引言
定量核磁共振(Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance,qNMR)作为组分定量和成分鉴定的最有力的分析工具之一,具有非侵入性、不需要标准物质以及核磁共振活性核普遍存在等优点.近年来,qNMR已广泛应用于食品科学[1⇓⇓⇓-5]、医药科学[6⇓-8]、化学反应监测[9⇓-11]、质量控制[12⇓⇓-15]等多个领域.绝大多数有机化合物由碳、氢、氮等元素组成,在许多应用场景下需要对它们的混合物进行分析.一维1H NMR谱灵敏度高、易于获取,但低分辨率限制了它的应用[16].二维谱可以提高分辨率,但间接维数据的采集耗时较长.一维13C NMR谱作为另一种重要补充手段具有比较高的分辨率,但是对NMR有响应的同位素13C天然丰度只有1.1%,且其旋磁比(
能够提高一维13C NMR灵敏度的方法有许多.除了改进NMR谱仪[17,18]和优化实验条件外,还可以通过两种不同的NMR现象,即核Overhauser效应(Nuclear Overhauser Effect,NOE)[19]和极化转移[20],来有效提高13C NMR的灵敏度.与极化转移相比,稳态NOE效应的增强效果理论上更小,且对弛豫机制和分子运动的细节更敏感,很难预测其增强效率,不能适当地控制以用于量化.所谓“极化”就是自旋在不同能态的布居数之差,NMR信号强度正比于极化,施加适当的脉冲即可将不同能级上的粒子数进行反转或交换,可由此利用J耦合将1H的极化转移到13C上,从而增强13C的信号.INEPT[20]、DEPT[21]、HSQC[22]均利用了极化转移原理. 极化转移效率取决于13C核上附着的质子数、一键碳-氢耦合常数(1JCH)和极化转移时间(Δ),传统INEPT、DEPT、HSQC脉冲序列的Δ和读脉冲翻转角度(θ)是单一固定的值,因而次甲基(CH)、亚甲基(CH2)和甲基(CH3)基团的质子-碳极化转移效率不相等,不能直接应用于定量实验.
在传统HSQC中,相关信号峰的体积(
不同的1JCH都对应一个最佳的极化转移时间,即Δ=1/(21JCH).两个INEPT模块的极化转移时间根据样品分子的1JCH期望值进行调整,一旦设定为某一个值,比如将Δ设定为与1JCH=145 Hz相对应的值,实际1JCH与此有偏差的分子信号强度将与偏差值的大小相关.Heikkinen等[23]最先建立了一种极化转移均匀的能定量的Q-HSQC,在1JCH为115~190 Hz的范围内,通过最小化相关峰体积的最大值和最小值之差,迭代优化选出4个Δ值,作为一个列表在每一步相位循环中循环一遍,使115~220 Hz范围内的响应相对偏差在±2%以内.
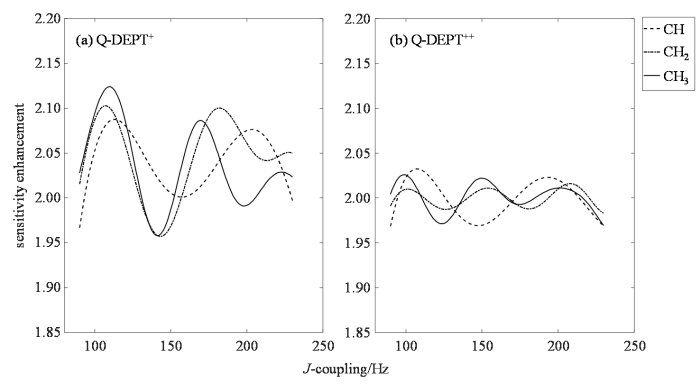
γI表示1H的旋磁比,γs表示13C的旋磁比,ISI、ISI2、ISI3分别表示CH、CH2和CH3中13C的磁化强度.同样通过迭代优化出4个θ,作为一个列表在每一步相位循环和每一个Δ中循环一遍,Q-DEPT的灵敏度能达到传统碳谱的200%~300%.(1)~(4)式的组合综合考虑了旋磁比、13C核上附着的质子数、1JHC、Δ和θ对极化转移效率的影响,但它们仅对CH的描述是准确的,对CH2和CH3的描述却不准确,以此为基础优化得到的结果必将不理想,灵敏度的增强范围为200%~300%,这个宽度便是其不利影响的表现.
Jiang等[26]使用精确的函数关系对Henderson的方法进行了进一步的优化,提出Q-DEPT+.DEPT脉冲序列中CH3、CH2和CH基团的质子-碳极化转移效率完整精确的灵敏度增强函数如下:
其中
随后,Mäkelä等[28]又提出了Q-INEPT-CT,其信号强度与INEPT时长和重聚时长相关,用C语言测试二者在指定范围内的所有组合,经多种方案初步计算后,选择出8对调制时间,该情况下三种碳原子的响应最均匀,再使用GRG(Generalized Reduced Gradient)准牛顿非线性回归算法,对这些粗略优化的调制进一步优化.并将碳通道的两个π脉冲用Shaka等[29]研制的六元复合脉冲替代,以克服偏共振效应,在大的频域宽带上表现出更好的反转和重聚特性.Manu等[30]随后使用遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm,GA)优化了Q-INEPT-CT,在不损失准确性的情况下,将实验时长缩短了一半.
