引言
磁共振成像(Magnetic Resonance Imaging,MRI)对软组织分辨率高且不存在辐射危害,是临床常用的检查方式.但MRI主要缺点是成像速度慢,限制了临床使用范围,加速成像一直是MRI领域待解决的问题.成像速度与扫描和重建两个过程有关,使用欠采样可以加快扫描速度,但也使得重建算法变得复杂.
压缩感知技术(Compressed Sensing,CS)[1]通过利用信号的稀疏性和采集信号与观测矩阵的不相关性[2],可以从不遵循采样定理的欠采样
另一类用于加速MRI成像的深度学习网络是基于“物理模型展开”网络[5],将CS-MRI物理模型与深度学习网络结合,通过网络模块的堆叠来模拟优化算法的迭代步骤,使网络更具可解释性.2016年,Sun等将交替方向乘子算法(Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers,ADMM)用数据流图展开成ADMM-Net[11],首次用网络模块来自动学习模型中的变换和收缩函数.2018年,Hammernik等提出的变分网络[12]采用CNN网络展开,利用多个卷积核滤波模拟对图像进行多种稀疏化操作,并运用高斯径向基函数模拟势函数求偏导的非线性操作,对迭代梯度下降CS-MRI重建算法进行网络实现,克服了原算法中人工确定稀疏变换和势函数的缺陷.基于“物理模型展开”网络的运用实例还有采用U-net计算线圈灵敏度的端到端
变量拆分(分裂)网络(Variable Splitting Network,VS-Net)[19]通过引入辅助变量,将原变量拆分成多个变量,使计算更加高效.VS-Net通过不同的网络模块来对应迭代步骤,网络结构简单,便于端到端训练,但网络训练过程中指标波动较大,迭代次数决定网络的级联数和复杂度,并影响重建图像质量.
为了让网络训练过程更加稳定,提高网络迭代的效率,加快网络训练速度,本研究以VS-Net网络为基本框架,提出一种基于物理模型的ISTAVS-Net多线圈MRI重建网络,做出两项改进:(1)将ISTA算法与VS-Net网络结合,提出了多线圈MRI图像重建的闭合解和深度学习的网络结构,网络的功能模块与迭代过程相对应,可解释性强;(2)在网络输入与输出之间引入残差机制,而且稀疏变换形式、收缩阈值以及正则化参数在训练中自动学习,进一步提高了网络的非线性映射能力.
1 理论
1.1 基于VS-Net的MRI重建模型
香农定理要求采样频率必须大于信号最高频率的2倍,而CS-MRI技术突破了该定理的限制,可以从远低于采样频率的欠采样
其中,
现代磁共振扫描仪大都含多个接收线圈,结合多线圈并行采集的CS-MRI的k空间数据可重新写成:
其中,
MRI重建任务就是从获得的多线圈采集数据
其中,
若采用VS-Net网络的变量拆分法[19],可引入新的辅助变量z和
将约束条件写成惩罚项,多线圈CS-MRI模型又变成一个无约束的优化问题,公式为:
其中,α、β为惩罚权重.可用三个子问题优化来求
其中,
在VS-Net重建模型中,(5.2)(5.3)式都使用L2范数,有直接求解法,可通过最小二乘法迭代解决.(5.1)式通过求解最优的
针对这一问题,VS-Net网络采用了深度学习的网络模块来学习正则化变换R(z)和权重
1.2 多线圈ISTA改进算法
ISTA是一种用于稀疏优化问题的迭代算法[16],已用于实现CS-MRI重建.当正则化用某个线性稀疏变换P域的L1范数表示时,基于(1)式的CS-MRI的优化表达式为:
其中,非线性正则化变换
其中,k为迭代次数,
根据一阶近端原理,(7.2)式的近端映射的表达式和求解方法为:
其中,
收缩软阈值操作能有效消除噪声,降低信号波动幅度,同时不让图像平滑过度,很好的保留病灶细节,更有利于疾病的诊断.因此,我们将软阈值拓展到多线圈VS-Net重建中.
