引言
桥小脑角区位于后颅窝前侧,此区集中了听神经、面神经、三叉神经、岩静脉、小脑前上动脉等.在该区出现的占位性病变会逐渐损伤上述组织而产生桥小脑角区综合征.桥小脑角区是颅内肿瘤好发的部位之一,约占颅内肿瘤的10%[1],最为常见的是听神经瘤和脑膜瘤.其中听神经瘤约占桥小脑角区肿瘤的85%[2],脑膜瘤约占10%~15%.磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)可以准确的显示解剖结构,反应组织病理学特征,并且具有高软组织对比度和无颅骨伪影影响等特点,在后颅窝和桥小脑角区的肿瘤诊断中独具优势.听神经瘤的磁共振图像表现为:T1WI呈等信号或低信号,T2WI呈高信号,增强后病灶明显强化.脑膜瘤的磁共振图像表现为:T1WI呈等信号或略低信号,T2WI呈高信号,增强后呈均匀强化.两种肿瘤的磁共振图像表现不具有特征性,临床表现相似.通过医学影像对两种肿瘤的诊断有一定的难度,需要高度依赖临床医生的知识和经验.
近年来,深度学习技术已大量用于医学图像的分析处理[3⇓⇓⇓-7].基于深度学习的肿瘤病灶检测可以辅助临床医生对肿瘤进行诊断,通常的流程是先通过预处理方式识别标注出特定区域,再对特定区域进行病灶分类[8].基于磁共振影像的脑肿瘤自动分割利用深度学习技术将肿瘤区和正常组织进行分割标注,对辅助脑肿瘤的诊疗具有重要作用[9].而脑部因结构复杂,包含众多重要器官、功能区、神经系统等,对脑肿瘤的准确分割尤为重要.Havaei等[10]提出了基于深度神经网络(deep neural network,DNN)的全自动脑肿瘤分割方法对低级别和高级别胶质瘤磁共振图像进行分割,该方法利用了图像的局部和全局特征,并在最后采用卷积全连接层,大幅提升了分割效率.Wu等[11]提出了基于多尺度、多路注意力机制的多模态高等级脑胶质瘤语义分割网络,在全肿瘤区、肿瘤核心区、增强肿瘤区的dice系数分别为0.909 7、0.877 3、0.839 6.
目前,基于深度学习对桥小脑角区肿瘤的研究还不多.Lou[12]等采用3D卷积神经网线路(convolutional neural network,CNN)网络,对桥小脑角区脑膜瘤与听神经瘤进行分类研究,分类的准确率达到0.918,曲线下面积0.913 4.Liu等[13]采用结合改进特征金字塔网络(feature pyramid networks,FPN)的掩膜区域卷积神经网络(mask region convolutional neural network,Mask RCNN),对桥小脑角区脑膜瘤和听神经瘤进行分类定位研究,均值平均精度(mean average precision,mAP)达到0.90.上述研究完成了对桥小脑角区脑膜瘤和听神经瘤的分类或定位的研究,为实现对桥小脑角区肿瘤检测和病灶分割,不仅需要在数据集处理中由放射科医师更精确标注病灶范围,而且模型还需进一步的提升性能以获得更精确的病灶分割结果.
Mask RCNN在图像处理的任务中,可以实现目标框回归、检测和掩膜分割[14⇓-16].例如Zhang等[17]利用Mask RCNN对复合材料超声图像中的褶皱缺陷进行检测,且算法中的语义分割可显示褶皱缺陷的位置和形状,结果显示对不同缺陷的识别准确率达到0.921、0.909和0.933.因此基于Mask RCNN网络,可以完成对桥小脑角区听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的检测和病灶分割的任务.对肿瘤的检测可以辅助临床医生进行诊断,对病灶的分割可在后续的肿瘤放射治疗中辅助临床医生进行病灶的勾画等工作.另外,在模型中引入注意力机制,可以通过注意力机制对图像特征权重的调整增强模型的特征学习[18⇓-20],进一步提升模型的鲁棒性和性能.
本文基于听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的轴位T1WI增强序列图像,构建融合卷积注意力机制的Mask RCNN深度学习模型,实现对两种肿瘤的检测和病灶分割.对经筛选后的2 467张听神经瘤图像和872张脑膜瘤图像进行增强等预处理后,由放射科高年资医师利用labelme软件进行病灶勾画及肿瘤分类标注,生成数据集.然后采用Mask RCNN进行模型训练,将主干网络分别设置为VGG19、Resnet50和Resnet101,并在测试集上进行对比.然后对表现良好的两个模型进行结构调整,加入卷积注意力机制,并在测试集上进行对比,以评价注意力机制对模型性能的影响.综合选择性能最优的模型,可为桥小脑角区肿瘤的临床诊疗提供有效帮助.
1 实验部分
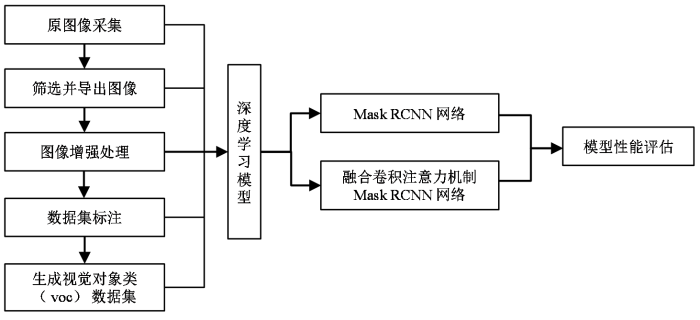
本文的实验流程如图1所示.
图1
1.1 数据资料和设备
本文回顾性收集了2015年1月至2017年12月,在上海伽玛医院经病理或临床诊断确诊为桥小脑角区的听神经瘤427例和脑膜瘤116例.本研究过程中遵守国家生物医学研究伦理标准.
所有病例均使用美国GE公司的 Signa HDxt 1.5 T磁共振扫描仪,采用单通道头部线圈扫描,T1WI增强序列的扫描参数如下:扫描层厚为2 mm,层间距为0 mm,重复时间(repetition time,TR)为580 ms,回波时间(echo time,TE)为8 ms,矩阵为256×256,扫描视野(field of view,FOV)为280 mm×280 mm,激励次数为2,回波链长度(echo train length,ETL)为3,带宽(band width,BW)为25 kHz.对比剂使用钆喷酸葡胺注射液(北京北陆药业股份有限公司生产),注射剂量为0.2 mL/kg,通过肘前静脉以1.5 mL/s的速率注入.
