引言
永磁体的温度稳定性较差,导致主磁场强度B0随环境温度变化较大,从而影响信号测量.在波谱仪中,通常配备温控系统来保持永磁体的温度稳定,然而常规的温度控制器精度有限,不能实现ppm(百万分之一)级别的控温.场频联锁是一种常用的保持主磁场稳定方法[4],该方法通过探测非氢元素(如氟、氘等)的信号激发补偿系统控制流过补偿线圈的电流进行磁场矫正,使磁场回到锁定值,以保证磁场的长期稳定.桌面式波谱仪体积紧凑,对高分辨率的追求要求主磁场B0有极高的均匀度,磁体内用来提高B0均匀度的主被动匀场装置占据了本就狭小的磁体内部空间[5⇓-7],留给射频探头的空间更加有限,因此研发一套适用于紧凑型磁体且带有锁场的探头对桌面式磁共振系统开发十分关键.
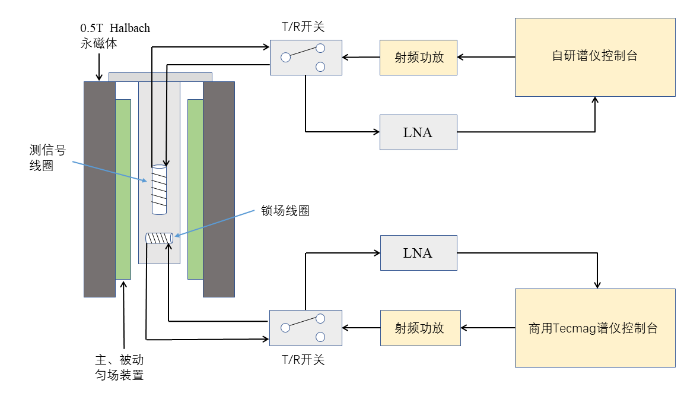
本文基于实验室的0.5 T Halbach永磁体设计了一款集成信号检测与外部锁场的双通道探头.首先利用有限元仿真软件COMSOL针对目标区域分析了不同构型线圈的性能指标,并优化了螺线管线圈模型的结构参数;然后基于仿真结果,制作了线圈实物,并配合调谐匹配电路板加工安装;最后将锁场探头装入磁体,与外围的收/发开关(T/R Switch)、低噪声前置放大器(LNA,Low Noise Amplifier)、射频功放、谱仪控制台一起进行测试,验证所设计探头的性能.
1 射频线圈构型选择及结构参数优化
1.1 射频线圈构型选择
探头是磁共振系统的重要组成部分,起着发射射频脉冲和接收磁共振信号的作用,其性能直接决定了探测到的信号质量.射频线圈是探头的核心,射频线圈构型是影响探头性能的重要因素.Halbach阵列磁体结构紧凑、且无需液氦,运行成本低,十分适用于桌面式磁共振波谱仪[11].高场超导磁体产生的磁场沿轴向方向,而Halbach磁体的磁场方向垂直于轴向(本文中定义为y方向),因此超导成像系统中的鸟笼线圈等不再适用,可以采用产生轴向磁场的螺线管和亥姆霍兹等线圈实现射频场激励.
B1场不均匀度(δ
其中,{{B}_{\max }}、{{B}_{\min }}、{{B}_{\text{av}}}分别为感兴趣区域内射频激发场方向磁场的最大值、最小值和平均值,单位为T.
相对信噪比(SNR)计算公式为:
其中,I为施加至线圈的激励电流,单位为A;R为线圈的交流电阻,单位为Ω;{{B}_{\text{av}}}为感兴趣区域内磁场的平均值,单位为T.
品质因子Q计算公式为:
其中,ω为线圈的拉莫尔角频率,单位为rad/s;L为线圈的电感,单位为H;R为线圈的交流电阻,单位为Ω.