(5.1)与(7.2)式结构相同,因此可以快速求解多线圈CS-MRI重建问题的(5.1)式,公式为:
传统方法需手动设置稀疏变换,如小波变换
1.3 ISTAVS-Net重建网络
本文提出一种结合ISTA算法和多线圈VS-Net的优化算法,取名为ISTAVS算法.我们通过(11)式的软阈值操作来实现(5.1)式的去噪功能,将(5)式重新写成完整的闭合解,公式表示为:
其中,
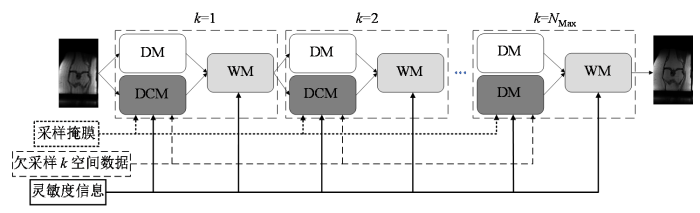
将ISTAVS算法展开搭建成ISTAVS-Net重建网络,结构如图1所示.网络由Nmax个子网络级联而成,每个子网络又包含三个模块:收缩阈值去噪模块(Denoising Module,DM)、数据一致性模块(Data Consistency Module,DCM)和加权模块(Weighting Module,WM).每个模块分别与(12)式中的三步迭代相对应,大大增加了网络的可解释性.迭代次数与网络层数对应,非线性稀疏变换
图1
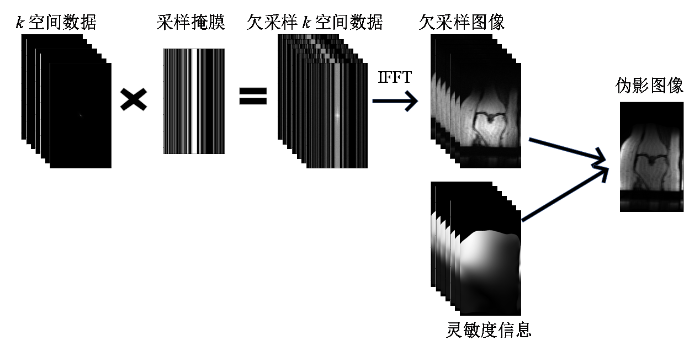
与加速扫描相关的数据有三种:欠采样k空间数据、灵敏度信息、采样掩膜,它们都为多线圈复数数据(
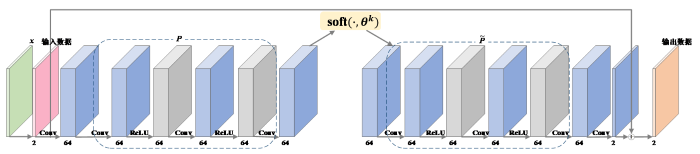
DM为网络的核心模块,其结构如图2所示,由左右两部分及中间的soft
图2
DCM模块和WD模块则根据数学公式进行求解,其输出放在网络中作为交替迭代的中间变量.其中涉及的模型参数(收缩阈值
本文提出的ISTAVS-Net网络实现MRI图像重建的流程为:
1)首先对输入的伪影图进行预处理,得到DM模块的输入数据
2)DCM模块先将图像
3)将前两步得到的输出结果与灵敏度图像一起送入WM模块,将灵敏度加权的多线圈图像
4)重复前面三个步骤,直到第
2 模型实现与训练
2.1 数据集预处理
本研究使用的数据集来自Globus网站公开的NYULH Radiology Reconstruction Data临床膝关节数据集(
本研究使用笛卡尔采样,分别仿真设计了在相位编码方向进行2、4、6和8倍加速下的欠采样掩膜,在中心区域保留24行全采样数据信息,周围进行随机欠采样.