1.2 图像预处理及分类标注
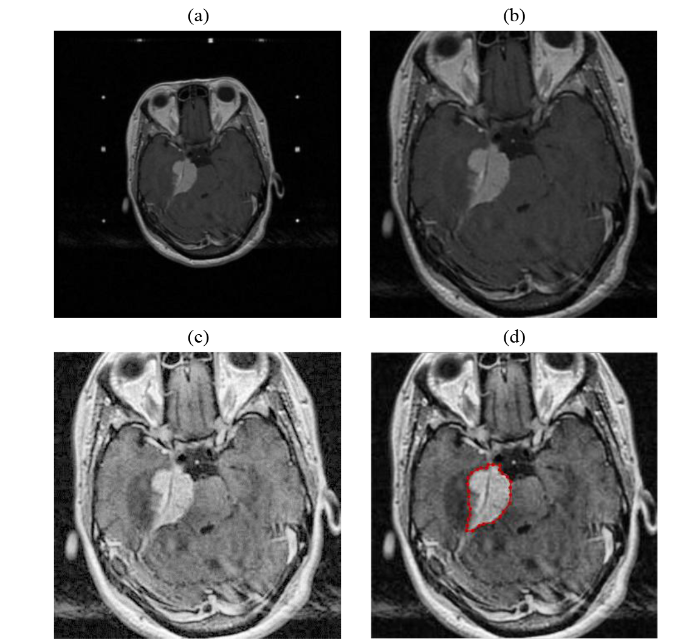
从影像归档和通信系统(picture archiving and communication system,PACS)中导出储存格式为DICOM的病例图像,然后使用MicroDICOM软件进行读取,筛选出病灶并无明显伪影的图像后,导出并以JPG格式储存,JPG图像像素为512×512.筛选后的图像集包括听神经瘤图像2 467张和脑膜瘤872张.应用Matlab 2016a软件对图像进一步预处理.首先,对图像进行裁剪,去除原始图像[图2(a)]周围无信息的空白区域,以使模型关注有效区域,并减少无效区域对训练的干扰和对计算资源的浪费.使用imcrop函数进行图像裁剪的批处理,设置裁剪后的宽和高均为300像素[图2(b)].再利用限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化(contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization,CLAHE)的方法进行图像增强处理[21].CLAHE是在自适应直方图均衡化(adaptive histogram equalization,AHE)的基础上,优化升级而来.AHE算法存在过度放大图像中相同区域噪声的问题,CLAHE通过限制局部直方图的高度来限制局部对比度的增强幅度,从而限制噪声的放大及局部对比度的过度增强,实现对图像的限制对比度的增强处理[22].使用adapthisteq函数进行图像CLAHE增强的批处理后[图2(c)],病灶区域和正常组织的对比度进一步提高.
图2
图2
图像预处理及分类标注.(a)原始图像,像素为512×512;(b)裁剪后图像,像素为300×300;(c) CLAHE增强后的图像,病灶处对比度增大;(d)标注图像,对病灶处勾画标注
Fig. 2
Preprocessed and labeled image. (a) Original image, pixels 512×512; (b) Cropped image, pixels 300×300; (c) Increased contrast of the focus after CLAHE processing; (d) Labeled image, labelling the focus
预处理后的图像由放射科高年资医师利用labelme软件勾画病灶区域并进行标注[图2(d)].脑膜瘤的标签为Meningiomas,听神经瘤的标签为AcousticNeuroma.应用Python 3.7将标注生成的json文件与图像一一对应生成xml文件,制作为voc2012数据集.将数据集按近似7:1.5:1.5比例随机生成训练集(train)、验证集(val)和测试集(test).其中train共包含听神经瘤1 726张和脑膜瘤602张,用于训练模型;val包含听神经瘤370张和脑膜瘤129张,用于训练中测试模型,对模型参数进行调整;test包含听神经瘤371张和脑膜瘤141张,用于在模型训练结束后,评估模型性能.
1.3 Mask RCNN深度学习模型
模型构建环境为Windows 10操作系统,Intel(R)Core(TM)i5-9400F CPU,32.0 GB内存,编译软件为Pycharm,编译环境为Python 3.7,Pytorch 1.12.0.
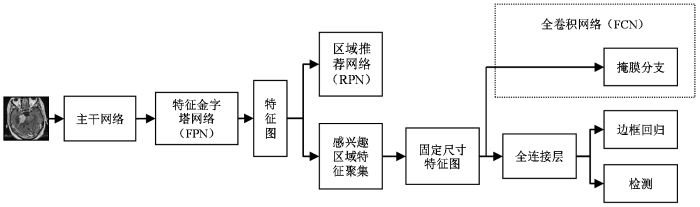
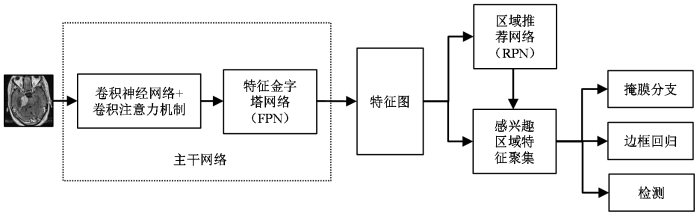
本研究中构建的结合了FPN的Mask RCNN深度学习模型用于完成桥小脑角区听神经瘤和脑膜瘤检测和病灶分割的任务.模型结构见图3,具体流程是,将预处理后的图像输入一个主干网络(backbone)中提取图像特征,经FPN[23]进行特征融合后,获取对应的图像特征图(feature map);对特征图上的每一个点预设感兴趣区域(region of interest,ROI),获取多个候选的ROI;让候选的ROI进入区域推荐网络(region proposal networks,RPN)进行二值分类(前景、后景)和边界框回归(bounding box regression),过滤掉一部分候选ROI;对剩余的ROI进行感兴趣区域特征聚集(ROIAlign)处理,将ROI映射回到特征图中,生成固定尺寸特征图(fixed size feature map);最后,对ROI进行检测、边框回归和掩膜生成.
图3
其中,主干网络是一系列用于提取特征图的CNN.文献[13]中采用VGG16[24]与Resnet50[25]、Resnet101[25]作为主干网络进行桥小脑角区听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的分类定位研究,结果表明Resnet101作为主干网络的模型性能最优.文献[24]中提出的视觉几何群网络(visual geometry group network,VGG),表明了增加网络深度可以提升网络性能,而VGG19相比VGG16有着更深层次的网络结构,预期有着更好的模型性能.本文分别构建了VGG19、Resnet50和Resnet101三种网络作为主干网络,根据本研究的图像输入尺寸对网络进行了优化.并分析三种网络作为主干网络对Mask RCNN模型性能的影响.