Q-DEPT+通过设计合适的Δ和θ的循环,消除不同的1JCH和13C核连接1H核数目对灵敏度增强影响,以获得均匀的信噪比用于定量研究,这是一个涉及多个变量的优化问题,且信号强度与这些变量的数值关系是非线性的.遗传算法能够比较好地适用于这个问题,因此在本文中,我们提出Q-DEPT++,在Q-DEPT+的基础上,使用遗传算法进一步优化Δ和θ,获得更均匀的灵敏度增强,以提高定量13C NMR实验的精度.
1 理论原理
传统的DEPT脉冲序列中CH、CH2和CH3基团的质子-碳极化转移效率函数为(5)~(7)式.对于传统的DEPT脉冲序列,Δ和θ都是固定数值,CH、CH2和CH3基团的质子-碳极化转移效率是不相等的,因此无法直接用于定量.根据(8)~(10)式,Q-DEPT+通过将一系列不同Δ和θ值的DEPT谱累加在一起,将13C核上附着的质子数、1JHC、Δ和θ的影响平均掉,使信号强度仅与碳原子的数量相关,而与碳原子的化学环境、实验参数的相关性尽可能减弱甚至消除,以便直接用于定量.在Q-DEPT+的基础上,我们做了进一步的优化.
在MATLAB软件中,调用GA全局搜索优化Δ和θ.设定1JCH值为90~230 Hz范围内(有机化合物中1JCH基本上处于该范围内),Δ值为1~8 ms范围内(Δ值搜索范围主要依据1JCH确定,在传统DEPT中,不涉及定量准确性的问题,我们简单认为极化转移效率正比于sin(πΔ1JCH),Δ=1/(21JCH)时极化转移效率最高,比如1JCH=145 Hz,则Δ=3.45 ms,根据1JCH的范围为90~230 Hz计算,Δ约为2~6 ms.在此前的 Q-DEPT+参数优化中,一系列Δ值位于1~8 ms范围内,因此为了缩小搜索空间,我们将Δ值搜索范围限定在该范围内),θ值为0.01°~90°范围内(在此范围内,正弦和余弦均为正,灵敏度增强更易获得较大的值,且脉冲的翻转角度越小准确性越高,因而没有必要超过90°).分别设定个体的基因为16个Δ和16个θ、8个Δ和6个θ、12个Δ和12个θ(三种方案的GA代码见附件材料),根据(8)~(10)式计算种群中个体的目标灵敏度增强值的标准偏差,此值即个体的适应度,越接近0,适应度越好.GA自动生成初始种,并根据个体的适应度进行优胜劣汰,模拟自然界的进化过程,选择适应度好的个体进行复制、对基因进行配对交叉和变异等遗传操作,演化一定代数后,得到一组适应度较好的种群,并给出它们的基因和适应度.经三种方案初步计算后,再对比它们的定量效果,得到的最佳优化方案为12个Δ和12个θ.表1中列出了Q-DEPT+参数列表和优化后得到的Q-DEPT++参数列表.
表1 Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT++的极化转移时间(Δ)和读脉冲翻转角度(θ)列表*
Table 1
| Δ/ms | θ/° | |
|---|---|---|
| Q-DEPT+ | 1.384, 1.536, 2.173, 3.319, 3.319, 4.234, 5.331, 7.041 | 35.3, 48, 50.6, 78.5, 87.5, 87.9 |
| Q-DEPT++ | 3.892, 1.693, 2.834, 2.759, 4.409, 2.496, 5.413, 1.719, 2.071, 7.998, 5.164, 6.197 | 38.2, 39.82, 78.1, 67.4, 90.0, 87.7, 16.7, 46.8, 35.8, 56.4, 70.3, 78.3 |
* Q-DEPT+的Δ与θ为两套独立的循环,因此实验中为Δ/θ双重循环;而Q-DEPT++的Δ与θ为一对一配对的单重循环.
图1
图1
Q-DEPT+ (a)与Q-DEPT++ (b)灵敏度增强的拟合曲线
Fig. 1
Fitting curve of sensitivity enhancement of Q-DEPT+ (a) and Q-DEPT++ (b)
因为13C NMR的化学位移范围在0 ppm到200 ppm以上,是1H的20多倍,这导致13C通道中的偏共振效应影响严重.我们进一步优化了Q-DEPT+脉冲序列(称为Q-DEPT++),使用G5组合脉冲代替180°硬脉冲,以补偿脉冲的错误校准、偏共振效应和π脉冲执行过程中J耦合演化共同导致的13C通道中的严重信号损失,这将使化学位移远离谱中心的碳原子的翻转角度更加准确,从而提高定量准确性.