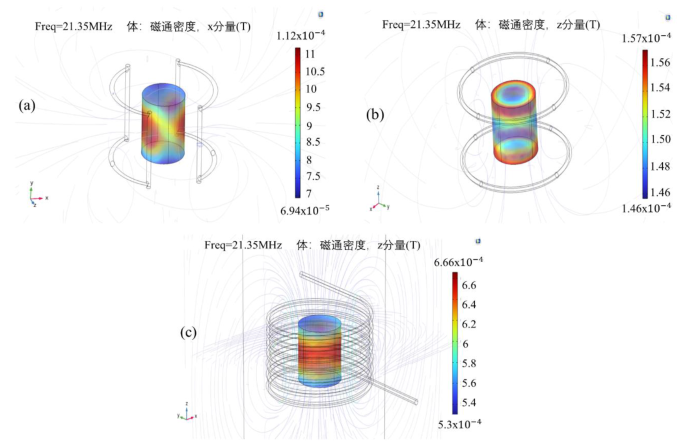
在COMSOL中对三种线圈进行建模,并采用大小为1 A、频率为21.35 MHz的电流激励.针对不同的线圈结构,选择激发场方向,保证与主磁场方向正交.图1显示了三种线圈在感兴趣圆柱体区域的B1场分布.
图1
图1
(a)鞍型、(b)亥姆霍兹、(c)螺线管线圈在感兴趣圆柱体区域的B1场分布.其中:磁通密度指感兴趣圆柱体内各位置的磁感应强度,圆柱体内颜色由蓝到红表示磁感应强度由弱到强.螺线管和亥姆霍兹线圈磁场方向沿z方向,鞍型线圈磁场方向沿x方向
Fig. 1
The B1 field distribution of the saddle (a), Helmholtz (b) and solenoidal (c) coils in the cylindrical region of interest, respectively. Where: Magnetic flux density refers to the magnetic induction strength at each location within the cylinder of interest, with the colours within the cylinder ranging from blue to red indicating weak to strong magnetic induction. The magnetic field direction is along the z-direction for solenoids and Helmholtz coils, and along the x-direction for saddle coils
根据仿真得到各构型线圈的电感、交流电阻以及感兴趣区域内激发场方向上磁场的最大值、最小值和平均值,计算得到的三种构型的线圈的性能参数如表1所示.整体来看,鞍型线圈的三项指标都较差;亥姆霍兹线圈的磁场均匀度最好,但其相对信噪比与品质因数都低于螺线管线圈;螺线管线圈磁场均匀度低于亥姆霍兹线圈,但相对信噪比与品质因数指标最优.相对信噪比是线圈最重要的参数,因此对于本文中直径和高度都为5 mm的圆柱体感兴趣区域来说,螺线管线圈是作为射频激发线圈的较优选择,我们选择针对螺线管线圈进行进一步优化.
表1 三种线圈的性能参数
Table 1
| 鞍型 | 亥姆霍兹 | 螺线管 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1场不均匀度(δ) | 49.49% | 8.2% | 23.89% |
| 相对信噪比(SNR) | 3.6×10-4 | 5.43×10-4 | 1.03×10-3 |
| 品质因数(Q) | 87.11 | 95.41 | 210.89 |
1.2 螺线管线圈最优结构参数仿真
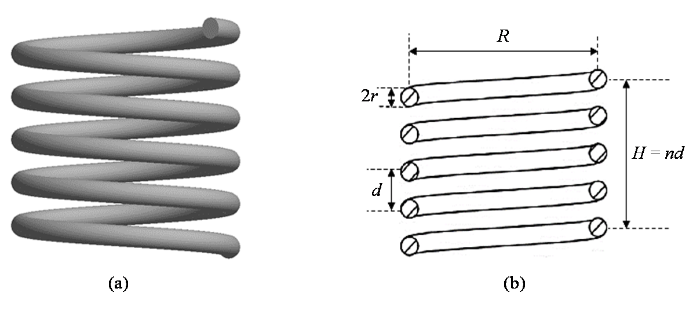
图2
图2
螺线管线圈. (a)三维结构;(b)理论参数模型
Fig. 2
Solenoid coil. (a) 3D structure; (b) Theoretical parametric model
