引言
核自旋单重态具有特殊的对称性,不受自旋间偶极-偶极相互作用的影响,从而表现出长寿命的特点[1,2]. 该特性使得核自旋单重态具有一些特殊的用途,如用于磁共振分子滤波[3],q空间成像[4],研究分子的慢扩散和慢运动[5]等.单重态的应用主要包含三个步骤,首先需要施加特定的脉冲,将核自旋的状态由热平衡态转化为单重态,之后是单重态的保存,可以通过施加连续波脉冲平均自旋之间的化学位移差异,或者将核自旋从高磁场环境移到低磁场或者零磁场环境中.最后,当需要探测单重态的信号时,通过施加射频脉冲,将自旋信号从单重态转化为可观测态[6].在此过程中,核自旋单重态的制备效率决定了单重态自旋信号的灵敏度,是判断单重态应用是否有效的关键步骤.
目前文献中提出了多种制备核自旋单重态的方法,包括基于多个组合硬脉冲的M2S脉冲和gM2S脉冲[7,8]、基于两自旋之间J耦合的SLIC脉冲[6]、基于优化控制和数值计算的优化脉冲以及基于渐变过程的绝热脉冲[9]等.这些脉冲的提出主要针对两自旋体系,当制备单重态的自旋受到其它核自旋的耦合作用时,单重态的制备效率往往会降低[10],进而影响单重态自旋的信号强度及其应用范围[11].本课题组前期的工作中,针对多自旋体系,提出将单重态自旋和非单重态自旋的耦合作用一并输入脉冲计算程序,设计了能高效地制备核自旋单重态同时又能避免非单重态自旋耦合影响的优化脉冲序列,并在三自旋及五自旋体系实验验证了脉冲序列的有效性[12⇓-14].但将非目标自旋考虑到脉冲计算过程时,会大大增加脉冲计算的复杂性.由此我们考虑,是否存在具有某种特征的多自旋体系,在该体系中可以使用普适的针对二自旋的单重态制备脉冲高效地制备单重态.
本文讨论了单重态制备脉冲在不同耦合构型下受其它非单重态自旋的影响.考虑一个由三个质子组成的三自旋体系(H1, H2, H3),质子间存在J耦合相互作用,如果将H1与H2当成孤立的自旋体系,可以计算得到制备其单重态的脉冲,但实验施加脉冲期间,其状态必然受到第三个自旋H3的影响,即自旋H3与单重态自旋(H1和H2)之间的耦合作用会在一定程度上降低单重态的制备效率.本文模拟了不同耦合情况下单重态效率降低的幅度,研究发现:链式耦合构型时,单重态的制备效率随着非单重态自旋对单重态自旋耦合作用的增加逐渐降低;而强耦合网状构型中,当非单重态自旋与单重态自旋对的耦合值呈现出对称性时,单重态制备效率并不会随着耦合值的增大而快速下降,而是保持一定的稳定性.该结论在N-乙酰-L-天门冬氨酸(NAA)分子体系中得到了实验验证.
1 理论与模拟
处于高磁场中的两个自旋量子数I = 1/2的核自旋,通常包含四个能级,当两个自旋处于弱耦合时,能级对应的本征态可以表示为:
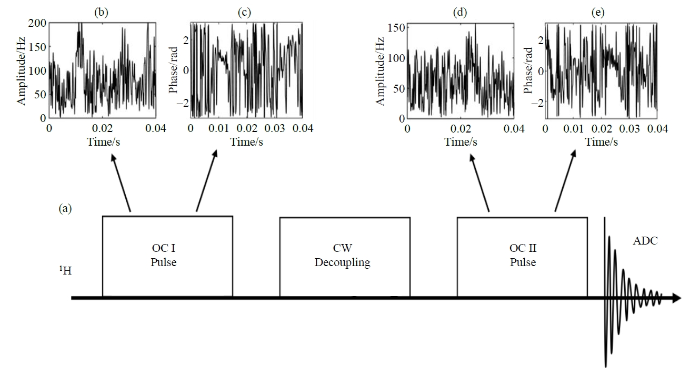
图1
图1
(a)制备以及检测单重态的脉冲序列图[3];(b) OC I脉冲的幅度调制图;(c) OC I脉冲的相位调制图;(d) OC II脉冲的幅度调制图;(e) OC II脉冲的相位调制图
Fig. 1
(a) Preparation and detection of singlet pulse sequence[3]; (b) Amplitude modulation diagram of OC I pulse; (c) Phase modulation diagram of OC I pulse; (d) Amplitude modulation diagram of OC II pulse; (e) Phase modulation diagram of OC II pulse of OC II pulse
无论哪种单重态制备脉冲,当设计脉冲时只考虑单重态自旋对的化学参数,而实际体系中该自旋对还受到其它自旋的耦合作用时,单重态的制备效率会因为其它自旋的耦合作用而降低,降低的程度与自旋之间耦合常数的关系可以通过体系密度矩阵的演化过程进行量化.