图2中细黑条和粗黑条分别是90°和180°脉冲.灰色条为读脉冲,其翻转角度为θ.Δ和θ为非定值,相位循环的每一步内,均按表1中的两组参数列表循环整数倍.图2(a)为Q-DEPT+脉冲序列,脉冲和接收机的相位循环如下:Φ1=0(x),0(x); Φ2=0(x), 0(x); Φ3=1(y), 3(−y); Φ4=0(x), 0(x); Φ5=0(x) ,0(x);Φrec=0(x), 2(−x).图2(b)为优化的Q-DEPT++脉冲序列,其中的一组灰色条是三重补偿的π脉冲(G5),脉冲和接收机的相位循环如下:Φ1=0(x), 0(x);Φ2=0(x), 0(x); Φ3=1(y), 3(−y);Φ4=0(x), 0(x); Φ5=0(x), 0(x). Φrec =O(x), 2(−x).
图2
图2
(a) Q-DEPT+脉冲序列和(b)优化的Q-DEPT++脉冲序列
Fig. 2
(a) Q-DEPT+ pulse program and (b) optimized Q-DEPT++ pulse program
值得注意的是,被直接检测的“转移”项对应的是13C自旋磁化强度,却与1H自旋的玻尔兹曼因子成正比[39],这意味着信号强度与1H的热平衡极化有关,而与13C无关,因此脉冲前等待时间由1H的纵向弛豫时间T1决定.通常情况下,对于有机小分子的1H NMR实验,脉冲前等待时间可以设定为4 s,而大分子可以设定为1~2 s,对于利用了极化转移增强信号的DEPT脉冲程序的13C NMR谱也按这个标准来设置采样参数;对于利用反门控去耦脉冲序列(zgig)[40]的13C NMR谱,则需要设定到20 s.在需要准确定量时,这个值还需要根据样品的弛豫时间进行适当调整,将脉冲前等待时间设置为最大纵向弛豫时间的5倍.在样品浓度不高或样品数量很多时,相较基于zgig的13C NMR定量实验,Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT++因为单次扫描的灵敏度更高,扫描次数可以更少,且每次扫描的脉冲前等待时间更短,可以节省大量实验时间.
2 NMR实验
NMR实验在Bruker AVANCE III 600 MHz高分辨液体NMR谱仪上进行,使用的是5 mm三共振液氦超低温探头.样品为胆固醇乙酸酯(C29H48O2)的氘代氯仿溶液.分别用zgig、Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT++采集了定量碳谱.通过反转恢复法测得所有碳原子的T1,最大值为7.6 s,为了使zgig的恢复时间足够,所有实验的脉冲前等待时间d1设置为40 s.实验中,不能直接设置读脉冲的翻转角度(θ),需要根据氢通道90°硬脉冲的脉宽将角度转化成脉冲宽度,作为VPLIST的文件参与脉冲程序的运行.G5组合脉冲文件作为形状脉冲参与脉冲程序的运行,其功率等于碳通道硬脉冲的功率,脉宽为90°硬脉冲脉宽的10倍,无需普通形状脉冲那样的脉宽与功率拟合优化.为了完成两个列表的整数倍循环与脉冲程序的相位循环,使用原始参数的Q-DEPT+实验的累加次数需要为96的整数倍,使用优化参数的Q-DEPT++实验的累加次数需要为24的整数倍,本文中3个实验的累加次数均设置为96.
3 结果与讨论
3.1 定量准确性分析
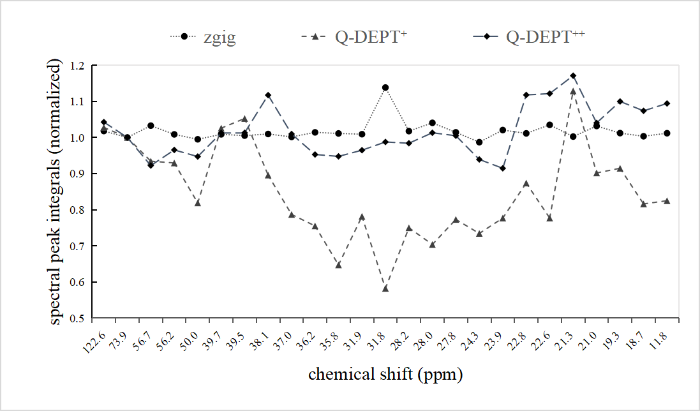
对胆固醇乙酸酯的氘代氯仿溶液定量13C NMR谱中25个非季碳碳原子的信号进行积分,并分别相对于δC 73.85处的信号(依据数据库Spectral Database for Organic Compounds SDBS[41]中的归属信息,此处信号为4号碳原子——CH)进行归一化处理,然后作折线图(图3),可直观地对3个实验的定量准确性进行对比.理论上,忽略同位素的影响,同一分子中各种13C的个数在溶液中相等,那么在同一定量13C NMR谱图中,其谱峰面积应基本相等,因而折线的波动情况能反映3种实验方法的定量准确性.其中,zgig获得的曲线最为平稳,因为它直接激发13C,不受极化转移不均匀的影响.对比另外两组,能很明显地看出,Q-DEPT++比Q-DEPT+的波动要小得多.
