线性坐标显示 (c) 对数坐标显示
Fig. 1
(a) Different distributions of decaying factors, and the corresponding decay signals (b) linear scale (c) logarithmic scale
1.2 扩散谱定性分析的多解性
在扩散NMR的数据处理中,很多情况下并不需要得到精准的定量结果,而仅需要将不同成分所对应的信号分离开来,这类任务通常被称为定性分析.上一小节我们提到扩散系数的定量估计可能存在多解,而定性分析是否唯一呢?
在扩散NMR(或DOSY)的数据处理中,实验采集的二维信号有一个维度代表演化时间,另一个维度代表与梯度强度相关的演化量b:
其中,γ是旋磁比,δ是梯度脉冲宽度,g为梯度场强,
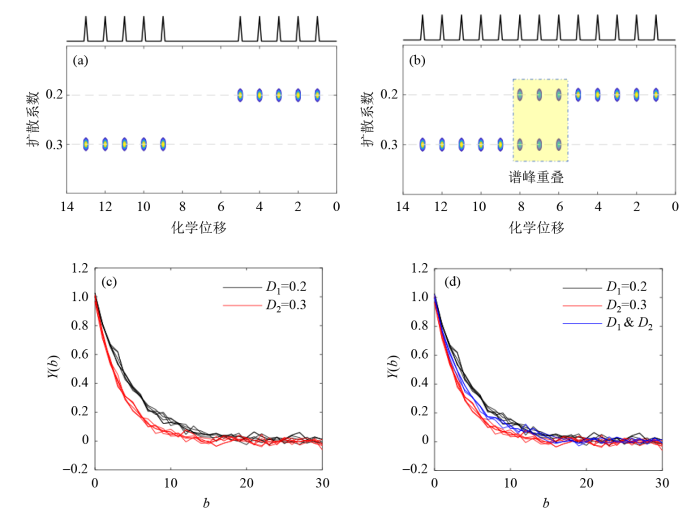
图2
图2
含有两个扩散成分的仿真DOSY谱:(a)谱峰无重叠,(b)谱峰有重叠;对应的实验仿真信号:(c)谱峰无重叠,(d)谱峰有重叠
Fig. 2
DOSY spectra with two diffusion components: (a) without peak overlap, (b) with peak overlap; and corresponding experimental signals: (c) without peak overlap, (b) with peak overlap
图3
图3
两个实际样品的实验采集数据 (a) QGC(包含奎宁、香叶醇、莰烯)(b) GSP(包含葡萄糖、蔗糖、聚乙二醇600)
Fig. 3
The DOSY experimental data of two samples (a) QGC (containing quinine, geraniol, and camphene) (b) GSP (containing glucose, sucrose, and PEG 600)
因此,无论是定量分析还是定性分析,Laplace NMR的数据处理均涉及不适定的逆问题求解,这意味着可能存在多个解.不同的算法可以通过不同的约束来限制解的空间,从而得到符合预期的结果.在经典的Laplace NMR信号处理算法中,将采用人为给定的信号模型或正则化约束项,这些条件是依据理想信号的先验信息而设计的,在下一节中我们将对这类经典算法进行介绍.
2 经典Laplace NMR信号处理算法
根据解的构造形式的不同,经典的Laplace NMR信号处理算法可以分成两大类:一是参数拟合算法,二是网格化重建算法,另外近年来也出现了二者的结合算法,下面我们将分别进行介绍.
2.1 基于给定成分数量的参数拟合算法
参数拟合算法需要事先给定理想的信号模型,不仅包含衰减函数(例如:指数衰减),还需要包含具体的成分数量.比如,若假设分散体系样本是均匀且单一的,则采集到的扩散NMR将具有单指数衰减的形式,如(2)式所示.而如果分散体系不单一,我们需要预先给定明确的信号物理模型,如:
其中P代表预先给定的成分数量,
其中
依据处理序列的并行或串行形式,参数拟合算法又分为单变量拟合(Univariate Fitting)与多变量拟合(Multivariate Fitting).在单变量拟合中[17⇓-19],(6)式中的
而多变量拟合方法则对所有序列进行并行处理,代表性算法包括:直接指数曲线解析算法(DECRA,direct exponential curve resolution algorithm)[23⇓⇓-26],NMR成分分析方法(CORE,component resolved NMR)[27⇓-29],成分分析加速算法(SCORE,speedy component resolution)[30],多参数曲线解析(MCR,multivariate curve resolution)[31],谱图成分优化解析算法(OUTSCORE,optimized unmixing of true spectra for component resolution)[32].与单变量拟合方法中依次处理各个衰减Y_{i}不同的是,多变量拟合方法将同时处理
其中
其中
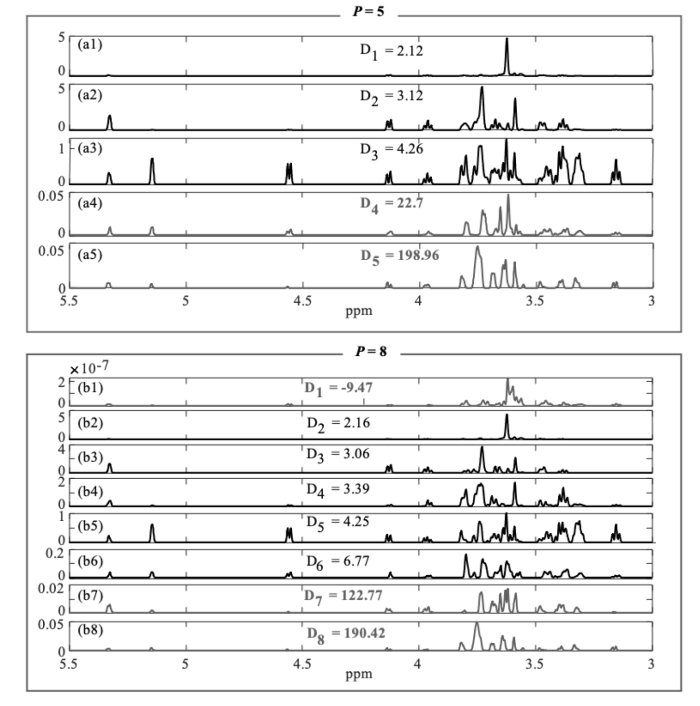
然而,多参数拟合方法在实际应用时会因为预设信号模型(5)式与实际信号的差别而产生错误的参数估计结果.例如,若设定的成分数P不等于实际样品中的成分数,则算法结果会与实际有较大差别,甚至无法收敛.举个具体例子,选择两种标准混合物样品GSP与QGC的DOSY数据(即图3所示的两组数据),采用SCORE并选择不同的P值进行多参数拟合,算法收敛需要迭代的步数及计算时间如表1所示.这两个样品中均包含3种不同的成分,故理想的P值应该设置为3,在P = 3时SCORE计算GSP数据只需要不到100步即可收敛,而在P > 3时收敛过程将显著变慢,并且计算过程中采用非负最小二乘法常出现无法达到计算精度要求的报错提醒.