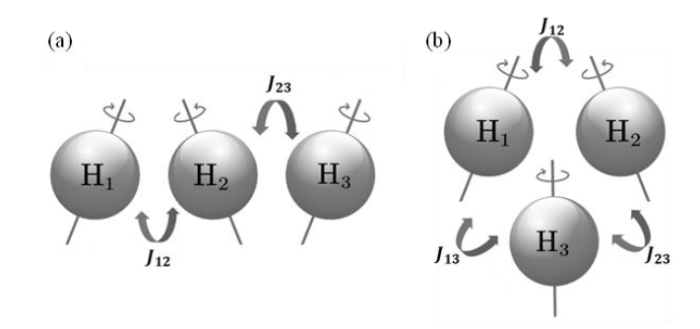
考虑一个三自旋体系(H1、H2、H3),假设H1与H2为制备单重态的自旋对,H3为外部自旋,该体系可能存在如图2所示的两种耦合形式,其中(a)为链式耦合,(b)为网状耦合.当体系处于外磁场
这里
图2
图2
两种三自旋体系构型示意图.(a)链式耦合构型,H1和H3之间的长程耦合可以忽略不计;(b)网状耦合构型,体系中每两个氢之间都有J耦合
Fig. 2
Schematic of two three-spin system structure. (a) chain-coupled configuration, where the long-range coupling between H1 and H3 is negligible; (b) reticular-coupled structure, where there is J-coupling between every two hydrogens in the system
假设三个自旋H1、H2、H3的共振频率分别为$\omega_{1} / 2 \pi, \omega_{2} / 2 \pi, \omega_{3} / 2 \pi$,自旋之间的J耦合分别为J12、J13、J23.当仅考虑H1和H2之间的相互作用时,制备单重态的优化脉冲可以利用SIMPSON软件计算出脉冲形状(计算相应脉冲的脚本文件见附件材料S1).实际体系中单重态的制备效率与耦合常数J13及J23的关系可以通过MATLAB模拟程序(程序脚本见附件材料S2)进行计算,计算方法如下给出.
式中$\rho_{\mathrm{F}}^{+}$和$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}^{+}$分别代表末态算符与单态序算符矩阵的共轭转置. 此时单重态的制备效率则为0.67$\eta $.为了简化,下面的模拟中,我们主要讨论$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$的制备效率.