图3
图3
3种定量13C NMR谱图的定量准确性对比
Fig. 3
Comparison of quantification accuracy among the three quantitative 13C NMR experiments
表2列出了3个实验中所有非季碳原子归一化积分面积的标准偏差,如上所述,理论上同一化合物中各种13C的个数在溶液中相等,那么同一定量13C NMR谱中其谱峰面积的标准偏差等于0.但实际上即便是使用zgig脉冲序列也达不到这个效果,其获得的定量13C NMR谱中各种13C信号的归一化积分面积的标准偏差为0.028 1.对于灵敏度增强的定量13C NMR谱,我们的目标便是尽可能的减小这个值.Q-DEPT+获得的定量13C NMR谱中各种13C信号的归一化积分面积的标准偏差为0.132 5,而Q-DEPT++为0.070 5,降低了46.79%.
表2 谱峰积分面积标准偏差(归一化)
Table 2
| 实验名称 | zgig | Q-DEPT+ | Q-DEPT++ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 谱峰积分标准偏差 | 0.0281 | 0.1325 | 0.0705 |
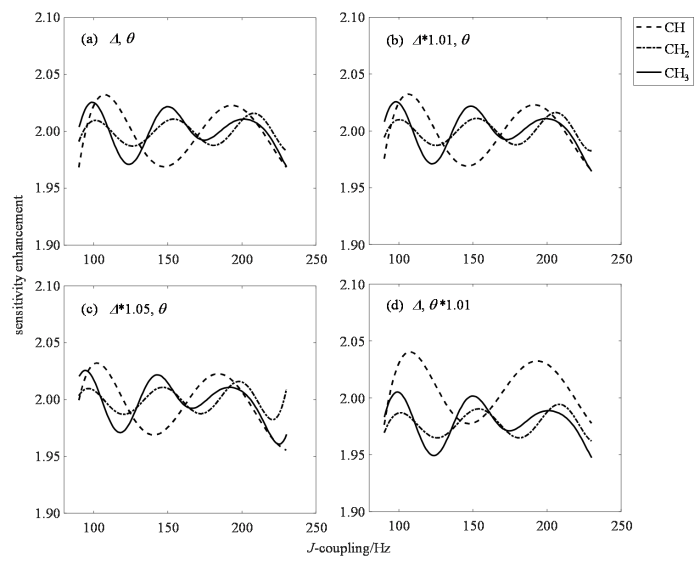
图4(a)为Q-DEPT++的灵敏度增强拟合曲线.4(b)中将Δ值乘以1.01,即Δ有1%的偏差,灵敏度增强拟合曲线几乎没有变化,4(c)中将Δ值乘以1.05,即Δ有5%的偏差,灵敏度增强拟合曲线变化仍然不算大,说明Q-DEPT++对Δ的偏差敏感性很低.4(d)中将θ值乘以1.01,即θ有1%的偏差,灵敏度增强拟合曲线发生明显变化:CH的曲线上移,CH3和CH2的曲线下移,说明Q-DEPT++对θ的偏差敏感度较高.在图4(d)中,同等浓度下,次甲基的信号响应将比甲基和次甲基的强,定量实验的结果会有很大偏差.因此,为了定量的准确性,实验时要特别注意氢通道脉冲的准确性,实验前须对90°高功率脉冲进行脉宽测定和校准.
图4
图4
Q-DEPT++对Δ和θ偏差的敏感性
Fig. 4
Sensitivity of Q-DEPT++ to the deviation of Δ and θ
3.2 信噪比分析
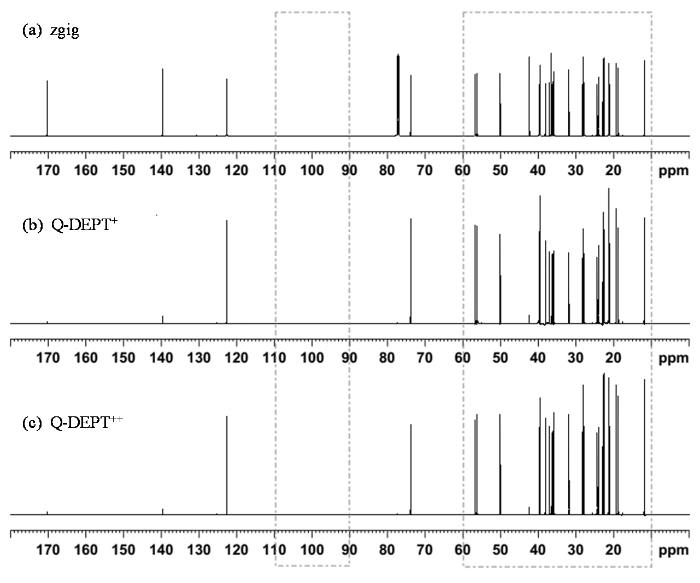
图5展示了分别用zgig、Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT++三种方法采集的胆固醇乙酸酯氘代氯仿溶液的定量 13C NMR谱,这3张谱图采用相同的纵向显示刻度.在Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT++采集的谱图中,胆固醇乙酸酯的季碳(δC 170.4/139.7/42.4/33.7)和氘代氯仿的季碳(δC 77.2)信号峰几乎消失,因为两者13C核上没有直接连接1H核,极化转移作用几乎可以忽略.在同样的纵向显示刻度下,Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT++谱图中的谱峰强度明显高于zgig的定量13C NMR谱,这说明这2种实验的灵敏度较常规定量13C NMR谱有明显增强.