表1 SCORE算法收敛步数与P值的关系
Table 1
| P | 3 | 5 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSP | 计算时间/s | 11 | 110 | 650 |
| 收敛步数 | 91 | 906 | 4847 | |
| QGC | 计算时间/s | 50 | 244 | 1988 |
| 收敛步数 | 101 | 435 | 3389 |
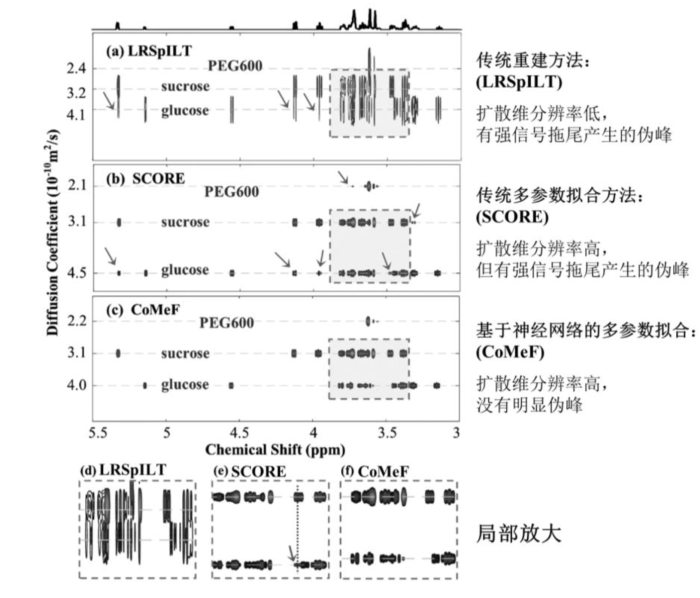
同时,我们在图4中展示了在P = 5与P = 8时SCORE对GSP数据的计算结果.P = 5时,计算中出现两个具有较大扩散系数的无效成分,如图4(a4)、(a5)所示;而P = 8时出现了3个无效成分,如图4(b1)、(b7)、(b8)所示,并且把实际中的3个成分拆分成了5个成分,出现了过拟合.无效成分的存在将使拟合方程中的系数矩阵更加病态,比如在扩散系数值D特别大的时候,序列
图4
图4
采用SCORE算法对混合物GSP的DOSY谱成分分离结果. (a1)~(a5)设置P=5时得到的5个成分对应的频谱;(b1)~(b8)设置P=8时得到的8个成分对应的频谱. 红色标注谱图为无效成分
Fig. 4
Separated spectra of SCORE on a three-component-mixture GSP. (a1)~(a5) the spectra of 5 components when P is set to 5; (b1)~(b8) the spectra of 8 components when P is set to 8. Red color denotes the ineffective components
2.2 基于正则化约束的网格化重建算法
与参数拟合方法不同,网格化重建算法不需要给定成分个数,该类算法把参数维划分成网格,并在由网格点构成的信号空间中进行实验数据的表征.人们习惯将这样的结果称为“重建”谱图,因为它等同于对处理信号进行了一次包含编解码的重新表征过程.从(3)式中可以看出,待求解的衰减参数分布
在将(3)式中的
其中
不同的正则化约束会带来不一样的谱图结果,常见的约束项有非负性约束、稀疏约束、光滑性约束等.非负性约束可保证Laplace重建谱图具有明确的物理意义,即(8)式中的S矩阵所有元素均需要大于等于0,或(5)式中每个衰减成分的强度值均需大于等于0.稀疏性约束对应于S的l1范数正则化项(即
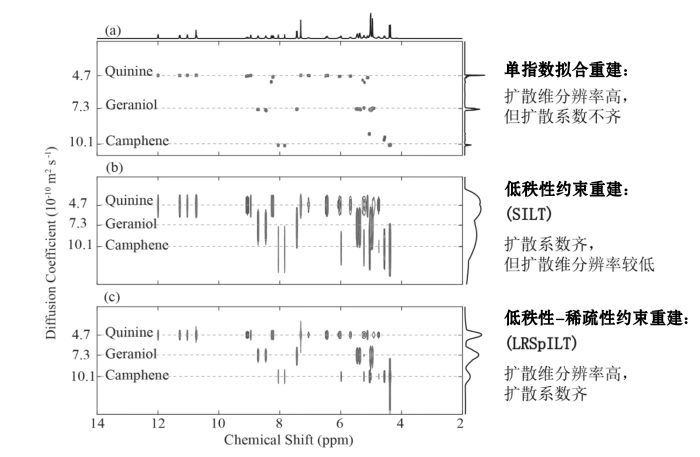
具体而言,英国曼彻斯特大学的Morris等人在其重建算法中采用谱图的l2范数正则化项[18],法国德特拉斯堡大学的Delsuc等用最大熵约束法[41],英国萨塞克斯大学的Day等人用Tikhnov正则化方法平滑重建结果和增强算法稳定性[42],这几种方法都可归为基于l2范数的光滑性约束;波兰华沙大学的Urbańczyk等人用稀疏性(即l1范数)与非负性约束保证重建结果的有效性,该方法被称为多指数衰减的迭代阈值算法(ITAMed,iterative thresholding algorithm for multiexponential decay)[35].本课题组在ITAMed算法基础上改进了优化算法,采用TNIPM算法获得了更高效且效果更好的重建谱图[40].