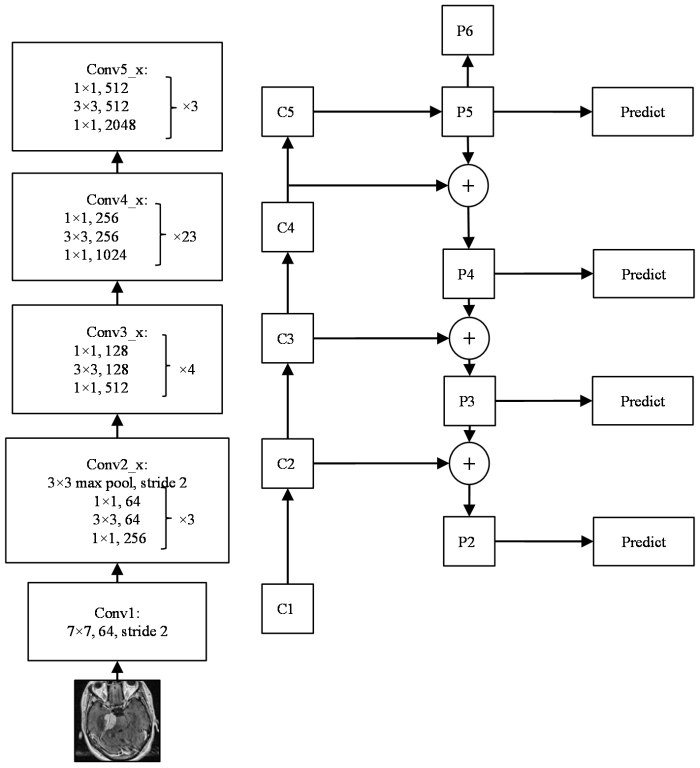
使用FPN的目的是为实现更好的特征图融合.以往的目标检测网络模型大多只使用最后一层的特征图,虽包含了丰富的语义信息,但缺少了位置和分辨率信息.FPN的作用就是融合了低层到高层的特征图,使网络可以充分的利用各阶段的图像特征.图4是以本文中构建的Resnet101作为主干网络为例,展示利用FPN对CNN提取的特征图进行融合的流程(Resnet50和VGG19作为主干网络时,FPN对CNN提取的特征图进行融合的流程见附件材料,可在论文网页版获取).FPN自然的使用了CNN层级特征中的金字塔结构,设计了自上而下的路径和横向连接,以此来融合低层的高分辨率信息和高层的丰富语义信息,实现从单尺度的单张输入图像中,迅速构建在各尺度上都具有丰富信息的特征金字塔.如图4所示,左侧为Resnet101的网络结构,输入图像在Conv1中经过7×7,64的卷积,步长(stride)为2.Conv2_x中先经过3×3的最大池化层,步长为2,后经过3个构成结构(building block),每个building block中先用1×1的卷积将256维降到64维,通过中间3×3的卷积层可以在减少计算量的同时保持精度,最后再通过1×1的卷积恢复到256维.Conv3_x、Conv4_x、Conv5_x与Conv2_x类似.经过Resnet101的卷积核处理,图像特征图的尺寸逐渐减小,当特征图的输出与原输入的大小一致时,称为相同的网络阶段,如在Conv3_x中,输入与输出的尺寸是相同的,只有通道维度上的改变.将每个网络阶段的最后一层输出作用下一网络阶段的输入,即C1~C5.特征图经FPN融合处理后,C2~C5对应的融合特征层为P2~P5,C1不再参与后续网络处理,P6由P5经步长为2的下采样得到.如C4经过1×1的卷积得到与P5相同的通道数,P5经上采样后得到与C4相同的尺寸,两者相加得到融合层P4,其余融合层以相同的方法得到.P2~P5用于后续边界框回归、掩膜生成等,P2~P6用于训练RPN,其中P6只用于RPN网络中.
图4
RPN用以提取目标检测候选框.ROIAlign由感兴趣区域池化(ROI Pooling)改进而来,采用了双线性插值的方法解决了ROI Pooling因量化操作导致候选框无法对齐的问题.采用的双线性插值方法获得坐标为浮点数的像素点上的图像数值,将图像特征聚集的过程转变为一个整体的操作,提高了模型检测和分割的精度.
全卷积网络[26](fully convolutional networks,FCN)的构建用于掩膜子网络的语义分割.FCN有三个特点:不含全连接层,可适应任意尺寸的输入;增大数据尺寸的反卷积层,可输出更加精细的结果;结合不同深度层结果的跳级结构,同时保证鲁棒性和精确性.
本次构建的Mask RCNN模型在训练中对每一个ROI定义一个多任务损失函数L,L=Lcls+Lbox+Lmask.Lcls是分类损失函数,Lbox是回归框损失函数,Lmask是掩膜损失函数.
1.4 构建融合注意力机制的深度学习模型
注意力机制是模拟人脑注意力机制的模型,关注图像中的重要特征,忽略无效特征.注意力机制在深度学习快速发展后广泛应用于各领域[27].
卷积注意力模块[28](convolutional block attention module,CBAM)是一个轻量集成的注意力卷积模块.它包含了两个独立的模块,包括通道注意力模块(channel attention module,CAM)和空间注意力模块(spatial attention module,SAM),分别对图像特征进行通道和空间上的处理.
通道注意力提取每个通道特征对关键信息的重要程度,为不同的通道按重要程度分配权重,使网络有选择性的关注权重大的特征,提高通道特征的表达.
空间注意力关注特征的空间位置信息,根据特征的位置信息与任务区域的相关性,对不同特征分配权重,增强了网络对空间特征的表达.
CBAM作为一个集成模块可以添加到现有的网络模型中,并使模型性能得到提高.如图5所示,CBAM由输入、CAM、SAM、输出组成.输入特征为F∈RC×H×W,CAM一维卷积Mc(F)∈RC×1×1,将一维卷积的结果与原图像相乘得到CAM的输出F′=Mc(F)⋅F,再将CAM输出作为SAM输入,进行SAM的二维卷积Ms(F′)∈R1×H×W,再将二维卷积的输出结果与输入相乘得到的F″=Ms(F′)⋅F′,就是经过CBAM后的输出特征.