为了获得网络的输入数据,首先对多线圈
图3
网络输入为重建图像的初始值
其中,
2.2 实验环境与评价指标
本研究使用Python编程,在Pytorch框架下完成网络的训练与测试.网络批次大小设为4,初始学习率为0.001,学习率每30轮衰减一半.使用Adam优化器,指数衰减率为
其中,
其中,
对重建图像质量的评价采用MRI重建领域常用的3个指标[23],归一化均方误差(Normalized Mean Square Error,NMSE)、峰值信噪比(Peak Signal-To-Noise Ratio,PSNR)和结构相似性(Structure Similarity Index Measurement,SSIM),且所有指标均采用测试数据的指标平均值来表示.指标计算的公式分别为:
其中,x代表金标准图像,
3 结果与分析
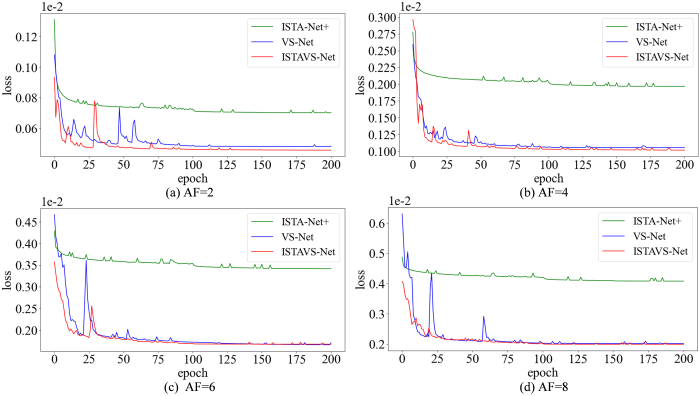
图4为基于模型的三种深度学习网络(ISTA-Net+、VS-Net、ISTAVS-Net)在冠状位数据中的训练损失曲线.ISTA-Net+、VS-Net、ISTAVS-Net网络训练时间分别为10 h 20 min、9 h 30 min、12 h 20 min,网络训练参数量分别为0.986 M、0.782 M、1.018 M.从图4可见,在各加速因子下,三种网络在130轮后都收敛稳定.VS-Net的训练损失值(蓝色)虽远小于ISTA-Net+网络(绿色),但训练中波动较大.本文提出的ISTAVS-Net损失值(红线)在三者中最小,并且在AF=4, 6, 8时比VS-Net(蓝线)震荡的波峰幅值降低,收敛更快速平滑.可见,VS-Net的变量拆分可使重建图像质量更优,而ISTA采用收缩软阈值去噪使网络收敛更快更平稳,ISTAVS-Net在结合ISTA去噪后,稳定性比VS-Net得到了较大提升.
图4
图4
加速因子为(a) 2、(b) 4、(c) 6、(d) 8时ISTA-Net+、VS-Net、ISTAVS-Net网络的训练损失曲线
Fig. 4
Training loss curves of ISTA-Net+,VS-Net and ISTAVS-Net with AF of (a) 2, (b) 4, (c) 6, and (d) 8
表1为两种传统算法(L1-ESPIRiT、ISTA)和4种深度学习网络(U-Net、ISTA-Net+、VS-Net、ISTAVS-Net)在冠状位数据重建结果中的评价指标(PSNR、SSIM、NMSE)的平均值.从表1中可见,4种深度学习网络的性能指标均优于传统算法.且本文提出的ISTAVS-Net网络相较于另外三种深度学习网络,性能指标均有提高.两种算法和四种深度学习网络的性能排序为:ISTAVS-Net>U-Net>VS-Net>ISTA-Net+>ISTA>L1-ESPIRiT.比较不同加速因子下评价指标可见,当AF=2时,四种网络差距较小,PSNR均超过40 dB.AF=4时,ISTAVS-Net的PSNR达到了37.724 dB,相比另三种网络有较大提升.AF=6时,ISTAVS-Net的SSIM依旧能保持在0.9以上.在高加速因子(AF=8)下,ISTAVS-Net的重建指标虽然也最好,但网络指标值下降较为明显.