上述这类方法均属于单变量算法,即在处理类似DOSY的多衰减序列时,各衰减序列的ILT重建过程实质上是相互独立的.因此,这类算法重建的谱图对齐性较差,也就意味着同一分子的不同谱峰可能显示多个扩散系数值,而理想情况下同一分子的所有谱峰应该显示同一扩散系数值.因此,重建谱的对齐性不佳将直接影响混合物分子的组分分析.
近些年来,出现了一些多变量的网格化重建方法,相比于单变量方法而言,多变量的方法中各衰减序列的ILT重建并不是独立的,需要联合优化以实现完整的谱图重建,而一般这一过程也是由特殊的正则化项所控制的.比如,中国科学院精密测量科学与技术创新研究院的刘买利和张许课题组用低秩性约束使重建结果具有规整的对齐性,该方法被称为Laplace NMR的联合反演算法(SILT,simultaneous inversion of Laplace transform)[43].在这一方法中,所采用的正则化项为谱图矩阵S的核范数:
针对于SILT的重建结果在扩散维分辨率低的问题,本课题组开发了同时约束低秩性与稀疏性的DOSY谱重建算法,得到了兼具高分辨率和规整对齐性的谱图.该算法被称为结合低秩和稀疏的Laplace反演(LRSpILT,low-rank and sparse inverse Laplace transform)[44],其目标函数中加入了两个正则化项:
图5
2.3 参数拟合结合正则化约束的算法
上文中提到,网格化重建方法获取的是参数的分布,但可能出现谱峰过宽、分辨率低的问题,这是因为网格化重建对成分个数没有限制,导致谱图无法进一步简化.而拟合方法可直接获取参数值,但需要指定信号模型,容易受实测数据中的噪声等不理想因素影响,使重建结果出现相同成分的谱峰不对齐、或伪峰太多等问题,这本质上是由于拟合方法的目标函数中对重建谱图属性的约束不够.
针对于以上两大类方法的问题,本课题组于2022年提出一种混合式的算法,称为协同多指数拟合(CoMeF,Coordinated Multi-exponential Fitting)[45].在这一方法中,我们在多参数拟合模型中加入了正则化项,以限制拟合模型的复杂度,避免数据过拟合,如(11)式所示:
如拟合算法一样需要给定成分数P,但与(7)式不同的是,在(11)式中多了一个正则化项,为了约束重建谱图的稀疏性以减少伪峰的出现,我们采用的是加权l1范数.而这种带正则化项的多参数拟合模型比单纯只含保真项的目标函数复杂,且具有非凸特性,若采用前文提及的经典优化算法均无法得到收敛且有效的结果,因此我们设计了一种基于神经网络的优化算法[46]对其进行求解,最终得到了相比于传统算法而言更优的拟合结果.
图6
该算法中虽然引入了神经网络,但也仅仅将其作为优化器,算法的关键在于设计目标函数,其中需要加入人为定义的正则化项.因此,尽管使用了神经网络,该算法仍应归类于经典算法.
2.4 经典算法的总结
第2部分我们介绍了Laplace NMR数据处理的经典方法,从中可以看出整体上经典方法有两大问题:首先,预设信息是很重要的,在参数拟合算法中需要用户给出预设的信号模型(包括成分个数),而在网格化重建方法中需要设定先验信息,并需要根据不同的数据调整正则化参数.在这个过程中将有大量的人工干预,对于相同的数据,不同用户可能会给出不同的重建结果.其次,经典方法十分依赖优化算法的设计,涉及大量数学公式推导以及收敛条件的摸索,算法的适用性与鲁棒性均受到复杂数据条件下的挑战.
3 基于深度学习的Laplace NMR谱图重建
近年来,机器学习与人工智能技术在信号处理领域有了不少成功的应用,也为Laplace反演问题提供了全新的解决思路.在磁共振领域,研究者们基于深度学习开发出很多比传统方法而言更高效准确的信号处理方法.比如,厦门大学陈忠和屈小波课题组应用深度学习实现了非均匀采样核磁共振谱的高效重建[50],重建二维谱的时间是经典低秩算法重建时间的4%~8%,而重建三维谱的时间是经典压缩感知算法的12%~22%.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院梁栋课题组使用自编码机对磁共振图像的先验信息进行学习,并结合传统的图像重建方法实现了磁共振图像欠采样数据的高保真度重建[51].尽管深度学习在磁共振领域已经得到广泛应用,但在Laplace NMR的数据处理问题上基于深度学习的方法相对较少.需要注意的是,Laplace NMR与一般的基于傅里叶变换的NMR技术有着显著不同.首先,实验测量的数据并不要求等间隔采样,不同实验参数条件下的数据条件(如梯度序列或回波间隔时间等)较难以统一.此外,衰减速率的计算与频率参数的计算具有本质的不同,衰减参数计算的分辨率与实际采样条件的联系并无法用类似傅里叶变换的理论进行分析.因此,能较好处理传统NMR谱图的深度学习网络框架并不一定能适用于Laplace NMR.