图5
图6
1.5 模型评估
对于检测任务的目标框,Mask RCNN先采用非极大值抑制(non-maximum suppression,NMS)清除冗余重复的目标框[29],再对剩余目标框进行检测.交并比(intersection over union,IOU)用于评估预测目标框与真实框的接近程度,即两个框交集面积与并集面积之比,其值在0~1之间.本实验将IOU值设定为0.5,即当IOU>0.5时,认为检测成功保留目标框,IOU≤0.5则认为检测失败.
使用公共对象上下文(common objects in context,coco)指标评价模型的检测和分割的性能.首先TP即正样本并预测为正样本,TN为负样本并预测为负样本,FP为负样本并预测成为正样本,FN为正样本并预测成为负样本.对于检测任务,TP是IOU>0.5的检测框数目,FP是IOU≤0.5的检测框数目,FN是没有检测到真实框的数目,无法统计TN的数量.对于分割任务,TP表示肿瘤区域预测正确,TN表示正常区域预测正确,FP表示正常区域被预测为肿瘤区域,FN表示肿瘤区域预测为正常区域.
然后,利用(1)式和(2)式计算得到精确率(precision,P)和召回率(recall,R).本实验IOU=0.5,通过设置目标检测置信阈值由小到大的变化,可以得到一系列的TP、FP、FN的值,从而得到一系列的精确率与召回率,由此可以绘制出精确率与召回率(precision-recall,PR)曲线.平均精度(average precision,AP)定义为PR曲线下的面积,本文是通过对插值后的PR曲线的各块面积累加得到AP.AP综合考量了精确率和召回率的影响,能综合反映模型对于某个类型识别的性能.mAP取所有类型AP的平均值,衡量模型在所有类型上的性能.平均召回率(average recall,AR)是IOU在(0.5,1)之间所有R值的平均,以IOU的值为横坐标,对应的最大R值为纵坐标,可以绘制R-IOU曲线,则AR可计算为曲线下面积的两倍.mAR是对所有类型的AR值求平均.因此,本文最终采用mAP和mAR两个指标验证模型性能.
P、R、mAp、mAR的计算公式[30]如下所示:
(3)式中,Ri表示PR曲线中升序排列的R值,PRi+1表示在Ri+1值处曲线对应的P值.(4)式中,R(o)表示召回率R对IOU的函数,do表示对IOU的微分,∫10.5R(o)do计算的是R-IOU曲线下面积,N(classes)表示所有类型的AP/AR值数量.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 各模型的结果对比
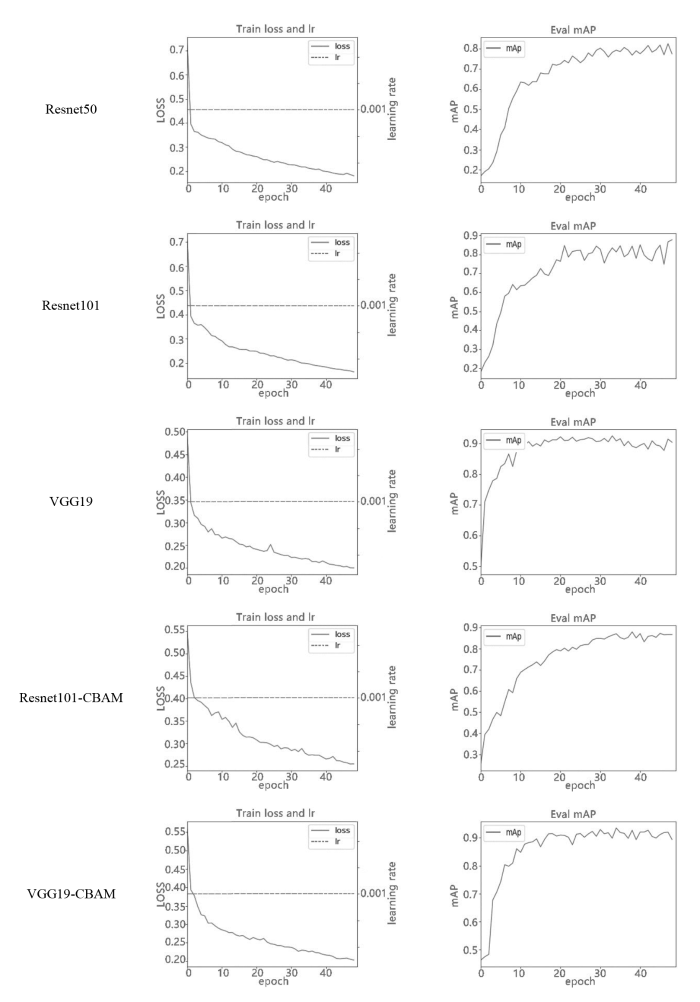
图7所示为5个模型在验证集上的loss曲线和mAP曲线.训练epoch为50次,学习率(learning rate,LR)为0.001.Train loss and lr表示模型在训练过程中验证集上的loss曲线和对应的LR曲线,Eval mAP表示模型在训练过程中验证集上评估的mAP曲线.由图中可以看到,5个模型的loss曲线都收敛良好.mAP曲线显示随着epoch的增加,VGG19的mAP快速上升并达到稳定状态,且mAP值优于Resnet50和Resnet101. 相比Resnet101-CBAM,融合CBAM模型的VGG19-CBAM的mAP曲线也是随epoch增加,快速升高达到稳定状态且mAP的值更高.说明在本研究任务中,VGG19模型优于Resnet模型.融合CBAM模型的VGG19-CBAM和Resnet101-CBAM的mAP曲线相比VGG19、Resnet101在精度和稳定性上都有提升,例如VGG19-CBAM的mAP曲线随着epoch的增加,相比VGG19的鲁棒性更好,未出现mAP下降并且mAP值略优于VGG19. 说明融合CBAM可以增强特征学习,从而提升模型性能.
图7
图7
5种模型验证集的loss曲线和mAP曲线.各模型的loss曲线都收敛良好,VGG19-CBAM的mAP曲线稳定性和精度最优
Fig. 7
Loss curves and mAP curves of 5 models in validation set. The loss curves of each model converge well, and the stability and accuracy of the mAP curve of VGG19-CBAM are optimal
表1为五种模型在测试集中得到的评价指标.从表中可以看到,融合CBAM的模型相比原模型的大部分指标有一定程度的提升,说明CBAM可以通过增强特征学习提升模型性能.综合发现,VGG19-CBAM模型除了分割指标mAR略低于VGG19外,其它检测和分割指标均更优,在五种模型中性能最好,可以在临床中辅助医生诊疗.