表1 两种传统算法(L1-ESPIRiT、ISTA)和4种深度学习网络(U-Net、ISTA-Net+、VS-Net、ISTAVS-Net)在冠状位数据重建结果中的评价指标平均值
Table 1
| 评价指标 | AF | L1-ESPIRiT | ISTA | U-Net | ISTA-Net+ | VS-Net | ISTAVS-Net |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR/dB | 2 | 32.671 | 34.051 | 40.926 | 40.879 | 40.675 | 42.021 |
| 4 | 28.868 | 30.390 | 36.911 | 36.281 | 36.478 | 37.724 | |
| 6 | 27.234 | 29.567 | 34.052 | 33.808 | 33.932 | 34.609 | |
| 8 | 26.976 | 28.446 | 33.287 | 32.713 | 33.184 | 33.341 | |
| SSIM | 2 | 0.8802 | 0.9301 | 0.9573 | 0.9470 | 0.9547 | 0.9604 |
| 4 | 0.8275 | 0.8680 | 0.9257 | 0.9128 | 0.9208 | 0.9311 | |
| 6 | 0.7608 | 0.8424 | 0.8950 | 0.8807 | 0.8936 | 0.9002 | |
| 8 | 0.7020 | 0.8205 | 0.8825 | 0.8679 | 0.8833 | 0.8839 | |
| NMSE | 2 | 0.0205 | 0.0160 | 0.0107 | 0.0113 | 0.0109 | 0.0105 |
| 4 | 0.0384 | 0.0362 | 0.0189 | 0.0193 | 0.0190 | 0.0183 | |
| 6 | 0.0478 | 0.0438 | 0.0277 | 0.0280 | 0.0275 | 0.0271 | |
| 8 | 0.0578 | 0.0567 | 0.0347 | 0.0350 | 0.0316 | 0.0304 |
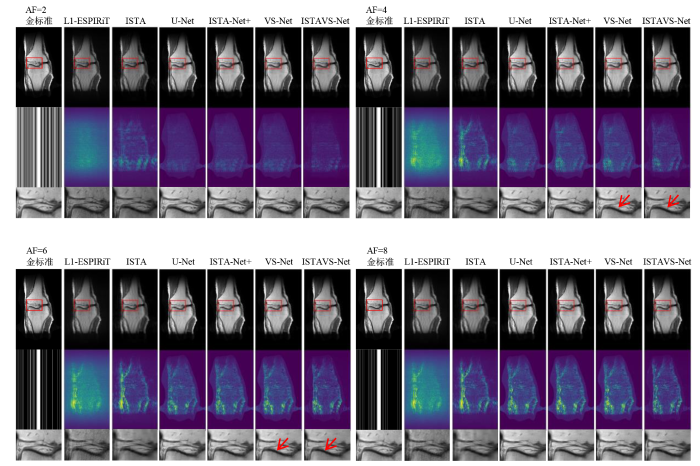
图5为AF=2, 4, 6和8时,两种传统算法和四种深度学习网络在冠状位数据中的重建结果.第一行为金标准图像和六种重建图像,第二行为欠采样mask和误差图像,第三行为第一行中红色框内的放大图.从图中可见,在AF不高时,四种深度学习网络都得到了很好的重建图像.而传统算法只有在AF=2时较好,AF=4时结果已出现很强的伪影,不适于临床.而提出的ISTAVS-Net误差最小,图像细节恢复更好.在AF=4时,红色方框处ISTAVS-Net重建结果明显更清晰,伪影更少,红色箭头处的软骨损伤清晰可见.