射频线圈的相对信噪比与填充因子成正比,为了获得高的相对信噪比,线圈越贴近样品越好.实际测试中使用5 mm标准核磁管装样品,考虑到支架厚度(1 mm壁厚)以及样品管顺畅插拔,确定线圈直径 R = 7.4+2r(下述线圈尺寸符号的单位均为mm).Hoult等[16]和Medhurst[17]指出,对于微型螺线管线圈,当高度与直径比H/R = 1~1.5时,线圈有较高的相对信噪比;当漆包线直径与匝间距比2r/d = 0.5~0.7时,线圈有较高的品质因数[16,17].本文取H/R = 1,2r/d = 0.5,则线圈高度H = 7.4+2r,匝间距d = 4r,匝数 n = H/d = (7.4+2r)/4r,线圈的所有参数全部转化为与漆包线半径r有关的函数.根据实际制作工艺取 r = 0.1~0.5 mm,每间隔0.05 mm取值,共计9个r值.使用COMSOL中的参数化扫描功能对每个r值对应的线圈模型进行仿真,得到表征线圈性能的B1场不均匀度、相对信噪比和品质因数.相对信噪比直接影响最终信号的信噪比,品质因数影响线圈的频率选择特性,B1场不均匀度影响射频场的有效激发范围.在NMR系统中最看重磁共振信号的信噪比,因此本文中相对信噪比是螺线管线圈最重要的性能参数.
定义线圈的综合性能M=(品质因数Q×相对信噪比SNR)/B1场不均匀度δ.其中,品质因数和相对信噪比与线圈性能成正比,故放在分子上;B1场不均匀度与线圈性能成反比,故放在分母上.将9组线圈对应的相对信噪比数据组、品质因数数据组和B1场不均匀度数据组分别在各自组内进行归一化处理,然后将归一化后的数据按照各参数重要程度以6:2:2的比例(相对信噪比最重要,故其占比最大)分别代入综合性能M的表达式中,即:
仿真及计算结果如表2所示.从表中可得,当r = 0.4 mm时,螺线管线圈的综合性能最佳,此时H = R = 8.2 mm,d = 1.6 mm,n = 5.125(考虑到实际制作精度,线圈实物匝数为5),此优化结果用于制造锁场探头的主线圈和锁场线圈实物.
表2 不同漆包线半径对应螺线管线圈的性能参数
Table 2
| 漆包线半径r/mm | 相对信噪比SNR | 品质因数Q | B1场不均匀度δ | 综合性能M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 1.61×10-3 | 132.69 | 25.95% | 0.79 |
| 0.15 | 1.56×10-3 | 126.54 | 26.76% | 0.51 |
| 0.20 | 1.55×10-3 | 130.86 | 25.77% | 0.63 |
| 0.25 | 1.52×10-3 | 130.66 | 25.21% | 0.61 |
| 0.30 | 1.53×10-3 | 144.09 | 24.38% | 0.96 |
| 0.35 | 1.51×10-3 | 148.15 | 23.91% | 1.06 |
| 0.40 | 1.48×10-3 | 146.73 | 23.07% | 1.10 |
| 0.45 | 1.47×10-3 | 163.60 | 25.28% | 0.87 |
| 0.50 | 1.45×10-3 | 161.85 | 24.26% | 0.89 |
由表2中品质因数一栏的数据趋势可得:漆包线半径也即螺线管线圈直径越大,品质因数越高.在本节中为了获得高相对信噪比,螺线管线圈要紧贴在样品管周围,优化后的螺线管直径为8.2 mm,而1.1节中的未经优化的螺线管直径为12 mm,因此优化后螺线管线圈的品质因数低于优化前的.但优化后的螺线管线圈相对信噪比有明显提升,相当于牺牲了部分品质因数换取更高的相对信噪比.