1.1 链式耦合模拟结果与讨论
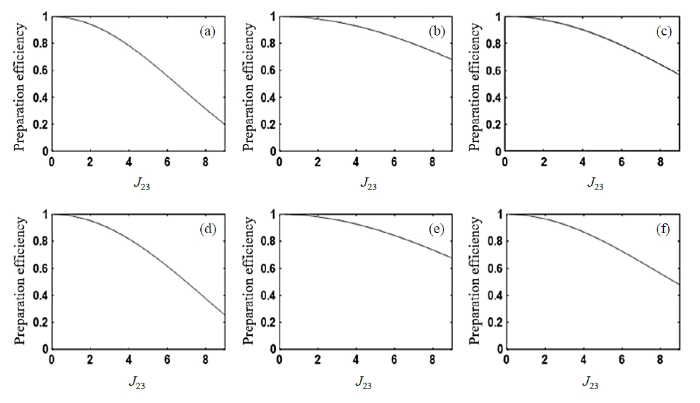
链式耦合构型广泛存在于分子中碳链的邻碳氢之间,在不含双键的碳链中其耦合值通常在2~9 Hz,选取J23的变化范围为0~9 Hz,定义目标自旋对之间的耦合J12为7 Hz,H1与H2之间的化学位移差值取不同的值进行模拟,分别为:5 Hz、10 Hz、15 Hz、20 Hz、50 Hz与100 Hz,目的是让自旋体系由中间耦合逐渐过渡到弱耦合,逐一计算外部耦合J23的变化对$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$态制备效率$\eta\left(J_{23}\right)$的影响.对于不同的化学位移差值,制备单重态的优化脉冲OC I和OC II的形状见附件材料S3.模拟结果如图3所示,链式构型中,无论单重态的自旋对处于中间耦合还是弱耦合,其$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$态的制备效率均随着非单重态自旋耦合常数J23的增加而下降.其中,在J23足够小的时候,$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$量子态的制备效率$\eta\left(J_{23}\right)$并未出现显著下降,这表明小的外部耦合并不会显著影响$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$态制备效率.由$\frac{\mathrm{d}^{2} \eta}{\mathrm{d} J^{2}}$可知,链式构型中外部耦合J23越大,其制备单重态的过程更易被外部耦合所影响.
图3
图3
H1与H2之间的J耦合常数为7 Hz,化学位移差值定为(a) 5 Hz、(b) 10 Hz、(c) 15 Hz、(d) 20 Hz、(e) 50 Hz和(f) 100 Hz时,$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$态制备效率随J23变化的模拟图
Fig. 3
Simulated singlet state preparation efficiency varying with J23. (a)~(f) corresponds to the chemical shift 5 Hz, 10 Hz, 15 Hz, 20 Hz, 50 Hz, 100 Hz, respectively, when the J-coupling constant between H1 and H2 is 7 Hz
1.2 网状耦合构型模拟结果与讨论
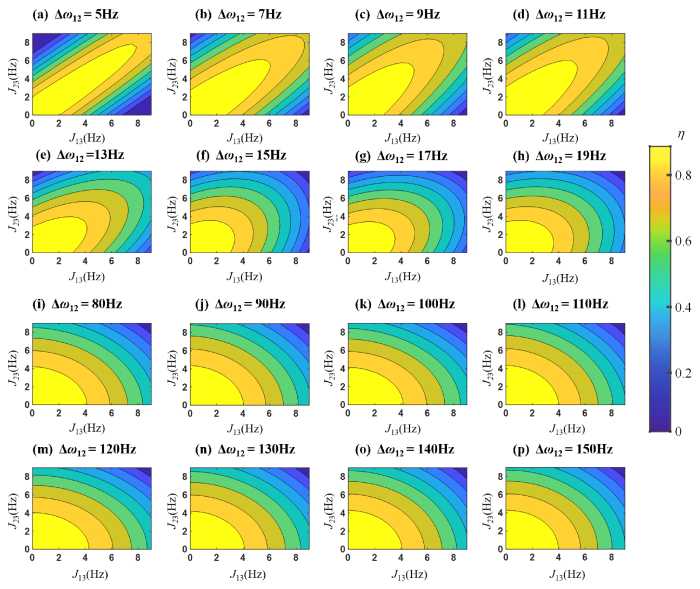
网状耦合构型大多存在于亚甲基的一对非等价同碳氢原子核以及一个邻碳氢原子核中,以
图4
图4
H1与H2之间J耦合常数(J12)为15 Hz,化学位移差值(Δω12)分别为5 Hz (a)、7 Hz (b)、9 Hz (c)、11 Hz (d)、13 Hz (e)、15 Hz (f)、17 Hz (g)、19 Hz (h)、80 Hz (i)、90 Hz (j)、100 Hz (k)、110 Hz (l)、120 Hz (m)、130 Hz (n)、140 Hz (o)和150 Hz (p)时,$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$态制备效率随J13和J23变化的模拟图
Fig. 4
Simulated singlet state preparation efficiency varying with J13 and J23. (a)~(f) corresponds to the chemical shift 5 Hz, 7 Hz, 9 Hz, 11 Hz, 13 Hz, 15 Hz, 17 Hz, 19 Hz, 80 Hz, 90 Hz, 100 Hz, 110 Hz, 120 Hz, 130 Hz, 140 Hz, 150 Hz, respectively, when the J-coupling constant between H1 and H2 is 15 Hz. The horizontal and vertical axes are the coupling values of J13 and J23
2 实验部分
2.1 仪器与试剂
仪器:Bruker Avance III 500型NMR谱仪(5 mm液体BBO探头).