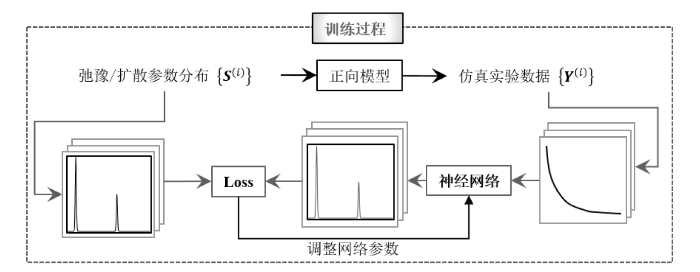
目前已有一些工作将数据驱动深度学习方法成功应用于Laplace NMR领域[52⇓-54].与经典方法不同,深度学习方法无需事先设定数据对应的信号模型,也无需人为给定先验信息,而是通过神经网络自动从训练数据集中学习输入到输出之间的映射关系,以及理想谱图的先验属性.Laplace NMR谱图重建是典型的逆问题,其前向的物理模型是已知的,即,若已知弛豫时间或扩散系数的分布情况,则可以通过物理模型仿真得到实验中可能采集到的Laplace NMR数据.在这种情况下,我们可以通过前向物理模型构建训练数据集,并训练网络完成从Laplace NMR数据到弛豫时间或扩散系数分布情况的“逆向推理”.这一方案也是深度学习用于很多科学领域逆问题求解的一种常用范例,该过程可以由示意图7代表.
图7
图7
神经网络完成Laplace NMR数据分析问题的训练过程
Fig. 7
Training procedures of the neural network for Laplace NMR data processing
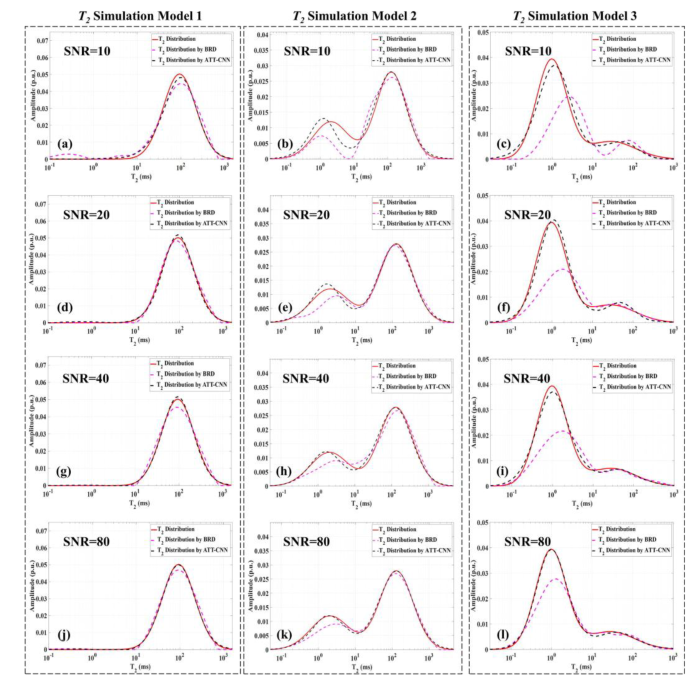
在下文中我们挑选其中两种方法作为代表进行介绍.在2022年,中国石油大学Luo等人采用深度学习方法实现了横向弛豫实验数据的分析[53],在该工作中尝试了用全连接层搭建起的自编码机、和加入注意力机制的多尺度卷积神经网络(ATT-CNN,attention multi-scale convolutional neural network)等几种网络结构以实现T2分布的计算.其中在ATT-CNN网络结构中,作者采用了一个全连接层构成的去噪模块对输入的含噪序列进行去噪;接着用一个注意力层提取序列中的能量变化过程,并依此对序列加权,以使网络更关注有效的信号特征;随之使用卷积层提取出不同尺度的特征,并最终通过全连接层转换为T2的分布曲线.该方法在低信噪比的条件下能取得比经典方法更鲁棒的效果(图8).其中,BRD代表Butler-Reeds-Dawsons方法[55],是类似于CONTIN的加了Tikhnov正则化约束的经典优化算法.从中可以看到,即使是在低信噪比条件下,深度学习方法仍可以得到较接近于理想分布的结果,相比于经典算法的优势很明显.