2 探头制作及性能测试
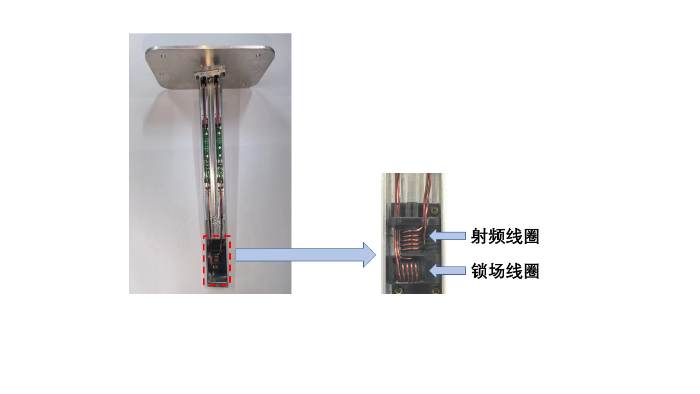
图3
参照1.2节中仿真得到的最优螺线管线圈参数,将直径为0.8 mm的漆包线均匀绕在3D打印且带有 1 mm深螺纹凹槽的中空线圈支架上,漆包线两端接到调谐匹配电路板,并将线圈和调谐匹配板安装在特别设计的带盖子的屏蔽铝壳内.另外在下方安装相同规格的螺线管线圈用作外部锁场通道,两个通道线圈的磁场方向相互正交实现空间上的解耦,探头放入磁体部分的宽度为22 mm.探头及线圈实物如图4所示.
图4
图5
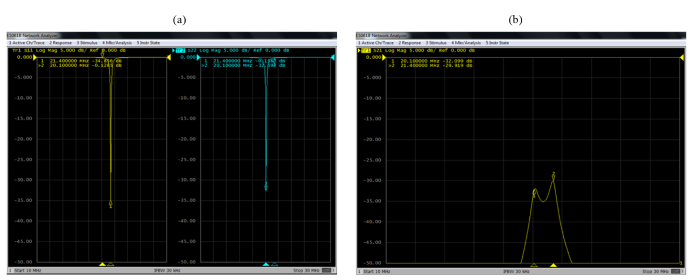
选用氢核为样品信号检测核,氟核为锁场核,调节调谐匹配电路板上的可调电容使线圈谐振在0.5 T下两元素各自的拉莫尔频率(氢核为21.35 MHz、氟核为20.1 MHz),并完成50 Ω阻抗匹配.使用Agilent公司的 E5061B矢量网络分析仪测试两线圈的回波损耗S11和隔离度S21,结果如图6所示.氢、氟线圈的S11分别为-34.8 dB、-32.5 dB,S21在-30 dB左右,从图中可以看出两组线圈实现了良好的调谐匹配且二者之间的串扰较小.
图6
图6
氢、氟线圈的S参数测量结果.(a)氢线圈S11为-34.8 dB,氟线圈S11为-32.5 dB;(b)两线圈之间的隔离度S21在-30 dB左右
Fig. 6
S-parameter measurements for hydrogen and fluorine coils. (a) S11 -34.8 dB for hydrogen coil and S11 -32.5 dB for fluorine coil; (b) Isolation between the two coils S21 is around -30 dB
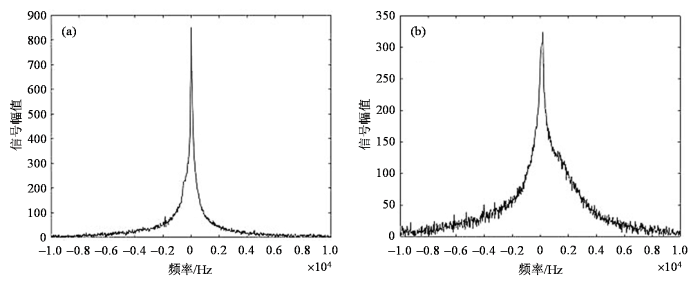
使用硬脉冲进行锁场探头信号测试,调整脉冲的幅值和持续时间实现最佳的90˚脉冲激发,两通道的样品分别为6.4 g/L的CuSO4溶液和99%浓度的三氟甲苯溶液,商用谱仪和自研谱仪同时发射射频脉冲,测试结果如图7所示.结果显示锁场探头信号之间没有串扰,主通道信号的信噪比达到50以上,锁场位置信号的信噪比达到20以上.值得注意的是,由于分离式的锁场导致样品位置不在磁体中心,磁场不均匀度导致谱线对称性存在缺陷,因此传统场频联锁根据色散线积分实现电流的负反馈进而控制补偿电流的方式在紧凑型磁体的外部锁场中并不适用.我们可以通过检测锁场信号的中心频率波动,结合补偿线圈的电流常数进行磁场补偿.