试剂:D2O(99.9%,阿拉丁),NAA(99%,Sigma-Aldrich),氘代氢氧化钠(NaOD,99%,Sigma-Aldrich).试剂未经进一步纯化,直接使用.
2.2 NMR模拟与实验
模拟谱图使用软件:SIMPSON.
模拟参数设置:模拟谱图的单脉冲均为脉宽为0的理想脉冲,模拟使用的OC脉冲波形见附件材料S3和S4,谱宽均设置为5 000 Hz,采样点数(TD)设置为19 998,CW的功率为0.1 W,持续时间$\tau_{\mathrm{C}}$为0.1 s.
试剂配制:将87 mg的NAA溶解在5 mL D2O中,配成浓度为0.1 mol/L的NAA溶液,此时pH为2.3,吸取450 µL溶液至NMR样品管.另外使用浓NaOD将剩余溶液的pH值调节至12.3,吸取450 µL溶液至NMR样品管.
实验参数设置:对常规的单脉冲实验,累加次数(NS)设置为4,谱宽定为5 000 Hz,TD为19 998,接收机增益(RG)设置为32,90˚激发脉冲采用矩形脉冲,脉宽为10 µs,脉冲功率为21.8 W,实验时射频中心(O1)定为δH 4.701.
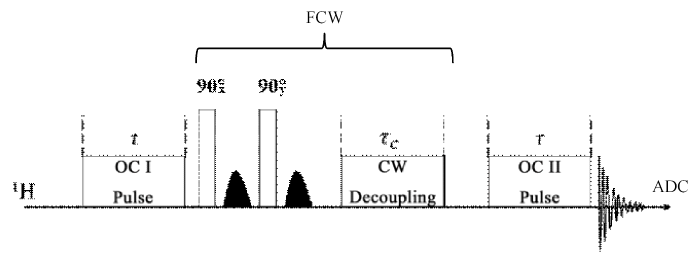
对基于优化脉冲序列的单重态滤波实验,使用的脉冲序列如图5所示,不同实验对应的OC I和OC II的波形图及其对应的参数在附件材料S5和S6给出,CW的功率为0.1 W,持续时间$\tau_{\mathrm{C}}$为0.1 s.滤波模块中90˚激发脉冲采用矩形脉冲,脉宽为10 µs,脉冲功率为21.8 W,梯度脉冲幅度为25%,持续时间为800 µs. 这里,OC1脉冲后增加了一个滤波模块,包含两个90˚脉冲和两个梯度脉冲.理论上,该模块不会影响单重态,但会将单重态以外的信号散相.