图8
图8
不同信噪比条件下不同算法对T2分布的计算结果[53].红色线代表参考理想值,红色虚线为经典算法(BRD)计算结果,黑色虚线为加入注意力机制的多尺度卷积神经网络(ATT-CNN)计算结果
Fig. 8
T2 distribution results of different algorithms under different SNR conditions[53]. Red solid lines denote the ground truth, red dashed lines are the results of classic algorithm BRD, and black dashed lines represent results of ATT-CNN
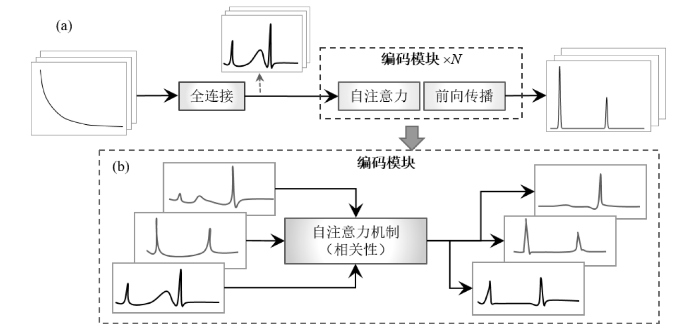
而在2023年,本课题组也提出一种深度学习方法,称为数据驱动指数曲线翻译器(DRECT,data-driven exponential curve translator)以处理Laplace NMR问题[54],既包括弛豫参数的计算,又包括DOSY谱重建.在处理这两类问题时,网络结构和训练集数据有所区别.在处理DOSY谱重建问题时,我们采用了简化的Transformer[56]结构,该网络在自然语言处理与计算视觉等领域均有十分广泛的应用.而应用于Laplace NMR数据处理问题时,我们仅保留了前端的全连接层,以及由多头注意力机制(multi-head attention)与前向传播(feed forward)组成的编码模块.在图9(a)中展示了网络的结构,输入序列
的是,在Transformer中最引人注目的是其自注意力单元,这种自注意力机制在DOSY谱重建问题中起到了非常关键的作用.自注意力单元将对
图9
图9
采用简化的Transformer实现DOSY谱重建的示意图.(a)整体框架;(b)编码模块的功能示意
Fig. 9
DOSY spectral reconstruction based on simplified Transformer. (a) Framework; (b) Function of the encoding module
图10
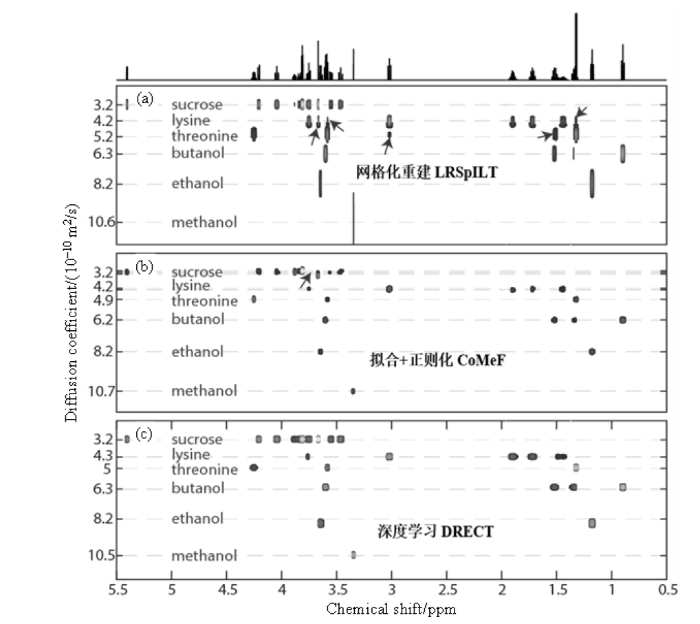
而在表2中将经典算法与深度学习方法的使用过程进行了对比.以LRSpILT[44]与CoMeF[45]为例的经典方法需要经过繁琐的参数调整,针对于不同样品所设置的正则化参数均有很大的不同.尤其值得注意的是,在类似于CoMeF的参数拟合算法中需要给定组分数量,但在样本成分较复杂、不同成分扩散系数较为接近等情况下,往往需要设定一个大于理想组分数的成分数量才可以较好地分离不同组分.例如在表2中CoMeF算法的成分数设定为10时才能清楚分离出6个组分的信号,这无疑为调参过程带来很大的挑战.而深度学习方法则无需这种调参过程,对于不同样品可采用相同的预训练网络进行分析.另外,经典算法的单次运行时间大概在数分钟,而深度学习方法仅需数秒即可解决问题.
表2 经典算法在三种不同样品上的正则化参数选择,及其与深度学习方法DRECT的运行效率比较
Table 2
| 样品 | LRSpILT参数设置 | CoMeF参数设置 | 单次运行时间(单位/s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ1 | λ2 | 迭代次数 | β | 成分数 | 迭代次数 | LRSpILT | CoMeF | DRECT | |||
| QGC | 0.005 | 0.0005 | 1500 | 0.1 | 3 | 30000 | 106 | 562 | 5 | ||
| GSP | 0.01 | 0.1 | 1500 | 0.8 | 3 | 30000 | 131 | 152 | 3 | ||
| M6 | 0.7 | 33 | 1500 | 0.1 | 10 | 100000 | 123 | 357 | 3 | ||
除了节省参数设置及单次运行时间之外,深度学习方法相比于经典算法还有个很重要的优势,即在噪声条件下可以更加鲁棒,从而增强Laplace NMR谱图重建的可靠性,如图8结果所示.经典的Laplace NMR谱图重建算法依赖于模型假设与人为设置的正则化项,无法灵活适应于不同类型、不同程度的噪声条件.相较而言,深度学习方法可以通过在训练集中加入各种复杂噪声以模拟实验数据中的干扰,并通过大规模的数据训练去捕捉信号与噪声之间的复杂关系,从而使得训练好的网络能够自适应地处理复杂噪声条件下的数据.
值得注意的是,本章所提两种基于深度学习的Laplace NMR数据重建方法得到的谱图具有很不一样的属性,在ATT-CNN[53]中生成的结果类似于CONTIN等经典的网格化重建方法,可以展示出T2的分布曲线,而在DRECT[54]中生成的结果更类似于参数拟合方法,谱峰较窄,并不能展示出衰减参数的分布情况.这种区别的主要根源在于训练集中数据的生成方式,在DRECT中衰减序列的生成用的是简化的信号模型((5)式,且采用P ≤ 3),并采用理想扩散系数为中心的窄高斯型谱峰组合而成理想DOSY谱图,故输入-输出对中只包含了衰减参数数值信息,并不包括其分布信息;而在ATT-CNN一文中则采用了相对较宽的高斯型谱峰组合成理想DOSY谱图,并且用(3)式的离散化形式计算对应的衰减序列,因此T2的分布信息是包含在输入-输出对中的.因此,深度学习算法的功能极大依赖于训练数据集的构建,用户需要根据所关心的问题(如:样品参数的分布范围、或者混合物成分的定性归属)而设计不一样的训练数据集让网络进行有针对性的学习.