图5
图5
利用(a) zgig、(b) Q-DEPT+、(c) Q-DEPT++获得的胆固醇乙酸酯氘代氯仿溶液的定量13C NMR谱
Fig. 5
Quantitative 13C NMR spectra of cholesterol acetate in CD3Cl obtained by (a) zgig, (b) Q-DEPT+, (c) Q-DEPT++
为了定量地比较3种实验的灵敏度,我们分别取δC 10~60区域内的信号与δC 90~110区域内(图5)的噪声进行信噪比分析.zgig所得的定量13C NMR谱图的信噪比最低,只有778.81.Q-DEPT+与Q-DEPT++的信噪比分别为1 282.79和1 366.78,也就是说,Q-DEPT+与Q-DEPT++的灵敏度分别为zgig的1.65倍和1.75倍.虽然图1显示Q-DEPT++虽然具有更好的灵敏度增强均匀性,但平均灵敏度增强稍低,实验结果却表明Q-DEPT++的信噪比稍高于Q-DEPT+.Q-DEPT++谱图之所以获得更高的信噪比,一方面是由于组合脉冲G5显著消除了13C脉冲频偏效应的影响;另一方面则可能源于这些13C核与相邻1H核的J偶合常数各异,因此,不能简单地认为图1中Q-DEPT++有较低的平均灵敏度增强,就必然导致实际实验中的信噪比更低.
4 结论
本文提出的新脉冲序列Q-DEPT++是在Q-DEPT+的基础上进行了两方面的优化:一是对极化转移时间(Δ)和读脉冲翻转角度(θ)的优化,以获得更均匀的灵敏度增强曲线;二是将13C通道的180°硬脉冲替换成G5组合脉冲,以尽量消除频偏效应对定量结果的影响,同时,因为对非谱中心位置的碳原子有更准确的激发而提高了灵敏度.与此同时,新脉冲序列对Δ和θ的循环模式进行了改变,从Δ与θ二者的独立双重循环,变为Δ与θ一一配对的单重循环,将循环基数从96变为24,有助于减少扫描次数和实验时间.以胆固醇乙酸酯为样品,利用zgig、Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT+获得的定量13C NMR谱图显示:相对于zgig序列,Q-DEPT+和Q-DEPT++均能使灵敏度显著增强,且Q-DEPT++相对于Q-DEPT+有更高的定量准确性和信噪比.
利益冲突
无
附件材料(可在《波谱学杂志》期刊官网 http://magres.wipm.ac.cn 获取)
1. 8个Δ和6个θ双重循环:1.1. 灵敏度增强公式v5;1.2. 基于灵敏度增强公式v5的偏差公式;1.3. test:代入Q-DEPT+的Δ和θ参数,计算error_qdept(x)与error_qdept_v3(x);1.4. 基于灵敏度增强公式v5及其相关偏差公式的遗传算法
2. 12个Δ和12个θ一一对应单重循环:2.1. 灵敏度增强公式v10;2.2. 基于灵敏度增强公式v10的偏差公式;2.3. 基于error_qdept(x)计算参数的灵敏度增强;2.4. test_ga:基于error_qdept(x)的遗传算法(ga),增强到2倍
3. 16个Δ和16个θ一一对应单重循环:3.1. 灵敏度增强公式v11;3.2. 基于灵敏度增强公式v11的偏差公式;3.3. 基于error_qdept_v2(x)的遗传算法
4. 结果比较:4.1. test:比较Q-DEPT+与Q-DEPT++的定量效果
参考文献
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based quantification on flavor-active and bioactive compounds and application for distinguishment of chicken breeds
[J].
DOI:10.5851/kosfa.2020.e102
PMID:33987551
[本文引用: 1]

The purpose of this study was to use H nuclear magnetic resonance (H NMR) to quantify taste-active and bioactive compounds in chicken breasts and thighs from Korean native chicken (KNC) [newly developed KNCs (KNC-A, -C, and -D) and commercial KNC-H] and white-semi broiler (WSB) used in. Further, each breed was differentiated using multivariate analyses, including a machine learning algorithm designed to use metabolic information from each type of chicken obtained using H-C heteronuclear single quantum coherence (2D NMR). Breast meat from KNC-D chickens were superior to those of conventional KNC-H and WSB chickens in terms of both taste-active and bioactive compounds. In the multivariate analysis, meat portions (breast and thigh) and chicken breeds (KNCs and WSB) could be clearly distinguished based on the outcomes of the principal component analysis and partial least square-discriminant analysis (R=0.945; Q=0.901). Based on this, we determined the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for each of these components. AUC analysis identified 10 features which could be consistently applied to distinguish between all KNCs and WSB chickens in both breast (0.988) and thigh (1.000) meat without error. Here, both H NMR and 2D NMR could successfully quantify various target metabolites which could be used to distinguish between different chicken breeds based on their metabolic profile.© Korean Society for Food Science of Animal Resources.