图5
图5
利用优化控制方法制备单重态并滤波的脉冲序列图. 初态经过OC I脉冲作用后转化为$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$态,之后的滤波模块(FCW)将非单重态信号散相,其中CW去耦脉冲用于保留单重态信号,两个90˚脉冲相位分别为x、y,OC II脉冲将$\rho_{\mathrm{SS}}$转化为单量子态,以观测磁共振信号
Fig. 5
Pulse sequence based on the optimal controlled singlet state preparation. OC I is to transfer the initial state into $\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$. The following filtering module is to dephase unwanted signals. The CW is used to store the singlet state. The phases of the two 90-degree pulses are x and y respectively. The OC II module is to convert $\rho_{\mathrm{SS}}$ to single quantum state
总体而言,初态经过OC I脉冲作用后转化为$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}=\eta_{1}\left(2 I_{1 x} I_{2 x}+2 I_{1 y} I_{2 y}\right)$,滤波模块(FCW)作用下$\rho_{\mathrm{SO}}$态转化为$\rho_{\mathrm{SS}}=\eta_{1} \eta_{2}\left(2 I_{1 x} I_{2 x}+2 I_{1 y} I_{2 y}+2 I_{1 z} I_{2 z}\right)$,OC II脉冲将$\rho_{\mathrm{SS}}$转化为单量子态$\rho_{x}=\eta_{1} \eta_{2} \eta_{3}\left(I_{1 x}+I_{2 x}\right)$.其中$0<\eta_{1}<1, \quad 0<\eta_{2}<2 / 3, \quad 0<\eta_{3}<1, \quad \eta_{1} \eta_{2}$可描述单重态制备效率,而$\eta_{1} \eta_{2} \eta_{3}$则可以描述脉冲序列的滤波效率.
2.3 实验结果与讨论
图6
图6
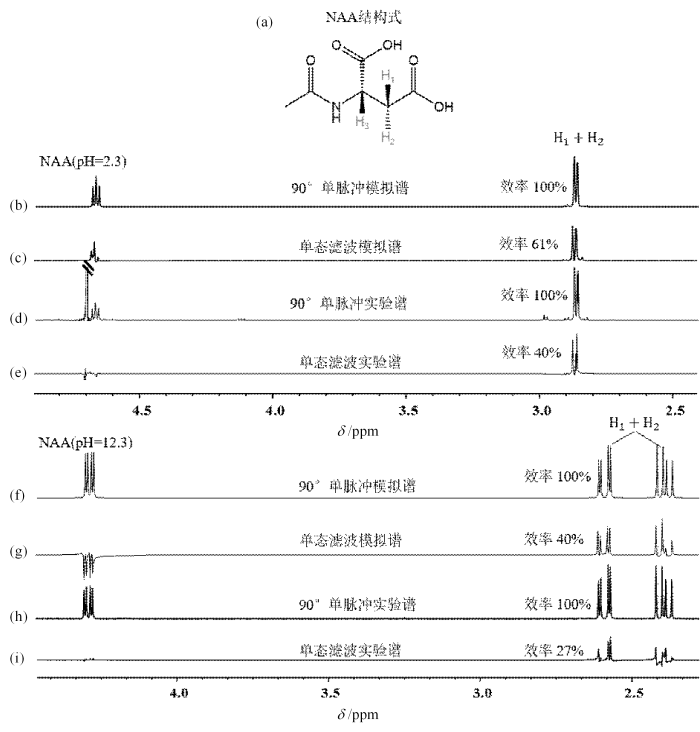
(a) NAA分子的结构示意图,其中H1、H2、H3为文中考虑的三自旋体系,H1、H2为单重态自旋对;(b) NAA三自旋在强耦合情况下的单脉冲模拟谱图;(c) NAA三自旋在强耦合情况下使用单重态滤波脉冲序列的模拟谱图;(d) NAA三自旋在强耦合情况下的单脉冲实验谱图;(e) NAA三自旋在强耦合情况下的单重态滤波脉冲序列的实验谱图;(f) NAA三自旋在弱耦合情况下的单脉冲模拟谱图;(g) NAA三自旋在弱耦合情况下使用单重态滤波脉冲序列的模拟谱图;(h) NAA三自旋在弱耦合情况下的单脉冲实验谱图;(i) NAA三自旋在弱耦合情况下的单重态滤波脉冲序列实验谱图
Fig. 6
(a) Schematic representation of the structure of NAA molecule, where H1, H2, H3 represent the three spin systems considered in the text; H1, H2 correspond to the target singlet spin pair; (b) Simulated spectrum of NAA three-spin system with strong coupling under single-pulse excitation; (c) Simulated spectrum of NAA three-spin system with strong coupling using singlet-state preparation pulse sequence; (d) Experimental spectrum of NAA three-spin system with strong coupling under single-pulse excitation; (e) Experimental spectrum of NAA three-spin system with strong coupling using singlet-state preparation pulse sequence; (f) Simulated spectrum of NAA three-spin system with weak coupling under single-pulse excitation; (g) Simulated spectrum of NAA three-spin system with weak coupling using singlet-state preparation pulse sequence; (h) Experimental spectrum of NAA three-spin system with weak coupling under single-pulse excitation; (i) Experimental spectrum of NAA three-spin system with weak coupling using singlet-state preparation pulse sequence