表1 测试集中,五种模型的结果对比
Table 1
| 模型 | 检测指标 | 分割指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAR | mAP | mAR | mAP | ||
| Resnet50 | 0.693 | 0.852 | 0.772 | 0.857 | |
| Resnet101 | 0.741 | 0.890 | 0.774 | 0.898 | |
| VGG19 | 0.725 | 0.914 | 0.808 | 0.922 | |
| Resnet101-CBAM | 0.743 | 0.918 | 0.795 | 0.923 | |
| VGG19-CBAM | 0.749 | 0.932 | 0.799 | 0.930 | |
2.2 各模型的识别结果
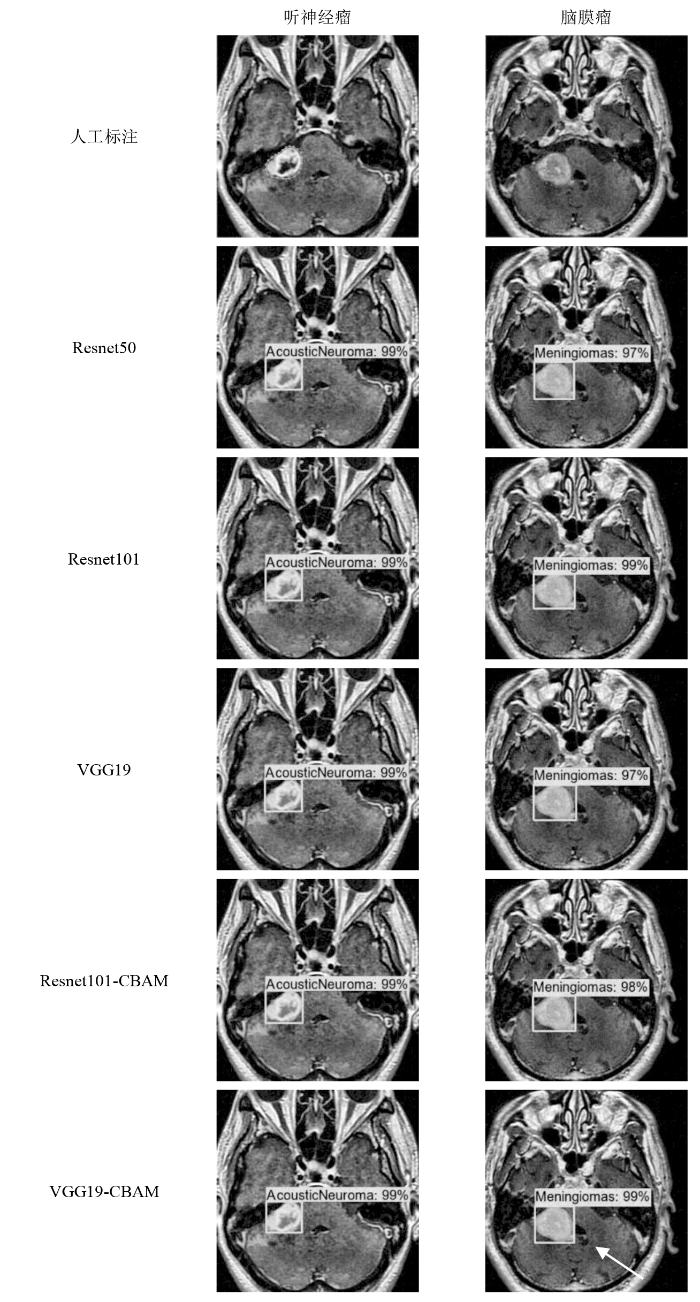
如图8所示,各模型分别对听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的检测和病灶分割的结果.如掩膜图所示,图中的数值为检测目标的置信度,表明了检测为此类别的概率.经临床医生判断,VGG19-CBAM模型的掩膜质量最优,边界清晰,与人工标注接近.如VGG19-CBAM脑膜瘤的掩膜图中箭头所示,在此边缘的掩膜分割与人工标注最接近.
图8
图8
各模型对听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的识别结果.VGG19-CBAM的掩膜最优
Fig. 8
The recognition results of each model for acoustic neuroma and meningioma, and the mask results of VGG19-CBAM are the best
2.3 讨论
桥小脑角区是颅内肿瘤的好发部位之一,其中听神经瘤和脑膜瘤是最常见的两种肿瘤.听神经瘤和脑膜瘤患者会患有桥小脑角区综合征,会出现头痛、耳鸣、听力下降、走路不稳等临床表现,且两种肿瘤的影像学表现相似,临床诊断具有一定的难度,易发生误诊.
基于深度学习的医学影像研究是当下的热点领域.CBAM通过对图像特征进行通道和空间的二维处理,增强了神经网络对图像特征的学习,而从提升模型精度.本研究构建融合CBAM的模型,Resnet101-CBAM和VGG19-CBAM,相比原模型在大部分性能指标上均有一定程度的提升.其中VGG19-CBAM在对桥小脑角区听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的检测和病灶分割任务中,mAP指标分别是0.932和0.930.对辅助临床诊断和病灶分割具有重要意义.
2.3.1 注意力机制的优势
注意力机制现已广泛的应用于深度学习各个领域中.2014年,Google Deep Mind率先在循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network,RNN)模型上使用注意力机制进行图像分类[31].将注意力机制与RNN的融合,解决了单独使用RNN时会导致处理复杂特征信息时出现的梯度爆炸,注意力机制可以提取关键的特征信息并忽略无关信息,为模型的数据处理提供便利.
本研究中,融合CBAM的模型Resnet101-CBAM与VGG19-CBAM,在检测、掩膜分割任务中mAP分别为0.918、0.923和0.932、0.930,而Resnet101和VGG19模型的mAP为0.890、0.898和0.914、0.922.融合CBAM的模型明显提高了模型精度.Li等[32]基于Faster RCNN网络,在特征提取网络中加入注意力机制对遥感目标进行检测,结果表明改进后算法比原Faster RCNN的检测结果提高12.2%,说明注意力机制可以大幅提高一些神经网络的性能.Xu等[33]将CBAM与残差神经网络Resnet50结合,在局部乳腺肿块切片数据集上的分类任务曲线下面积(AUC)为0.860 7,而Resnet50的AUC为0.834 8,即CBAM提高了神经网络对肿块病变特征的提取能力,与本研究的性能提升近似.由此可见,CBAM可以通过增强特征学习从而提升神经网络模型性能.