Simultaneous determination of fatty acids at sn-1,3 and sn-2 of triglyceride in edible oils by quantitative C-13-nuclear magnetic resonance
[J].
定量核磁共振碳谱同时测定食用油中甘油三酯的sn-1,3和sn-2脂肪酸含量
[J].
Quantitative determination of fatty acid compositions in edible oils using J-selective 13C QDEPT
[J].DOI:10.1007/s12161-019-01432-8 [本文引用: 1]
In situ determination of fructose isomer concentrations in wine using 13C quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
[J].DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03641 URL [本文引用: 1]
Application of magnetic resonance technique to quality and safety evaluation of food
[J].
磁共振技术在食品质量与安全研究中的应用
[J].
An isotope dilution LC-MS/MS-based candidate reference method for the quantification of androstenedione in human serum and plasma
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.clinms.2020.01.003
PMID:34820514
[本文引用: 1]

The accurate measurement of androstenedione in human serum and plasma is required for steroid profiling to assure the appropriate diagnosis and differential diagnosis of hyperandrogenism. In this work, we introduce an isotope dilution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) candidate reference measurement procedure for the quantification of androstenedione in human serum and plasma. The performance of the procedure enables its use in the evaluation and standardization of routine assays and for the evaluation of patient samples to ensure the traceability of individual patient results. As the primary standard, a certified reference material from NMIA (National Measurement Institute, Australia) was used. Additionally, a quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (qNMR) method was developed for the value assignment of the primary reference material, which ensures the direct traceability to SI units, as well as the independence from the availability of reference materials. C-labeled androstenedione was used as the internal standard. The introduced method allows the measurement of androstenedione in the range of 0.05-12 ng/mL, and the assay imprecision was found to be <2% between 5 and 12 ng/mL, 3.5% at 1.5 ng/mL, and 5.2% at 0.05 ng/mL, with an accuracy of 95-105% for the serum and 91-103% for the plasma matrix. The transferability to a second laboratory was validated by method comparison based on 112 patient samples. The comparison of the results obtained from the presented method and an LC-MS/MS routine assay, using 150 native patient samples, showed a good correlation with a bias of the routine method of ≤4.0%.© 2020 The Author(s).
Quantitative NMR as a tool for analysis of new psychoactive substances
[J].
Residual complexity does impact organic chemistry and drug discovery: The case of rufomyazine and rufomycin
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.8b00988
PMID:29792329
[本文引用: 1]

Residual complexity (RC) involves the impact of subtle but critical structural and biological features on drug lead validation, including unexplained effects related to unidentified impurities. RC commonly plagues drug discovery efforts due to the inherent imperfections of chromatographic separation methods. The new diketopiperazine, rufomyazine (6), and the previously known antibiotic, rufomycin (7), represent a prototypical case of RC that (almost) resulted in the misassignment of biological activity. The case exemplifies that impurities well below the natural abundance of C (1.1%) can be highly relevant and calls for advanced analytical characterization of drug leads with extended molar dynamic ranges of >1:1,000 using qNMR and LC-MS. Isolated from an actinomycete strain, 6 was originally found to be active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 2 μg/mL and high selectivity. As a part of lead validation, the dipeptide was synthesized and surprisingly found to be inactive. The initially observed activity was eventually attributed to a very minor contamination (0.24% [m/m]) with a highly active cyclic peptide (MIC ∼ 0.02 μM), subsequently identified as an analogue of 7. This study illustrates the serious implications RC can exert on organic chemistry and drug discovery, and what efforts are vital to improve lead validation and efficiency, especially in NP-related drug discovery programs.
Theory of the milieu dependent isomerisation dynamics of reducing sugars applied to D-erythrose
[J].