4 总结与展望
本文针对Laplace NMR的谱图处理问题进行了系统性的介绍.从该信号处理问题本身的不适定性开始,讨论了Laplace衰减参数精确定量的困难,以及扩散NMR中成分定性分析的模糊性.接着介绍了经典的两大类方法——参数拟合方法与网格化重建方法,拟合算法可以直接计算得到参数值,但其性能极大程度依赖于事先设定好的信号模型及成分个数;网格化重建方法无需给定成分个数,但需要将理想谱图的先验信息建模成正则化约束项加入目标函数中,不同的正则化项、不同的正则化参数设置将得到不同的重建结果.而为了减少在谱图重建过程中的人为干预,可采用数据驱动深度学习方法来解决Laplace NMR数据处理问题,其性能极大程度取决于训练集的构建,而我们所期待获取的重建谱图先验属性也应该在训练集中予以表现.
目前已出现的深度学习Laplace NMR数据处理方法并不是太多,未来我们期待在这一领域能出现更鲁棒、更智能化的方法,可针对用户的不同需求提供相应的训练集构建方式和网络模型.另外,本文仅讨论了一维Laplace NMR问题(DOSY虽然是二维数据,但处理时仅有一维需要经过Laplace反演),二维甚至更高维度的Laplace NMR[57⇓-59]数据处理问题将具有更严重的病态性,其理论解释、不确定度分析、高精度方法设计均面临着更大的挑战.需要特别注意的是,对于Laplace NMR等磁共振定量参数分析问题而言,仅关注算法性能并不够,不确定度分析也是至关重要的.目前深度学习的不确定度量化方法已在计算机视觉[60]以及医学成像[61]中有所应用,将不确定度分析引入Laplace NMR谱图分析中,不仅可以量化重建谱图的可信度,还能更全面地了解模型的局限性和潜在风险,这对于用户对数据的后续分析及决策具有重大意义.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Spin-noise-detected two-dimensional Fourier-transform NMR spectroscopy
[J].We introduce two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy detected by recording and processing the noise originating from nuclei that have not been subjected to any radio frequency excitation. The method relies on cross-correlation of two noise blocks that bracket the evolution and mixing periods. While the sensitivity of the experiment is low in conventional NMR setups, spin-noise-detected NMR spectroscopy has great potential for use with extremely small numbers of spins, thereby opening a way to nanoscale multidimensional NMR spectroscopy.
Ultrafast multidimensional Laplace NMR using a single-sided magnet
[J].
DOI:10.1002/anie.201511859
PMID:26960011
[本文引用: 1]

Laplace NMR (LNMR) consists of relaxation and diffusion measurements providing detailed information about molecular motion and interaction. Here we demonstrate that ultrafast single- and multidimensional LNMR experiments, based on spatial encoding, are viable with low-field, single-sided magnets with an inhomogeneous magnetic field. This approach shortens the experiment time by one to two orders of magnitude relative to traditional experiments, and increases the sensitivity per unit time by a factor of three. The reduction of time required to collect multidimensional data opens significant prospects for mobile chemical analysis using NMR. Particularly tantalizing is future use of hyperpolarization to increase sensitivity by orders of magnitude, allowed by single-scan approach. © 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Ultrafast diffusion exchange nuclear magnetic resonance
[J].
Diffusion-ordered two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
[J].
The integrated DOSY acquisition/processing module for Topspin NMR software
[J].
TopSpin核磁共振软件中集成的DOSY采集/处理模块DOSYm-(TM)
[J].
Utilizing 3D DOSY NMR in the characterization of organic compounds in coal chemical wastewater
[J].
Diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (DOSY-NMR): A novel tool for identification of phosphorus compounds in soil extracts
[J].
NMR relaxometry of oil paint binders
[J].
NMR application in unconventional shale reservoirs - A new porous media research frontier
[J].
Quantitative evaluation of shale pore structure using nuclear magnetic resonance data
[J].
利用核磁共振资料定量评价页岩孔隙结构
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20202856
[本文引用: 1]

页岩气储层的孔隙结构复杂且非均质性较强,导致储层表征及有效性评价面临极大挑战.为了建立页岩气储层孔隙结构的定量评价方法,本文选取了鄂西宜昌地区陡山沱组二段20块岩心,采用0.069 ms的回波间隔开展饱含盐水状态下的核磁共振(NMR)实验.在此基础上,对T<sub>2</sub>谱进行了多重分形特征分析,提取了对页岩气储层孔隙结构较敏感的参数,并建立了基于最小与最大广义分维数差值(D<sub>min</sub>-D<sub>max</sub>)和谱宽(Δα)划分页岩气储层类型的方法及标准.该方法对于有效提高页岩气储层的预测精度、指导开发选层等具有重要意义.
Protein dynamics revealed by NMR relaxation methods
[J].
Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient
[J].
Understanding NMR T2spectral uncertainty
[J].
High-resolution diffusion-ordered 2D spectroscopy (HR-DOSY) - a new tool for the analysis of complex mixtures
[J].
Resolution of discrete and continuous molecular size distributions by means of diffusion-ordered 2D NMR spectroscopy
[J].
Biexponential fitting of diffusion-ordered NMR data: Practicalities and limitations
[J].
Convergence properties of the Nelder-Mead simplex method in low dimensions
[J].
The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm: Implementation and theory
[C]//
Generalized rank annihilation method applied to a single multicomponent pulsed gradient spin echo NMR data set
[J].
Direct exponential curve resolution algorithm (DECRA): A novel application of the generalized rank annihilation method for a single spectral mixture data set with exponentially decaying contribution profiles
[J].
Resolving nuclear magnetic resonance data of complex mixtures by three-way methods: Examples of chemical solutions and the human brain
[J].
Using pulsed gradient spin echo NMR for chemical mixture analysis: How to obtain optimum results
[J].
Global least-squares analysis of large, correlated spectral data sets and application to chemical kinetics and time-resolved fluorescence
[J].