图7
图7
探头测试结果.(a)自研谱仪测得的氢信号;(b)商用谱仪测得的氟信号
Fig. 7
Probe test results. (a) Hydrogen signal measured by self-researched spectrometer; (b) Fluorine signal measured by commercial spectrometer
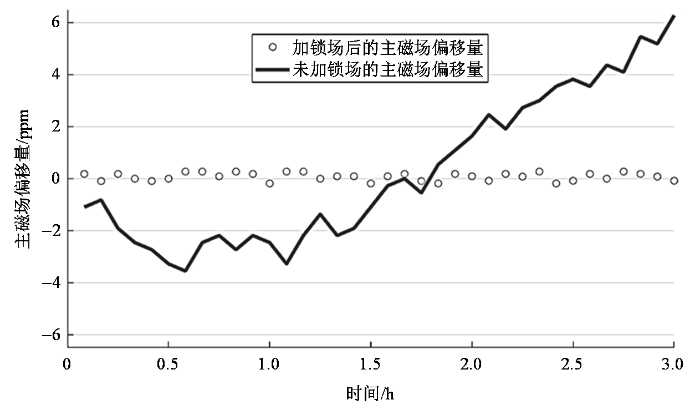
将上述探头应用于外部锁场实验,在不开启外部锁场的条件下每隔5 min测试一次主通道氢信号的中心频率,连续测量3 h,得到3 h内系统整体的频率漂移.然后开启外部锁场,重复之前的实验步骤,将两组数据进行对比,结果如图8所示.由图可得,不加外部锁场时,整体系统的频率漂移约为3.3 ppm/h,锁场开启后,整体系统的频率漂移约为0.2 ppm/h,锁场效果良好.由此可知,本文设计的锁场探头,提供了一种外部锁场设计方案,可用于紧凑型磁体的外部锁场.
图8
3 结论
本文设计了一套应用于桌面式永磁核磁共振波谱仪的具有信号检测与外部锁场功能的双通道锁场探头.使用有限元仿真软件COMSOL对3种常用的尺寸相同的线圈构型进行性能对比,针对其中综合性能最佳的螺线管线圈优化得到最优尺寸,并制作实物.两组线圈及其调谐匹配板装入铝制屏蔽盒并固定在磁体内,配合外围的T/R开关、LNA和谱仪系统同时激发两组线圈完成信号测试.结果表明,两线圈之间无串扰且样品信号检测线圈的信噪比较高,锁场线圈的信噪比也能满足外部锁场需求.最终在实验室的0.5 T Halbach磁体系统上进行锁场实验,添加锁场后整体系统的频率漂移约为0.2 ppm/h,验证了双通道锁场探头设计的可行性.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
[J].Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) complements magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a non-invasive means for the characterization of tissue. While MRI uses the signal from hydrogen protons to form anatomic images, proton MRS uses this information to determine the concentration of brain metabolites such as N-acetyl aspartate (NAA), choline (Cho), creatine (Cr) and lactate in the tissue examined. The most widely used clinical application of MRS has been in the evaluation of central nervous system disorders.MRS has its limitations and is not always specific but, with good technique and in combination with clinical information and conventional MRI, can be very helpful in diagnosing certain entities. For example, a specific pattern of metabolites can be seen in disorders such as Canavan's disease, creatine deficiency, and untreated bacterial brain abscess. MRS may also be helpful in the differentiation of high grade from low grade brain tumors, and perhaps in separating recurrent brain neoplasm from radiation injury.