DOI:S0008-6215(15)00333-X
PMID:26580710
[本文引用: 1]

Quantitative (1)H selective saturation transfer NMR spectroscopy ((1)H SST qNMR) was used to fully describe the milieu dependent dynamics of the isomeric system of d-erythrose. Thermodynamic activation parameters are calculated for acidic as well as for basic catalysis combining McConnell's modified Bloch equations for the chemical exchange solved for the constraint of saturating the non-hydrated acyclic isomer, the Eyring equation and Hudson's equation for pH dependent catalysis. A detailed mathematical examination describing the milieu dependent dynamics of sugar isomerisation is provided. Thermodynamic data show evidence that photo-catalysed sugar isomerisation as well as degradation has to be considered. Approximations describing the pH and temperature dependence of thermodynamic activation parameters are derived that indicate the possibility of photo-affecting equilibrium constants. Moreover, the results show that isomerisation dynamics are closely related to degradation kinetics and that sugars' reactivities are altered by the concentration of acyclic carbonyl isomer and the sum of its ring closing rate constants. Additionally, it is concluded that sugar solutions show a limited self-stabilising behaviour. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Molecular H2O promoted catalytic bicarbonate reduction with methanol into formate over Pd0.5Cu0.5/C under mild hydrothermal conditions
[J].DOI:10.1039/D0GC02785E URL [本文引用: 1]
Mechanical control of rate processes: Effect of ligand steric bulk on CO exchange in trisubstituted tetrairidium cluster catalysts
[J].DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c07962 URL [本文引用: 1]
A validated 1H NMR method for quantitative analysis of α-bisabolol in essential oils of Eremanthus erythropappus
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.032 URL [本文引用: 1]
Use of quantitative 1H and 13C NMR to determine the purity of organic compound reference materials: a case study of standards for nitrofuran metabolites
[J].DOI:10.1007/s00216-020-03134-1 [本文引用: 1]
A 1H NMR spectroscopic method for the quantification of propenylbenzenes in the essential oils: Evaluation of key odorants, antioxidants and post-harvest drying techniques for Piper betle L
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127278 URL [本文引用: 1]
Use of 13C-qNMR spectroscopy for the analysis of non-psychoactive cannabinoids in fibre-type Cannabis sativa L. (Hemp)
[J].
DOI:10.3390/molecules24061138
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Cannabis sativa L. is a dioecious plant belonging to the Cannabaceae family. The discovery of the presence of many biologically-active metabolites (cannabinoids) in fibre-type Cannabis (hemp) has recently given rise to the valorisation of this variety. In this context, the present study was aimed at the multi-component analysis and determination of the main non-psychoactive cannabinoids (cannabidiol, cannabidiolic acid, cannabigerol and cannabigerolic acid) in female inflorescences of different hemp varieties by means of 13C quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (qNMR). The method proposed here for the first time for the determination of cannabinoids provided reliable results in a competitive time with respect to the more consolidated HPLC technique. In fact, it gave sufficiently precise and sensitive results, with LOQ values lower than 750 μg/mL, which is easily achievable with concentrated extracts, without affecting the quality of 13C-qNMR spectra. In conclusion, this method can be considered as a promising and appropriate tool for the comprehensive chemical analysis of bioactive cannabinoids in hemp and other derived products in order to ensure their quality, efficacy and safety.
One-dimensional 13C NMR is a simple and highly quantitative method for enantiodiscrimination
[J].
DOI:10.3390/molecules23071785
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The discrimination of enantiomers of mandelonitrile by means of 1D 13C NMR and with the aid of the chiral solvating agent (S)-(+)-1-(9-anthryl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (TFAE) is presented. 1H NMR fails for this specific compound because proton signals either overlap with the signals of the chiral solvating agent or do not show separation between the (S)-enantiomer and the (R)-enantiomer. The 13C NMR method is validated by preparing artificial mixtures of the (R)-enantiomer and the racemate, and it is shown that with only 4 mg of mandelonitrile a detection limit of the minor enantiomer of 0.5% is obtained, corresponding to an enantiomeric excess value of 99%. Furthermore, the method shows high linearity, and has a small relative standard deviation of only 0.3% for the minor enantiomer when the relative abundance of this enantiomer is 20%. Therefore, the 13C NMR method is highly suitable for quantitative enantiodiscrimination. It is discussed that 13C NMR is preferred over 1H NMR in many situations, not only in molecules with more than one chiral center, resulting in complex mixtures of many stereoisomers, but also in the case of molecules with overlapping multiplets in the 1H NMR spectrum, and in the case of molecules with many quaternary carbon atoms, and therefore less abundant protons.
The status and challenge of the domestic manufacturing of superconduct magnetic resonance instruments in China
[J].
超导磁共振仪器设备国产化现状及挑战
[J].
Research progresses concerning the superconducting joints used in nuclear magnetic resonance magnets
[J].
核磁共振磁体超导接头工艺研究进展
[J].
Polarization of nuclei in metals
[J].DOI:10.1103/PhysRev.92.411 URL [本文引用: 1]
Enhancement of nuclear magnetic-resonance signals by polarization transfer
[J].DOI:10.1021/ja00497a058 URL [本文引用: 2]
Distortionless enhancement of NMR signals by polarization transfer
[J].
Natural abundance nitrogen-15 NMR by enhanced heteronuclear spectroscopy
[J].DOI:10.1016/0009-2614(80)80041-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative 2D HSQC (Q-HSQC) via suppression of J-dependence of polarization transfer in NMR spectroscopy: Application to wood lignin
[J].A quantitative method to record (1)H-(13)C correlation NMR spectra (Q-HSQC) is presented. The suppression of (1)J(CH)-dependence is achieved by modulating the polarization transfer delays of HSQC. In addition, the effect of homonuclear couplings, as well as relaxation during the pulse sequence are discussed. We developed the Q-HSQC approach for the quantitative analysis of wood lignin, a complex polymer where it has been difficult to obtain reliable data on the relative amounts of different structural units. The current method is applicable to a variety of complex mixtures, where normal 1D (1)H- and (13)C-NMR methods fail.