图5
图5
两种传统算法和四种深度学习网络在冠状位数据中的重建结果(左上:AF=2,右上:AF=4,左下:AF=6,右下:AF=8)
Fig. 5
Reconstruction results of two traditional algorithms and four deep learning networks in coronary data (upleft: AF=2, upright: AF=4, down left: AF=6, down right: AF=8)
AF=6和8时,传统算法的重建结果已很难应用于临床.在AF为6时,四种深度学习网络都能重建出图像,可区分不同组织.但随着AF增大,误差图变亮,图像质量变差,AF=8时折叠伪影较为严重.可见,高加速因子下(AF=8),四种深度学习网络都不能完全消除伪影.但ISTAVS-Net重建图像的折叠伪影相对更轻,对图像细节的恢复在四者中也是最强的.
表1和图5的测试结果证明提出的ISTAVS-Net网络在冠状位数据中的重建效果很好.为了验证该网络在其他方位重建的泛化,我们还对轴位数据集在6倍加速下的网络进行训练和测试,并与冠状位重建结果进行比较.同时展示了传统算法L1-ESPIRiT和ISTA的重建结果以便比较.两种数据集的重建评价指标平均值如表2所示.ISTAVS-Net网络的重建指标均远优于传统算法,且轴位和冠状位的SSIM值分别为0.938 2和0.900 2.相比冠状位,轴位重建效果更好,PSNR值更高,能达到38.952 dB.ISTAVS-Net重建时间只需1~2 s,比L1-ESPIRiT(~3 min)和ISTA(~80 s)快很多,且重建质量明显优于传统算法.
表2 轴位和冠状位的评价指标对比
Table 2
| 轴位 | 冠状位 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1-ESPIRiT | ISTA | ISTAVS-Net | L1-ESPIRiT | ISTA | ISATVS-Net | ||
| PSNR/dB | 31.743 | 34.051 | 38.952 | 27.234 | 29.567 | 34.609 | |
| SSIM | 0.8180 | 0.9089 | 0.9382 | 0.7608 | 0.8424 | 0.9002 | |
| NMSE | 0.0467 | 0.0395 | 0.0227 | 0.0478 | 0.0438 | 0.0271 | |
| Times/s | 196.12 | 71.66 | 2.11 | 153.95 | 80.13 | 1.04 | |
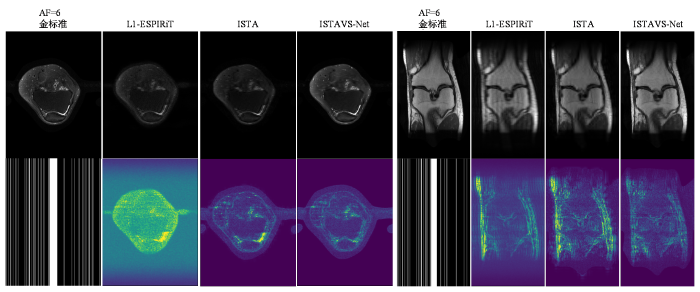
图6为AF=6时,一例病人的轴位与冠状位的重建图像对比图.两个方位的L1-ESPIRiT和ISTA重建图像都更模糊,信噪比较低,但ISTA算法优于L1-ESPIRiT.本文提出的ISTAVS-Net重建质量最优,组织边缘更清晰,消除了冠状位的大部分伪影.可见,ISTAVS-Net对两个不同扫描方位的重建效果均比传统算法提升了很多,网络泛化能力很强.
图6
图6
AF=6时轴位与冠状位的重建结果对比(左:轴位,右:冠状位)
Fig 6
Reconstruction results based on AF=6 (left: sagittal, right: transverse)
4 结论
本文提出了一种在VS-Net基础上结合ISTA去噪的ISTAVS-Net,实现了对多线圈CS-MRI加速采集数据的图像重建.ISTAVS-Net包含了两方面的改进:(1)相比使用简单卷积操作因而去噪不彻底的VS-Net,ISTAVS-Net使用改进的多线圈ISTA算法实现去噪模块,迭代软阈值去噪效果明显,能保持图像细节. (2)在去噪模块的输入与输出之间引入残差机制,避免了网络在训练中可能出现的梯度问题和性能退化,增加网络的非线性映射能力,提高了重建的准确性和稳定性.