表1
NAA中以
Table 1
| δ1 | δ2 | δ3 | J12 | J13 | J23 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH=2.3 | 1430.4 | 1437.2 | 2335.6 | -17.22 | 6.43 | 5.52 |
| pH=12.3 | 1198.5 | 1295.0 | 2146.4 | -15.70 | 10.03 | 3.86 |
相似地,针对pH=12.3的NAA弱耦合体系,其单脉冲模拟谱图以及施加图5所示脉冲序列后的模拟谱如图6(f)、(g)所示.选择对δH 2.30~2.70区间谱峰进行积分,以单脉冲的结果作为分母进行比值从而得到效率.模拟结果表明,施加图5所示脉冲序列得到的模拟谱图中理论的滤波效率为40%.施加图5所示脉冲序列进行实验采集得到的实验谱图如图6(h)、(k)所示.实验结果表明,施加优化脉冲序列所得到的实验的滤波效率27%.与理论相比,实验效率存在一定程度的降低,其原因主要来自于脉冲施加期间因为脉冲时长较长引起的弛豫衰减,单重态滤波模块$(\pi / 2-\operatorname{grad}-\pi / 2-\operatorname{grad}+\mathrm{CW})$中两个梯度脉冲导致的信号散相以及CW去耦脉冲期间单重态与三重态的分离引起的强度下降.
为了消除如文献[16]中讨论的实验因素(样品浓度、温度及射频发射中心)对单重态效率的影响,上述实验均设置了相同的样品浓度、温度及射频发射中心.值得注意的是,单重态的寿命长短主要与分子的结构相关,不管体系为链式耦合还是网络状强耦合,当分子结构和外部实验条件(温度、浓度等)确定后,单重态的寿命长短不会随制备脉冲的不同而变化.
上述理论和实验结果表明:网络状弱耦合体系中,单重态的制备效率容易受外部作用的影响,此时在设计单重态的制备脉冲时需要考虑同时压制外部耦合的影响;而网络状强耦合体系中,当外部耦合具有对称特征时$\left(J_{13} \approx J_{23}\right)$,单重态的制备效率不易受外部耦合的影响.
3 结论
总之,在网络状耦合构型中,单重态的制备效率会随非单重态自旋对其耦合的强弱表现出不同的特征,弱耦合网络构型中单重态制备效率会随着外部耦合的均方根$\sqrt{J_{13}^{2}+J_{23}^{2}}$近似单变量变化,而强耦合网络构型中单重态制备效率会在$J_{13} \approx J_{23}$附近呈现出极大效率,此现象表明在复杂分子体系中制备单重态时,应该选择具有良好对称性的强耦合自旋对作为目标自旋.
利益冲突
无
附件材料(可在《波谱学杂志》期刊官网 http://magres.wipm.ac.cn 获取)
S1 单重态制备与转化优化脉冲的SIMPSON程序示例
S2 利用优化控制脉冲进行模拟的MATLAB程序代码
S3 链式耦合构型模拟所用的脉冲波形图
S4 网状耦合构型模拟所用的脉冲波形图
S5 实验所用的脉冲波形图
S6 实验中所使用的优化脉冲下的算符演化图
参考文献
Long-lived nuclear spin states in high-field solution NMR
[J].Nuclear spin order may be stored in a liquid for a much longer time than the longitudinal relaxation time T1, by using rf fields to isolate states of different symmetry. The method is demonstrated on a sample containing AX spin systems.
Beyond the T1 limit: singlet nuclear spin states in low magnetic fields
[J].DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.153003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Preparation of long-lived states in a multi-spin system by using an optimal control method
[J].