Sensitivity-enhanced quantitative 13C NMR spectroscopy via cancellation of 1JCH dependence in DEPT polarization transfers
[J].DOI:10.1021/ja039261+ URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimized quantitative DEPT and quantitative POMMIE experiments for 13C NMR
[J].DOI:10.1021/ac8015455 URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative 13C NMR spectroscopy using refocused constant-time INEPT, Q-INEPT-CT
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2010.02.015 URL [本文引用: 1]
Composite pulses for ultra-broadband spin inversion
[J].DOI:10.1016/0009-2614(85)87040-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Fast and accurate quantification using Genetic Algorithm optimized 1H-13C refocused constant-time INEPT
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2013.06.013 URL [本文引用: 1]
Outline for a logical theory of adaptive systems
[J].DOI:10.1145/321127.321128 URL [本文引用: 1]
Genetic algorithms and solid state NMR pulse sequences
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2012.12.015
PMID:23357428
[本文引用: 1]

The use of genetic algorithms for the optimisation of magic angle spinning NMR pulse sequences is discussed. The discussion uses as an example the optimisation of the C7(2)(1) dipolar recoupling pulse sequence, aiming to achieve improved efficiency for spin systems characterised by large chemical shielding anisotropies and/or small dipolar coupling interactions. The optimised pulse sequence is found to be robust over a wide range of parameters, requires only minimal a priori knowledge of the spin system for experimental implementations with buildup rates being solely determined by the magnitude of the dipolar coupling interaction, but is found to be less broadbanded than the original C7(2)(1) pulse sequence. The optimised pulse sequence breaks the synchronicity between r.f. pulses and sample spinning.Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Improving excitation and inversion accuracy by optimized RF pulse using genetic algorithm
[J].In this study, a Genetic Algorithm (GA) is introduced to optimize the multidimensional spatial selective RF pulse to reduce the passband and stopband errors of excitation profile while limiting the transition width. This method is also used to diminish the nonlinearity effect of the Bloch equation for large tip angle excitation pulse design. The RF pulse is first designed by the k-space method and then coded into float strings to form an initial population. GA operators are then applied to this population to perform evolution, which is an optimization process. In this process, an evaluation function defined as the sum of the reciprocal of passband and stopband errors is used to assess the fitness value of each individual, so as to find the best individual in current generation. It is possible to optimize the RF pulse after a number of iterations. Simulation results of the Bloch equation show that in a 90 degrees excitation pulse design, compared with the k-space method, a GA-optimized RF pulse can reduce the passband and stopband error by 12% and 3%, respectively, while maintaining the transition width within 2 cm (about 12% of the whole 32 cm FOV). In a 180 degrees inversion pulse design, the passband error can be reduced by 43%, while the transition is also kept at 2 cm in a whole 32 cm FOV.
Design of magnetic resonance experiments by genetic
[J].
Genetic algorithm optimized triply compensated pulses in NMR spectroscopy
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2015.09.010
PMID:26473327
[本文引用: 1]

Sensitivity and resolution in NMR experiments are affected by magnetic field inhomogeneities (of both external and RF), errors in pulse calibration, and offset effects due to finite length of RF pulses. To remedy these problems, built-in compensation mechanisms for these experimental imperfections are often necessary. Here, we propose a new family of phase-modulated constant-amplitude broadband pulses with high compensation for RF inhomogeneity and heteronuclear coupling evolution. These pulses were optimized using a genetic algorithm (GA), which consists in a global optimization method inspired by Nature's evolutionary processes. The newly designed π and π/2 pulses belong to the 'type A' (or general rotors) symmetric composite pulses. These GA-optimized pulses are relatively short compared to other general rotors and can be used for excitation and inversion, as well as refocusing pulses in spin-echo experiments. The performance of the GA-optimized pulses was assessed in Magic Angle Spinning (MAS) solid-state NMR experiments using a crystalline U-(13)C, (15)N NAVL peptide as well as U-(13)C, (15)N microcrystalline ubiquitin. GA optimization of NMR pulse sequences opens a window for improving current experiments and designing new robust pulse sequences. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Enhancing the sensitivity of multidimensional NMR experiments by using triply-compensated π pulses
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s10858-017-0153-2
PMID:29164453
[本文引用: 1]

In multidimensional solution NMR experiments, π pulses are used extensively for inversion and refocusing operations on H, C and N nuclei. Pulse miscalibration, off-resonance effects, and J-coupling evolution during π pulse execution result in severe signal losses that are exacerbated at high magnetic fields. Here, we report the implementation of a triply-compensated π pulse (G5) optimized for both inversion and refocusing in widely used 2- and 3-dimensional experiments. By replacing most of the hard π pulses, adiabatic or composite pulses on the H, C and N channels with G5 pulses, we obtained signal enhancements ranging from 80 to 240%. We anticipate that triply-compensated pulses will be crucial for improving the performance of multidimensional and multinuclear pulse sequences at ultra-high fields.
Spectra of carbon-13 with the nuclear overhauser effect suppressed
[J].