
- Jul. 8, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 158-168.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20223036
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
TIAN Yu1,2,3,ZHOU Chen2,3,ZHANG Yanan2,3,4,WANG Peng4,ZHANG Caiyun4,SONG Tianwei2,3,4,QIAN Junchao1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-22
Published:2023-06-05
Online:2023-01-29
Contact:
QIAN Junchao
E-mail:qianjunchao@hmfl.ac.cn
CLC Number:
TIAN Yu,ZHOU Chen,ZHANG Yanan,WANG Peng,ZHANG Caiyun,SONG Tianwei,QIAN Junchao. In vivo MR Vessel Size Imaging of Brain Vascular Plasticity After Experimental Spinal Cord Injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 158-168.
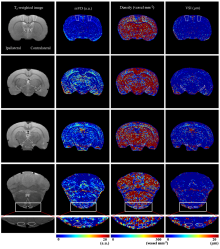
Fig. 2
Representative magnetic resonance images of different layers of a rat brain after spinal cord hemisection injury for four weeks. The ROIs were delineated on T2-weighted images and transferred to the mVD, Density and VSI images. CTX: cortex including primary motor cortex (M1); IC: internal capsule; CP: cerebral peduncle; PY: pyramid


Fig. 3
Quantitative analysis of mVD, Density, and VSI for each region of interest in the ipsilateral and contralateral brain regions of six rats after spinal cord hemisection injury for four weeks. CTX: cortex including primary motor cortex (M1); IC: internal capsule; CP: cerebral peduncle; PY: pyramid. Data were represented by mean ± standard deviation, ** p<0.01
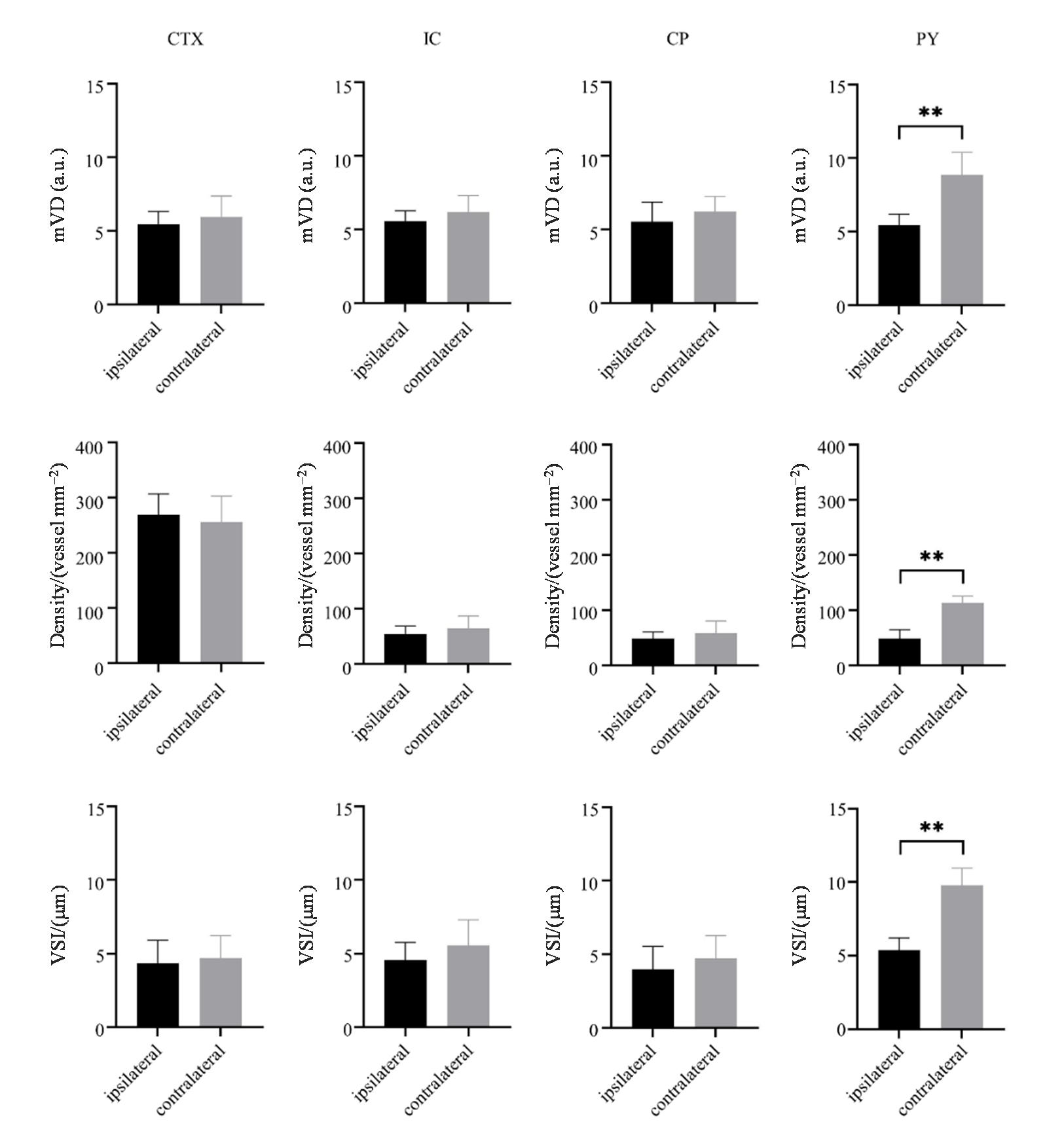
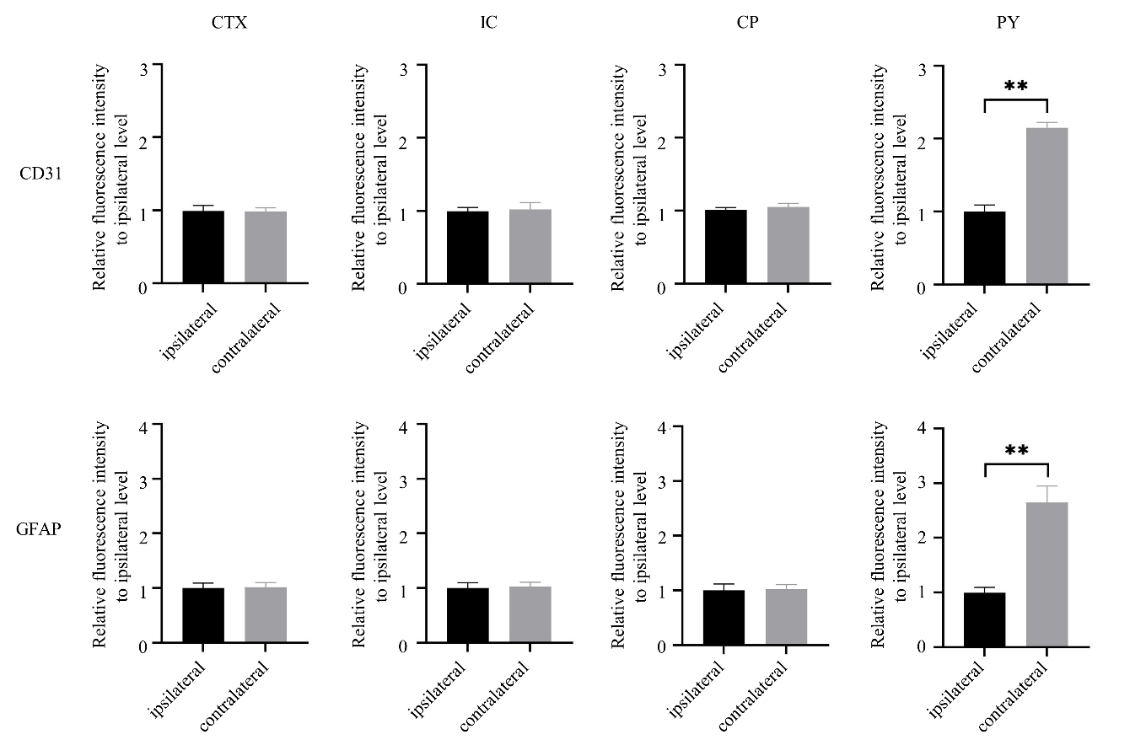
Fig. 5
Quantitative analysis of immunofluorescence intensity of CD31 and GFAP in the ipsilateral and contralateral brain regions of 6 rats after spinal cord hemisection injury for four weeks. CTX: cortex including primary motor cortex (M1); IC: internal capsule; CP: cerebral peduncle; PY: pyramid. Data were represented by mean ± standard deviation, ** p<0.01
| [1] |
WRIGLEY P J, GUSTIN S M, MACEY P M, et al. Anatomical changes in human motor cortex and motor pathways following complete thoracic spinal cord injury[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2009, 19(1): 224-232.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn072 pmid: 18483004 |
| [2] |