ISTAVS-Net是基于CS-MRI物理模型的,相比于黑盒网络,可解释性更强.且模型参数和正则化项都能自动学习,而非人为选取.网络在AF≤6时重建的图像质量高,能兼顾定量指标与视觉效果.基于模型的网络比传统迭代方法具有更好的灵活性,能提高MRI重建质量,推动了传统算法与网络模型的结合,这在工程中也更具实际意义.
当加速因子过高时(AF=8),虽然网络评价指标值较好,但图像伪影并不能完全消除,会影响临床诊断.后续可重新设计加速扫描方式、结合双域加速[25]等手段来优化网络,以获得更优的重建图像.总之,使用深度学习网络的方法实现MRI重建还存在许多问题尚未解决,离临床落地还有较远的路要走.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.21391
PMID:17969013
[本文引用: 1]

The sparsity which is implicit in MR images is exploited to significantly undersample k-space. Some MR images such as angiograms are already sparse in the pixel representation; other, more complicated images have a sparse representation in some transform domain-for example, in terms of spatial finite-differences or their wavelet coefficients. According to the recently developed mathematical theory of compressed-sensing, images with a sparse representation can be recovered from randomly undersampled k-space data, provided an appropriate nonlinear recovery scheme is used. Intuitively, artifacts due to random undersampling add as noise-like interference. In the sparse transform domain the significant coefficients stand out above the interference. A nonlinear thresholding scheme can recover the sparse coefficients, effectively recovering the image itself. In this article, practical incoherent undersampling schemes are developed and analyzed by means of their aliasing interference. Incoherence is introduced by pseudo-random variable-density undersampling of phase-encodes. The reconstruction is performed by minimizing the l(1) norm of a transformed image, subject to data fidelity constraints. Examples demonstrate improved spatial resolution and accelerated acquisition for multislice fast spin-echo brain imaging and 3D contrast enhanced angiography.(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Solving inverse problems in medical imaging with score-based generative models
[J].
HFIST-Net: High-throughput fast iterative shrinkage thresholding network for accelerating MR image reconstruction
[J].
A review and experimental evaluation of deep learning methods for MRI reconstruction
[J].
Accelerating magnetic resonance imaging via deep learning
[C]//
Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging
[J].
Analysis of deep complex-valued convolutional neural networks for MRI reconstruction and phase-focused applications
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.28733
PMID:33724507
[本文引用: 1]

Deep learning has had success with MRI reconstruction, but previously published works use real-valued networks. The few works which have tried complex-valued networks have not fully assessed their impact on phase. Therefore, the purpose of this work is to fully investigate end-to-end complex-valued convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for accelerated MRI reconstruction and in several phase-based applications in comparison to 2-channel real-valued networks.Several complex-valued activation functions for MRI reconstruction were implemented, and their performance was compared. Complex-valued convolution was implemented and tested on an unrolled network architecture and a U-Net-based architecture over a wide range of network widths and depths with knee, body, and phase-contrast datasets.Quantitative and qualitative results demonstrated that complex-valued CNNs with complex-valued convolutions provided superior reconstructions compared to real-valued convolutions with the same number of trainable parameters for both an unrolled network architecture and a U-Net-based architecture, and for 3 different datasets. Complex-valued CNNs consistently had superior normalized RMS error, structural similarity index, and peak SNR compared to real-valued CNNs.Complex-valued CNNs can enable superior accelerated MRI reconstruction and phase-based applications such as fat-water separation, and flow quantification compared to real-valued convolutional neural networks.© 2021 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
SwinGAN: A dual-domain swin transformer-based generative adversarial network for MRI reconstruction
[J].
Magnetic resonance image reconstruction of multi-scale residual Unet fused with attention mechanism
[J].