NMR q-space imaging of macroscopic pores using singlet spin states
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2010.03.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
Measurement of slow diffusion coefficients of molecules with arbitrary scalar couplings via long-lived spin states
[J].
Preparation of nuclear spin singlet states using spin-lock induced crossing
[J].DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.173002 URL [本文引用: 2]
Storage of nuclear magnetization as long-lived singlet order in low magnetic field
[J].
DOI:10.1073/pnas.1010570107
URL
[本文引用: 1]

\n Hyperpolarized nuclear states provide NMR signals enhanced by many orders of magnitude, with numerous potential applications to analytical NMR, in vivo NMR, and NMR imaging. However, the lifetime of hyperpolarized magnetization is normally limited by the relaxation time constant\n T\n 1\n, which lies in the range of milliseconds to minutes, apart from in exceptional cases. In many cases, the lifetime of the hyperpolarized state may be enhanced by converting the magnetization into nuclear singlet order, where it is protected against many common relaxation mechanisms. However, all current methods for converting magnetization into singlet order require the use of a high-field, high-homogeneity NMR magnet, which is incompatible with most hyperpolarization procedures. We demonstrate a new method for converting magnetization into singlet order and back again. The new technique is suitable for magnetically inequivalent spin-pair systems in weak and inhomogeneous magnetic fields, and is compatible with known hyperpolarization technology. The method involves audio-frequency pulsed irradiation at the low-field nuclear Larmor frequency, employing coupling-synchronized trains of 180° pulses to induce singlet–triplet transitions. The echo trains are used as building blocks for a pulse sequence called M2S that transforms longitudinal magnetization into long-lived singlet order. The time-reverse of the pulse sequence, called S2M, converts singlet order back into longitudinal magnetization. The method is demonstrated on a solution of\n 15\n N-labeled nitrous oxide. The magnetization is stored in low magnetic field for over 30 min, even though the\n T\n 1\n is less than 3 min under the same conditions.\n
Generalised magnetisation-to-singlet-order transfer in nuclear magnetic resonance
[J].
DOI:10.1039/d0cp00935k
PMID:32329499
[本文引用: 1]

A variety of pulse sequences have been described for converting nuclear spin magnetisation into long-lived singlet order for nuclear spin-1/2 pairs. Existing sequences operate well in two extreme parameter regimes. The magnetisation-to-singlet (M2S) pulse sequence performs a robust conversion of nuclear spin magnetisation into singlet order in the near-equivalent limit, meaning that the difference in chemical shift frequencies of the two spins is much smaller than the spin-spin coupling. Other pulse sequences operate in the strong-inequivalence regime, where the shift difference is much larger than the spin-spin coupling. However both sets of pulse sequences fail in the intermediate regime, where the chemical shift difference and the spin-spin coupling are roughly equal in magnitude. We describe a generalised version of M2S, called gM2S, which achieves robust singlet order excitation for spin systems ranging from the near-equivalence limit well into the intermediate regime. This closes an important gap left by existing pulse sequences. The efficiency of the gM2S sequence is demonstrated numerically and experimentally for near-equivalent and intermediate-regime cases.
Using optimal control methods with constraints to generate singlet states in NMR
[J].
DOI:S1090-7807(18)30089-2
PMID:29626735
[本文引用: 1]

A method is proposed for optimizing the performance of the APSOC (Adiabatic-Passage Spin Order Conversion) technique, which can be exploited in NMR experiments with singlet spin states. In this technique magnetization-to-singlet conversion (and singlet-to-magnetization conversion) is performed by using adiabatically ramped RF-fields. Optimization utilizes the GRAPE (Gradient Ascent Pulse Engineering) approach, in which for a fixed search area we assume monotonicity to the envelope of the RF-field. Such an approach allows one to achieve much better performance for APSOC; consequently, the efficiency of magnetization-to-singlet conversion is greatly improved as compared to simple model RF-ramps, e.g., linear ramps. We also demonstrate that the optimization method is reasonably robust to possible inaccuracies in determining NMR parameters of the spin system under study and also in setting the RF-field parameters. The present approach can be exploited in other NMR and EPR applications using adiabatic switching of spin Hamiltonians.Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Using optimal controlled singlet spin order to accurately target molecular signal in MRI and MRS
[J].