2.3.2 深度学习在脑肿瘤分割中的应用
本研究中,实现了对两种肿瘤的病灶分割.桥小脑角区听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的治疗方案也不同.听神经瘤目前的治疗方式有,定期MRI随访观察、显微手术治疗(microsurgery,MS)、立体定向放射外科手术(stereotactic radiosurgery,SRS)和靶向药物治疗等[35].其中,SRS目前已成为治疗听神经瘤的有效方法,表现出良好的肿瘤控制率和较低的副作用[36⇓-38]. 脑膜瘤的首选治疗是MS.但在临床中,部分脑膜瘤手术难以完全切除,或者因自身原因难以进行手术治疗.对于病灶体积较大或毗邻重要组织结构的脑膜瘤,需采用常规加速器放射治疗.在脑膜瘤的放射治疗中,需要临床医生对病灶进行靶区勾画,利用本研究对脑膜瘤的病灶分割结果,掩膜分割图可以为靶区勾画提供参考并提高靶区勾画的效率.
2.3.3 本研究的局限性
本研究存在一些局限性.第一,本研究是回顾性研究,后续可在目前研究的数据基础上,扩充图像采集来源,解决因图像采集不同导致的结果差异,使模型具有普适性.第二,本研究肿瘤病灶由放射科高年资医生手动标注,可能会出现个体差异.第三,因发病率的不同,听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的样本量不对称.
3 结论
综上所述,融合注意力机制的Mask RCNN模型在桥小脑角区的听神经瘤和脑膜瘤的识别中具有较好的分类性能,可为临床的肿瘤诊断、靶区勾画等提供参考,提高临床工作效率.后续研究可扩充数据量和数量来源,提升模型的普适性;并继续借鉴国内外深度学习的研究成果,如U-net及其改进网络模型或新的注意力机制模块,用以优化网络结构,进一步提升模型性能.
利益冲突
无
附件材料(可在《波谱学杂志》官网 http://magres.wipm.ac.cn 浏览该论文网页版获取)
图S1 Resnet50+FPN示意图
图S2 VGG19+FPN示意图
参考文献
Diagnosis and treatment of meningioma in cerebellopontine angle
[J].
桥小脑角区脑膜瘤的诊断及治疗
[J].
Well-differentiated neurocytoma: what is the best available treatment?
[J].
DOI:10.1215/S1152851704000584
PMID:15701284
[本文引用: 1]

Most neurocytomas are well differentiated, being associated with better long-term survival than the more aggressive atypical lesions. Atypical neurocytomas are characterized by an MIB-1 labeling index >3% or atypical histologic features. This analysis focuses on well differentiated neurocytomas in order to define the optimal treatment. A case with a follow-up of 132 months is presented. The patient developed two recurrences two and four years after first surgery, each showing an increasing proliferation activity. Furthermore, all published well-differentiated neurocytoma cases were reviewed for surgery, radiotherapy, and prognosis. Additional relevant data were obtained from the authors. Complete resection (CTR), complete resection plus radiotherapy (CTR + RT), incomplete resection (ITR), and incomplete resection plus radiotherapy (ITR + RT) were compared for outcome by using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test. Data were complete in 301 patients (CTR, 108; CTR + RT, 27; ITR, 81; ITR + RT, 85). Local control and survival were better after CTR than after ITR (P < 0.0001 and P = 0.0085, respectively). Radiotherapy improved local control after ITR (P < 0.0001) and after CTR (P = 0.0474), but not survival (P = 0.17 and P = 1.0, respectively). In the ITR + RT group, doses < or =54 Gy (n = 33) and >54 Gy (n = 32) were not significantly different for local control (P = 0.88) and survival (P = 0.95). The data demonstrated CTR to be superior to ITR for local control and survival. After CTR and ITR, radiotherapy improved local control, but not survival. A radiation dose of 54 Gy appeared sufficient. Application of postoperative radiotherapy should be decided individually, taking into account the risk of local failure, the need for another craniotomy, and potential radiation toxicity.
A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis
[J].
DOI:S1361-8415(17)30113-5
PMID:28778026
[本文引用: 1]

Deep learning algorithms, in particular convolutional networks, have rapidly become a methodology of choice for analyzing medical images. This paper reviews the major deep learning concepts pertinent to medical image analysis and summarizes over 300 contributions to the field, most of which appeared in the last year. We survey the use of deep learning for image classification, object detection, segmentation, registration, and other tasks. Concise overviews are provided of studies per application area: neuro, retinal, pulmonary, digital pathology, breast, cardiac, abdominal, musculoskeletal. We end with a summary of the current state-of-the-art, a critical discussion of open challenges and directions for future research.Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Deep convolutional neural networks for multi-modality isointense infant brain image segmentation
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.12.061
PMID:25562829
[本文引用: 1]

The segmentation of infant brain tissue images into white matter (WM), gray matter (GM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) plays an important role in studying early brain development in health and disease. In the isointense stage (approximately 6-8 months of age), WM and GM exhibit similar levels of intensity in both T1 and T2 MR images, making the tissue segmentation very challenging. Only a small number of existing methods have been designed for tissue segmentation in this isointense stage; however, they only used a single T1 or T2 images, or the combination of T1 and T2 images. In this paper, we propose to use deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for segmenting isointense stage brain tissues using multi-modality MR images. CNNs are a type of deep models in which trainable filters and local neighborhood pooling operations are applied alternatingly on the raw input images, resulting in a hierarchy of increasingly complex features. Specifically, we used multi-modality information from T1, T2, and fractional anisotropy (FA) images as inputs and then generated the segmentation maps as outputs. The multiple intermediate layers applied convolution, pooling, normalization, and other operations to capture the highly nonlinear mappings between inputs and outputs. We compared the performance of our approach with that of the commonly used segmentation methods on a set of manually segmented isointense stage brain images. Results showed that our proposed model significantly outperformed prior methods on infant brain tissue segmentation. In addition, our results indicated that integration of multi-modality images led to significant performance improvement. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Automatic segmentation of MR brain images with a convolutional neural network
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TMI.2016.2548501
PMID:27046893
[本文引用: 1]

Automatic segmentation in MR brain images is important for quantitative analysis in large-scale studies with images acquired at all ages. This paper presents a method for the automatic segmentation of MR brain images into a number of tissue classes using a convolutional neural network. To ensure that the method obtains accurate segmentation details as well as spatial consistency, the network uses multiple patch sizes and multiple convolution kernel sizes to acquire multi-scale information about each voxel. The method is not dependent on explicit features, but learns to recognise the information that is important for the classification based on training data. The method requires a single anatomical MR image only. The segmentation method is applied to five different data sets: coronal T-weighted images of preterm infants acquired at 30 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) and 40 weeks PMA, axial T-weighted images of preterm infants acquired at 40 weeks PMA, axial T-weighted images of ageing adults acquired at an average age of 70 years, and T-weighted images of young adults acquired at an average age of 23 years. The method obtained the following average Dice coefficients over all segmented tissue classes for each data set, respectively: 0.87, 0.82, 0.84, 0.86, and 0.91. The results demonstrate that the method obtains accurate segmentations in all five sets, and hence demonstrates its robustness to differences in age and acquisition protocol.