Global least-squares analysis of large, correlated spectral data sets: Application to component-resolved FT-PGSE NMR spectroscopy
[J].
FT-PGSE NMR study of mixed micellization of an anionic and a sugar-based nonionic surfactant
[J].
Speedy component resolution: An improved tool for processing diffusion-ordered spectroscopy data
[J].
DOI:10.1021/ac7025833
PMID:18407669
[本文引用: 2]

Diffusion-based NMR techniques (e.g., diffusion-ordered spectroscopy, DOSY), which can be used to distinguish between the signals of different components of a mixture, are steadily gaining in popularity. When processing data from a DOSY experiment it is often desirable to reconstruct the spectra of individual components; here, multivariate methods that take advantage of the covariance between the resonances of a given component can often be advantageous. This paper presents a minor variation on the established CORE method, speedy component resolution (SCORE), that gives a major improvement in performance. In common with CORE it can use any experimental sampling scheme and is adaptable to different experimental decay shapes, but unlike CORE it is very fast and relatively insensitive to starting guesses. The method is demonstrated on a mixture of quinine, geraniol, and camphene in deuteriated methanol, where all four component spectra can be extracted in less than 15 s.
Analysis of DOSY and GPC-NMR experiments on polymers by multivariate curve resolution
[J].Multivariate curve resolution (MCR) was successfully applied to the analysis of DOSY experiments on polymer mixtures and GPC-NMR experiments on industrial copolymer samples. MCR generates pure factors of spectral and concentration profiles using, successively, principal factor analysis, Varimax rotation, and alternating least-squares optimization. The method described is robust and can be directly applied to DOSY and GPC-NMR data and one obtains 1H NMR spectra of the individual compounds with their corresponding diffusion or elution profiles, respectively. Copyright 1998 Academic Press. Copyright 1998 Academic Press
Unmixing the NMR spectra of similar species-vive la différence
[J].
A constrained regularization method for inverting data represented by linear algebraic or integral equations
[J].
A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems
[J].
Iterative thresholding algorithm for multiexponential decay applied to PGSE NMR data
[J].
DOI:10.1021/ac3032004
PMID:23297715
[本文引用: 2]

Pulsed gradient spin echo (PGSE) is a well-known NMR technique for determining diffusion coefficients. Various signal processing techniques have been introduced to solve the task, which is especially challenging when the decay is multiexponential with an unknown number of components. Here, we introduce a new method for the processing of such types of signals. Our approach modifies the Tikhonov's regularization, known previously in CONTIN and Maximum Entropy (MaxEnt) methods, by using the l(1)-norm penalty function. The modification enforces sparsity of the result, which improves resolution, compared to both mentioned methods. We implemented the Iterative Thresholding Algorithm for Multiexponential Decay (ITAMeD), which employs the l(1)-norm minimization, using the Fast Iterative Shrinkage Thresholding Algorithm (FISTA). The proposed method is compared with the Levenberg-Marquardt-Fletcher fitting, Non-negative Least Squares (NNLS), CONTIN, and MaxEnt methods on simulated datasets, with regard to noise vulnerability and resolution. Also, the comparison with MaxEnt is presented for the experimental data of polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymer solutions and mixtures of these with various molecular weights (1080 g/mol, 11,840 g/mol, 124,700 g/mol). The results suggest that ITAMeD may be the method of choice for monodispersed samples with "discrete" distributions of diffusion coefficients.
Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers
[J].
Simultaneously sparse and low-rank abundance matrix estimation for hyperspectral image unmixing
[J].
A generally regularized inversion for NMR applications and beyond
[J].
An interior-point method for large-scale L1-regularized least squares
[J].
High-resolution reconstruction for multidimensional Laplace NMR
[J].
Maximum entropy processing of DOSY NMR spectra
[J].
On the inversion of diffusion NMR data: Tikhonov regularization and optimal choice of the regularization parameter
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2011.05.014
PMID:21683632
[本文引用: 1]

The analysis of diffusion NMR data in terms of distributions of diffusion coefficients is hampered by the ill-posed nature of the required inverse Laplace transformation. Naïve approaches such as multiexponential fitting or standard least-squares algorithms are numerically unstable and often fail. This paper updates the CONTIN approach of the application of Tikhonov regularization to stabilise this numerical inversion problem and demonstrates two methods for automatically choosing the optimal value of the regularization parameter. These approaches are computationally efficient and easy to implement using standard matrix algebra techniques. Example analyses are presenting using both synthetic data and experimental results of diffusion NMR studies on the azo-dye sunset yellow and some polymer molecular weight reference standards.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Reconstructing diffusion ordered NMR spectroscopy by simultaneous inversion of Laplace transform
[J].
DOI:S1090-7807(17)30066-6
PMID:28301804
[本文引用: 1]

2D diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy (DOSY) has been widely recognized as a powerful tool for analyzing mixtures and probing inter-molecular interactions in situ. But it is difficult to differentiate molecules with similar diffusion coefficients in presence of overlapped spectra. Its performance is susceptible to the number of chemical components, and usually gets worse when the number of components increases. Here, to alleviate the problem, numerical simultaneous inversion of Laplace transform (SILT) of many related variables is proposed for reconstructing DOSY spectrum (SILT-DOSY). The advantage of the proposed method in comparison to other methods is that it is capable of estimating the number of analytes more accurately and deriving corresponding component spectra, which in turn leads to the more reliable identification of the components.Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
High-resolution reconstruction for diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03865
PMID:31769652
[本文引用: 4]

Diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy (DOSY) presents an essential tool for the analysis of compound mixtures by revealing intrinsic diffusion behaviors of mixed components. The applicability of DOSY measurements on complex mixtures is generally limited by the performance of data reconstruction algorithms. Here, based on constraints on low rank and sparsity of DOSY data, we propose a reconstruction method to achieve high-resolution DOSY spectra with excellent peak alignments and accurate diffusion coefficients for measurements of complex mixtures even when component signals are congested and mixed together along the spectral dimension. This proposed method is robust and suitable for DOSY data acquired from common commercial NMR instruments; thus, it may broaden the scope of DOSY applications.