DOI:10.1038/s41598-023-28425-2
[本文引用: 1]

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) have made great successes in clinical diagnosis, medical research, and neurological science. MRI provides high resolution anatomical images of tissues/organs, and MRS provides information of the functional molecules related to a specific tissue/organ. However, it is difficult for classic MRI/MRS to selectively image/probe a specific metabolite molecule other than the water or fat in tissues/organs. This greatly limits their applications on the study of the molecular mechanism(s) of metabolism and disease. Herein, we report a series of molecularly targeted MRI/MRS methods to target specific molecules. The optimal control method was used to efficiently prepare the singlet spin orders of varied multi-spin systems and in turn greatly expand the choice of the targeted molecules in the molecularly targeted MRI/MRS. Several molecules, such as N-acetyl-l-aspartic acid (NAA), dopamine (DA), and a tripeptide (alanine-glycine-glycine, AGG), have been used as targeted molecules for molecularly targeted MRI and MRS. We show in vivo NAA-targeted 1H MRS spectrum of a human brain. The high-resolution signal of NAA suggests a promising way to study important issues in molecular biology at the molecular level, e.g., measuring the local pH value of tissue in vivo, demonstrating the high potential of such methods in medicine.
J-Stabilization of singlet states in the solution NMR of multiple-spin systems
[J].Long-lived singlet states have been observed in the solution NMR of spin systems containing more than two coupled spins, despite the fact that the singlet state is expected to be quenched by small long-range J-couplings. We show that the stability of localized singlet states may be explained by taking into account the intra-pair J-coupling between the two spins which participate in the singlet state. The relatively strong intra-pair J-coupling protects the singlet state against quenching by weaker out-of-pair J-couplings.
Preparation of long-lived nuclear singlet states in three-spin systems
[J].
三自旋体系长寿命核自旋单重态的制备
[J].
Preparation and lifetime studies of the singlet state of five spins in hexene molecules used to guide the preservation of the parahydrogen-induced nuclear polarization state
[J].
用于指导仲氢诱导核极化状态保存的己烯分子中五自旋的单重态制备和寿命研究
[J].
Preparing nuclear spin singlet state in a three-spin system and its application in 2D spectrum
[J].
三自旋体系核自旋单重态的制备与单重态二维谱的实现
[J].
Singlet NMR methodology in two-spin-1/2 systems
[J].
Preparation of nuclear spin singlet states and analysis of influencing factors on their conversion efficiency and lifetime
[J].
核自旋单重态的制备及其转化效率和寿命的影响因素分析
[J].
Optimal control in NMR spectroscopy: numerical implementation in SIMPSON
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2008.11.020
PMID:19119034
[本文引用: 1]

We present the implementation of optimal control into the open source simulation package SIMPSON for development and optimization of nuclear magnetic resonance experiments for a wide range of applications, including liquid- and solid-state NMR, magnetic resonance imaging, quantum computation, and combinations between NMR and other spectroscopies. Optimal control enables efficient optimization of NMR experiments in terms of amplitudes, phases, offsets etc. for hundreds-to-thousands of pulses to fully exploit the experimentally available high degree of freedom in pulse sequences to combat variations/limitations in experimental or spin system parameters or design experiments with specific properties typically not covered as easily by standard design procedures. This facilitates straightforward optimization of experiments under consideration of rf and static field inhomogeneities, limitations in available or desired rf field strengths (e.g., for reduction of sample heating), spread in resonance offsets or coupling parameters, variations in spin systems etc. to meet the actual experimental conditions as close as possible. The paper provides a brief account on the relevant theory and in particular the computational interface relevant for optimization of state-to-state transfer (on the density operator level) and the effective Hamiltonian on the level of propagators along with several representative examples within liquid- and solid-state NMR spectroscopy.
Localized singlet-filtered MRS in vivo
[J].DOI:10.1002/nbm.v34.1 URL