Detection and characterization of MRI breast lesions using deep learning
[J].
DOI:S2211-5684(19)30056-7
PMID:30926444
[本文引用: 1]

The purpose of this study was to assess the potential of a deep learning model to discriminate between benign and malignant breast lesions using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and characterize different histological subtypes of breast lesions.We developed a deep learning model that simultaneously learns to detect lesions and characterize them. We created a lesion-characterization model based on a single two-dimensional T1-weighted fat suppressed MR image obtained after intravenous administration of a gadolinium chelate selected by radiologists. The data included 335 MR images from 335 patients, representing 17 different histological subtypes of breast lesions grouped into four categories (mammary gland, benign lesions, invasive ductal carcinoma and other malignant lesions). Algorithm performance was evaluated on an independent test set of 168 MR images using weighted sums of the area under the curve (AUC) scores.We obtained a cross-validation score of 0.817 weighted average receiver operating characteristic (ROC)-AUC on the training set computed as the mean of three-shuffle three-fold cross-validation. Our model reached a weighted mean AUC of 0.816 on the independent challenge test set.This study shows good performance of a supervised-attention model with deep learning for breast MRI. This method should be validated on a larger and independent cohort.Copyright © 2019 Soci showét showé françaises de radiologie. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease based on multi-output three-dimensional convolutional neural network
[J].
基于多输出的3D卷积神经网络诊断阿尔兹海默病
[J].
Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges
[J].
医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战
[J].
Review of deep learning methods for MRI brain tumor image segmentation
[J].
MRI脑肿瘤图像分割的深度学习方法综述
[J].
Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks
[J].
DOI:S1361-8415(16)30033-0
PMID:27310171
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, we present a fully automatic brain tumor segmentation method based on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). The proposed networks are tailored to glioblastomas (both low and high grade) pictured in MR images. By their very nature, these tumors can appear anywhere in the brain and have almost any kind of shape, size, and contrast. These reasons motivate our exploration of a machine learning solution that exploits a flexible, high capacity DNN while being extremely efficient. Here, we give a description of different model choices that we've found to be necessary for obtaining competitive performance. We explore in particular different architectures based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), i.e. DNNs specifically adapted to image data. We present a novel CNN architecture which differs from those traditionally used in computer vision. Our CNN exploits both local features as well as more global contextual features simultaneously. Also, different from most traditional uses of CNNs, our networks use a final layer that is a convolutional implementation of a fully connected layer which allows a 40 fold speed up. We also describe a 2-phase training procedure that allows us to tackle difficulties related to the imbalance of tumor labels. Finally, we explore a cascade architecture in which the output of a basic CNN is treated as an additional source of information for a subsequent CNN. Results reported on the 2013 BRATS test data-set reveal that our architecture improves over the currently published state-of-the-art while being over 30 times faster.Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Multimodal high-grade glioma semantic segmentation network with multi-scale and multi-attention fusion mechanism
[J].
基于多尺度、多路注意力融合机制的多模态高等级脑胶质瘤语义分割网络
[J].
A deep learning algorithm for classifying meningioma and auditory neuroma in the cerebellopontine angle from magnetic resonance images
[J].
基于MRI和深度学习的桥小脑角区脑膜瘤与听神经瘤分类算法研究
[J].
Classification and localization of meningioma and acoustic neuroma in cerebellopontine angle based on Mask RCNN
[J].
基于Mask RCNN的桥小脑角区脑膜瘤与听神经瘤分类定位研究
[J].
Mask R-CNN
[C]//
Mask-RCNN with spatial attention for pedestrian segmentation in cyber-physical systems
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.comcom.2021.09.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Image splicing detection using mask-RCNN
[J].
Mask-RCNN recognition method of composite fold shape in ultrasound images
[J].
超声图像中复合材料褶皱形态的Mask-RCNN识别方法
[J].
Sequence to sequence learning with attention mechanism for short-term passenger flow prediction in large-scale metro system
[J].
Research advances on deep learning recommendation based on attention mechanism
[J].
基于注意力机制的深度学习推荐研究进展
[J].
U-NET CSF cells segmentation based on attention mechanism
[J].
DOI:10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.07.005
[本文引用: 1]

为解决脑脊液病理图像中部分细胞膜较为模糊,与图像背景难以区分的问题,采用了基于注意力机制的U-Net深度学习方法对脑脊液病理图像做全自动分割.在深度学习网络中加入注意力机制对细胞进行定位,抑制无关信息,提高语义的特征表达,提高对细胞整体分割的精确性.通过镜像、旋转等操作对数据集进行扩充预处理.采用VGG16预训练模型进行迁移学习,交叉熵与Dice损失相结合作为损失函数,分别在脑脊液临床图像与公开数据集2018 Data Science Bowl上进行验证;并与Otsu, PSPnet, Segnet, DeeplabV3+, U-Net进行对比,结果表明, 本文方法在各项指标上均优于其他分割方法.
基于注意力机制的U-Net脑脊液细胞分割
[J].
DOI:10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.07.005
[本文引用: 1]

为解决脑脊液病理图像中部分细胞膜较为模糊,与图像背景难以区分的问题,采用了基于注意力机制的U-Net深度学习方法对脑脊液病理图像做全自动分割.在深度学习网络中加入注意力机制对细胞进行定位,抑制无关信息,提高语义的特征表达,提高对细胞整体分割的精确性.通过镜像、旋转等操作对数据集进行扩充预处理.采用VGG16预训练模型进行迁移学习,交叉熵与Dice损失相结合作为损失函数,分别在脑脊液临床图像与公开数据集2018 Data Science Bowl上进行验证;并与Otsu, PSPnet, Segnet, DeeplabV3+, U-Net进行对比,结果表明, 本文方法在各项指标上均优于其他分割方法.
Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization
[C]//
Mammary image enhancement based on contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization
[J].Mammary images are enhanced by algorithm of Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization(CLAHE).Details of mammograph,such as calcifications breast,duct and other tissues in mammary image are enhanced effectively.Parameters of algorithm are optimized to improve the enhancement so that diagnostician can analyze image expediently.Comparing with the result of histogram equalization,it is shown that CLAHE is an effective algorithm to enhance mammary image and it is valuable in computer-aided mammary diagnosis.
基于对比度受限自适应直方图均衡的乳腺图像增强
[J].Mammary images are enhanced by algorithm of Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization(CLAHE).Details of mammograph,such as calcifications breast,duct and other tissues in mammary image are enhanced effectively.Parameters of algorithm are optimized to improve the enhancement so that diagnostician can analyze image expediently.Comparing with the result of histogram equalization,it is shown that CLAHE is an effective algorithm to enhance mammary image and it is valuable in computer-aided mammary diagnosis.
Feature pyramid networks for object detection
[J].DOI:10.1109/CVPR.2017.106 [本文引用: 1]
Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition
[C]//
Deep residual learning for image recognition
[C]//
Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation
[J].DOI:10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965 URL [本文引用: 1]
State attention in deep reinforcement learning
[J].
深度强化学习中状态注意力机制的研究
[J].
A comparative analysis of object detection metrics with a companion open-source toolkit
[J].
DOI:10.3390/electronics10030279
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Recent outstanding results of supervised object detection in competitions and challenges are often associated with specific metrics and datasets. The evaluation of such methods applied in different contexts have increased the demand for annotated datasets. Annotation tools represent the location and size of objects in distinct formats, leading to a lack of consensus on the representation. Such a scenario often complicates the comparison of object detection methods. This work alleviates this problem along the following lines: (i) It provides an overview of the most relevant evaluation methods used in object detection competitions, highlighting their peculiarities, differences, and advantages; (ii) it examines the most used annotation formats, showing how different implementations may influence the assessment results; and (iii) it provides a novel open-source toolkit supporting different annotation formats and 15 performance metrics, making it easy for researchers to evaluate the performance of their detection algorithms in most known datasets. In addition, this work proposes a new metric, also included in the toolkit, for evaluating object detection in videos that is based on the spatio-temporal overlap between the ground-truth and detected bounding boxes.
Recurrent models of visual attention
[C]//
Attention mechanism improves CNN remote sensing image object detection
[J].
注意力机制改进卷积神经网络的遥感图像目标检测
[J].
Mass classification of breast mammogram based on attention mechanism and transfer learning
[J].
基于注意力机制与迁移学习的乳腺钼靶肿块分类
[J].
Status of artificial intelligence in meningioma image
[J].
脑膜瘤影像人工智能应用进展
[J].
Progress in application of stereotactic radiosurgery in treatment of acoustic neuroma
[J].
立体放射治疗技术在听神经瘤治疗中的应用进展
[J].
Gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: tumor control and functional preservation in 70 patients.
[J].DOI:10.1097/COC.0b013e3181dbc2ab URL [本文引用: 1]
Analysis of risk factors associated with radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma
[J].
DOI:10.3171/jns.2001.95.3.0440
PMID:11565866
[本文引用: 1]

The aim of this study was to identify factors associated with delayed cranial neuropathy following radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma (VS or acoustic neuroma) and to determine how such factors may be manipulated to minimize the incidence of radiosurgical complications while maintaining high rates of tumor control.From July 1988 to June 1998, 149 cases of VS were treated using linear accelerator radiosurgery at the University of Florida. In each of these cases, the patient's tumor and brainstem were contoured in 1-mm slices on the original radiosurgical targeting images. Resulting tumor and brainstem volumes were coupled with the original radiosurgery plans to generate dose-volume histograms. Various tumor dimensions were also measured to estimate the length of cranial nerve that would be irradiated. Patient follow-up data, including evidence of cranial neuropathy and radiographic tumor control, were obtained from a prospectively maintained, computerized database. The authors performed statistical analyses to compare the incidence of posttreatment cranial neuropathies or tumor growth between patient strata defined by risk factors of interest. One hundred thirty-nine of the 149 patients were included in the analysis of complications. The median duration of clinical follow up for this group was 36 months (range 18-94 months). The tumor control analysis included 133 patients. The median duration of radiological follow up in this group was 34 months (range 6-94 months). The overall 2-year actuarial incidences of facial and trigeminal neuropathies were 11.8% and 9.5%, respectively. In 41 patients treated before 1994, the incidences of facial and trigeminal neuropathies were both 29%, but in the 108 patients treated since January 1994, these rates declined to 5% and 2%, respectively. An evaluation of multiple risk factor models showed that maximum radiation dose to the brainstem, treatment era (pre-1994 compared with 1994 or later), and prior surgical resection were all simultaneously informative predictors of cranial neuropathy risk. The radiation dose prescribed to the tumor margin could be substituted for the maximum dose to the brainstem with a small loss in predictive strength. The pons-petrous tumor diameter was an additional statistically significant simultaneous predictor of trigeminal neuropathy risk, whereas the distance from the brainstem to the end of the tumor in the petrous bone was an additional marginally significant simultaneous predictor of facial neuropathy risk. The overall radiological tumor control rate was 93% (59% tumors regressed, 34% remained stable, and 7.5% enlarged), and the 5-year actuarial tumor control rate was 87% (95% confidence interval [CI] 76-98%). Analysis revealed that a radiation dose cutpoint of 10 Gy compared with more than 10 Gy prescribed to the tumor margin yielded the greatest relative difference in tumor growth risk (relative risk 2.4, 95% CI 0.6-9.3), although this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.207).Five points must be noted. 1) Radiosurgery is a safe, effective treatment for small VSs. 2) Reduction in the radiation dose has played the most important role in reducing the complications associated with VS radiosurgery. 3) The dose to the brainstem is a more informative predictor of postradiosurgical cranial neuropathy than the length of the nerve that is irradiated. 4) Prior resection increases the risk of late cranial neuropathies after radiosurgery. 5) A prescription dose of 12.5 Gy to the tumor margin resulted in the best combination of maximum tumor control and minimum complications in this series.
A meta-analysis of treatment of vestibular schwannoma using gamma knife radiosurgery
[J].