Investigating protein-ligand interactions by solution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
[J].DOI:10.1039/C7CP90004J URL [本文引用: 1]
Preprocessing, analysis and quantification in single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy: experts’ consensus recommendations
[J].DOI:10.1002/nbm.v34.5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative 2H NMR spectroscopy with 1H lock extender
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2007.04.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
A passive shimming method for Halbach magnet based on magnetic sheet arrays
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2022.107210 URL [本文引用: 1]
Active shim coils design for Halbach magnet based on inverse boundary element method
[J].
A spherical harmonics decomposition method (SHDM) for irregular matrix coils design
[J].DOI:10.1109/TBME.2021.3111656 URL [本文引用: 1]
Field-frequency lock approach for 21.3-MHz high-performance NMR relaxation analyzer
[J].
DOI:10.1063/1.5038138
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Low-field NMR (LF-NMR) relaxation analyzers have been more and more widely used in food science, biomedicine, and petroleum exploration in recent years. An LF-NMR device analyzes various interactions between sample molecules through spin relaxation, diffusion, flow, and imaging experiments. However, temporal field fluctuations in the magnet limit the scope of application. A stable magnetic field is the basic guarantee for detecting weak signals with shorter relaxation time. This paper presents an approach involving a field-frequency lock for a 21.3-MHz high-performance NMR bipolar permanent magnet. The diameter spherical volume (DSV) of the magnet is only 60 mm. The field-frequency lock system uses 19F in a micro coil integrated into the main probe as a lock detector. The required magnetic field compensation can be calculated from the lock free induction decay (FID) signal frequency, which is measured by lock spectroscopy. The compensation coils used to produce the magnetic field were designed based on Helmholtz coils. The system determines the signal frequency by detecting the lock FID signal and calculates the required compensation-coil current to stabilize the main magnetic field of the analyzer. The results of practical locking experiments in a 21.3-MHz high-performance NMR relaxation analyzer showed that this new approach helps to reduce magnetic field fluctuations from 11 ppm/3h (11 × 10–6) to 0.4 ppm/3h (0.4 × 10–6), which meets the application requirements. This approach is especially viable and effective for a permanent magnet with large field fluctuations. This paper also provides observations of the effect of these fluctuations on NMR measurements before and after installation of the field-frequency lock system.
Low-field benchtop NMR spectroscopy: status and prospects in natural product analysis
[J].DOI:10.1002/pca.v32.1 URL [本文引用: 1]
NMR spectroscopy with compact instruments
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.trac.2016.02.014 URL [本文引用: 1]
Design of permanent multipole magnets with oriented rare earth cobalt material
[J].
Use of Helmholtz coils for magnetic measurements
[J].DOI:10.1109/20.3411 URL [本文引用: 1]
The sensitivity of the zeugmatographic experiment involving human samples
[J].
Solenoidal microcoil design—Part I: Optimizing RF homogeneity and coil dimensions
[J].DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0534 URL [本文引用: 1]
Solenoidal microcoil design—Part II: Optimizing winding parameters for maximum signal-to-noise performance
[J].DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0534 URL [本文引用: 2]
The signal-to-noise ratio of the nuclear magnetic resonance experiment
[J].
High frequency resistance and self-capacitance of single-layer solenoids
[J].
RF coils: A practical guide for nonphysicists
[J].DOI:10.1002/jmri.v48.3 URL [本文引用: 1]
A passive shimming method for Halbach magnet based on magnetic sheet arrays
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2022.107210 URL [本文引用: 1]