Neural network method for diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03883
PMID:35107988
[本文引用: 4]

Diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy (DOSY) presents an essential tool for the analysis of compound mixtures by revealing intrinsic diffusion behaviors of the mixed components. For the interpretation of the diffusion information, intrinsically designed algorithms for a DOSY spectrum reconstruction are required. The estimated diffusion coefficients are desired to have consistency for all the spectral signals from the same molecule and good separation of signals from different molecules. For this purpose, we propose a novel method that adopts a coordinated multiexponential fitting to ensure the consistency of diffusion coefficients and apply a sparse constraint to enhance the robustness. A lightweight neural network is applied as an optimizer to solve this highly nonlinear and nonconvex optimization problem. The proposed method provides estimated diffusion coefficients with excellent distinguishment between species and outperforms the state-of-the-art reconstruction algorithms, such as the Laplacian inversion and the multivariate fitting methods.
A neural network method for nonconvex optimization and its application on parameter retrieval
[J].
The GNAT: A new tool for processing NMR data
[J].
The DOSY toolbox: A new tool for processing PFG NMR diffusion data
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2009.07.022
PMID:19666235
[本文引用: 1]

The DOSY Toolbox is a free programme for processing PFG NMR diffusion data (sometimes loosely referred to as DOSY data), distributed under the GNU General Public License. NMR data from three major manufacturers can be imported and all processing is done in a user-friendly graphical user interface. The Toolbox is completely free-standing in the sense that all necessary basic processing of NMR data (e.g., Fourier transformation and phasing) is catered for within the programme, as well as a number of methods specific to DOSY data (e.g., DOSY and SCORE). The programme is written in MATLAB and as such can be run on any platform, but can also run independent of MATLAB in a free-standing compiled version for Windows, Mac, and Linux.
DOSY Toolbox, Manchester NMR methodology group
[EB/OL]. https://www.nmr.chemistry.manchester.ac.uk/?q=node/340.
Accelerated nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with deep learning
[J].
Highly undersampled magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction using autoencoding priors
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.27921
PMID:31429993
[本文引用: 1]

Although recent deep learning methodologies have shown promising results in fast MR imaging, how to explore it to learn an explicit prior and leverage it into the observation constraint is still desired.A denoising autoencoder (DAE) network is leveraged as an explicit prior to address the highly undersampling MR image reconstruction problem. First, inspired by the observation that the prior information learned from high-dimension signals is more effective than that from the low-dimension counterpart in image restoration tasks, we train the network in a multichannel scenario and apply the learned network to single-channel image reconstruction by a variables augmentation technique. Second, because of the fact that multiple implementations of artificial noise generation in DAE favors a better underlying result, we introduce a 2-sigma rule to complement each other for improving the final reconstruction. The whole algorithm is tackled by proximal gradient descent.Experimental results under varying sampling trajectories and acceleration factors consistently demonstrate the superiority of the enhanced autoencoding priors, in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio, structural similarity, and high-frequency error norm.A simple and effective way to incorporate the DAE prior into highly undersampling MR reconstruction is proposed. Once the DAE prior is obtained, it can be applied to the reconstruction tasks with different sampling trajectories and acceleration factors, and achieves superior performance in comparison with state-of-the-art methods.© 2019 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
T2 analysis using artificial neural networks
[J].
A study on multi-exponential inversion of nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation data using deep learning
[J].
High-quality reconstruction for Laplace NMR based on deep learning
[J].
Estimating solutions of first kind integral equations with nonnegative constraints and optimal smoothing
[J].
Attention is all you need
[J].
Dispersion of T1 and T2 nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in crude oils
[J].
Optimization of multidimensional MR data acquisition for relaxation and diffusion
[J].
Sensitivity analysis of T2-T1 2D NMR measurement parameters in shale oil reservoirs
[J].
页岩油储层T2-T1二维核磁共振测量参数敏感性分析
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20223025
[本文引用: 1]

为了提高二维核磁共振(NMR)在页岩油储层测量结果的可靠性,从NMR实验室岩心分析、井场移动式全直径岩心扫描、测井三类不同应用场景出发,分析了页岩油储层T<sub>2</sub>-T<sub>1</sub>二维NMR响应特征及影响因素.针对不同的应用场景,分别提出了页岩油储层的T<sub>2</sub>-T<sub>1</sub>二维NMR测量参数优化方法.实验室岩心NMR分析除了关注磁场强度、测量序列外,还需要注意回波间隔(T<sub>E</sub>)和回波组数的选择.井场移动式全直径岩心NMR扫描时,需要重点关注T<sub>E</sub>和最短等待时间(T<sub>w</sub>)的设置,为保证快弛豫组分T<sub>1</sub>维度的收敛,最短T<sub>w</sub>应至少设置为1 ms.NMR测井受限于采集条件,需要重点关注数据处理中的布点范围和平滑因子,以对不同信噪比的数据进行解释和修饰;页岩油NMR孔隙度小于5%为差储层,其低信噪比导致NMR结果的准确性难以保证.T<sub>2</sub>-T<sub>1</sub>二维NMR测量参数的系统性分析为页岩油储层二维NMR探测方法优化提供了参考依据,有助于提高NMR测量结果的精度,进而得到更加可靠的储层参数信息.
What uncertainties do we need in Bayesian deep learning for computer vision?
[C]//
DeepCEST 3 T: Robust MRI parameter determination and uncertainty quantification with neural networks-application to CEST imaging of the human brain at 3 T
[J].