融合注意力机制的多尺度残差Unet的磁共振图像重建
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20223040
[本文引用: 1]

为了提高磁共振图像在欠采样下重建的质量,本文融合注意力机制和多尺度残差卷积构建Unet网络,实现磁共振图像在欠采样下的重建算法.为增强网络特征的表现能力,以及防止网络训练中梯度消失与退化的问题,在Unet网络的编码路径中引入多尺度残差卷积,提取不同尺度的特征信息;为能准确地恢复图像的细节纹理特征,在Unet网络编码和解码路径的跳层拼接部分引入卷积注意力块,对细节纹理等关键信息进行不同程度的响应.实验表明,本文方法可通过欠采样k-空间数据快速重建出细节纹理清晰且无重叠伪影的高质量磁共振图像.
Fast multi-channel magnetic resonance imaging based on PCAU-Net
[J].
基于PCAU-Net的快速多通道磁共振成像方法
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20222992
[本文引用: 1]

多通道磁共振成像方法采用多个接收线圈同时欠采样k空间以加快成像速度,并基于后处理算法重建图像,但在较高加速因子时,其图像重建质量仍然较差.本文提出了一种基于PCAU-Net的快速多通道磁共振成像方法,将单通道实数U型卷积神经网络拓展到多通道复数卷积神经网络,设计了一种结构不对称的U型网络结构,通过在解码部分减小网络规模以降低模型的复杂度.PCAU-Net网络在跳跃连接前增加了1×1卷积,以实现跨通道信息交互.输入和输出之间利用残差连接为误差的反向传播提供捷径.实验结果表明,使用规则和随机采样模板,在不同加速因子时,相比常规的GRAPPA重建算法和SPIRiT重建方法,本文提出的PCAU-Net方法可高质量重建出磁共振复数图像,并且相比于PCU-Net方法,PCAU-Net减少了模型参数、缩短了训练时间.
Deep ADMM-Net for compressive sensing MRI
[C]//
Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.26977
PMID:29115689
[本文引用: 1]

To allow fast and high-quality reconstruction of clinical accelerated multi-coil MR data by learning a variational network that combines the mathematical structure of variational models with deep learning.Generalized compressed sensing reconstruction formulated as a variational model is embedded in an unrolled gradient descent scheme. All parameters of this formulation, including the prior model defined by filter kernels and activation functions as well as the data term weights, are learned during an offline training procedure. The learned model can then be applied online to previously unseen data.The variational network approach is evaluated on a clinical knee imaging protocol for different acceleration factors and sampling patterns using retrospectively and prospectively undersampled data. The variational network reconstructions outperform standard reconstruction algorithms, verified by quantitative error measures and a clinical reader study for regular sampling and acceleration factor 4.Variational network reconstructions preserve the natural appearance of MR images as well as pathologies that were not included in the training data set. Due to its high computational performance, that is, reconstruction time of 193 ms on a single graphics card, and the omission of parameter tuning once the network is trained, this new approach to image reconstruction can easily be integrated into clinical workflow. Magn Reson Med 79:3055-3071, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
End-to-end variational networks for accelerated MRI reconstruction
[J].
Pyramid convolutional RNN for MRI image reconstruction
[J].
MEDL-Net: A model-based neural network for MRI reconstruction with enhanced deep learned regularizers
[J].
A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems
[J].
ISTA-Net: Interpretable optimization-inspired deep network for image compressive sensing
[C]//
ISTA-NET++: Flexible deep unfolding network for compressive sensing
[C]//
VS-Net: variable splitting network for accelerated parallel MRI reconstruction
[C]//
Compressed sensing MRI: A review from signal processing perspective
[J].
A review and experimental evaluation of deep learning methods for MRI reconstruction
[J].
Compressed sensing in sodium magnetic resonance imaging: techniques, applications, and future prospects
[J].
FastMRI: an open dataset and benchmarks for accelerated MRI
[J].
ESPIRiT-an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: where SENSE meets GRAPPA
[J].
Dual-domain accelerated MRI reconstruction using transformers with learning-based undersampling
[J].