ILVESMäKI T, KOSKINEN E, BRANDER A, et al. Spinal cord injury induces widespread chronic changes in cerebral white matter[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2017, 38(7): 3637-3647.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.23619 pmid: 28429407 |
| [3] |
HE G, QIAN J. Phase imaging of axonal integrity of cranial corticospinal tract in experimental spinal cord injury at 9.4T[J]. Microsc Res Tech, 2017, 80(9): 1009-1017.
doi: 10.1002/jemt.v80.9 |
| [4] |
COHEN-ADAD J, EL MENDILI M M, LEHéRICY S, et al. Demyelination and degeneration in the injured human spinal cord detected with diffusion and magnetization transfer MRI[J]. Neuroimage, 2011, 55(3): 1024-1033.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.089 |
| [5] |
MOXON K A, OLIVIERO A, AGUILAR J, et al. Cortical reorganization after spinal cord injury: always for good?[J]. Neuroscience, 2014, 283: 78-94.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.06.056 pmid: 24997269 |
| [6] |
JURKIEWICZ M T, MIKULIS D J, MCILROY W E, et al. Sensorimotor cortical plasticity during recovery following spinal cord injury: a longitudinal fMRI study[J]. Neurorehabil Neural Repair, 2007, 21(6): 527-538.
doi: 10.1177/1545968307301872 |
| [7] | FASSETT H J, TURCO C V, EL-SAYES J, et al. Alterations in Motor Cortical representation of muscles following incomplete spinal cord injury in humans[J]. Brain Sci, 2018, 8(12). |
| [8] | WANG L, CHEN N. MRI research progresses of motor imagery on brain activity and network reorganization in patients with spinal cord injury[J]. Chin J Med Imaging Technol, 2019, 35(10):1586-1589. |
| 王玲, 陈楠. 运动想象对脊髓损伤患者大脑活动和脑网络重塑MR研究进展[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(10): 1586-1589. | |
| [9] |
TSUJIOKA H, YAMASHITA T. Neural circuit repair after central nervous system injury[J]. Int Immunol, 2021, 33(6): 301-309.
doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxaa077 pmid: 33270108 |
| [10] |
LIU J, YANG X, JIANG L, et al. Neural plasticity after spinal cord injury[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2012, 7(5): 386-391.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.05.010 pmid: 25774179 |
| [11] |
YU S, YAO S, WEN Y, et al. Angiogenic microspheres promote neural regeneration and motor function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 33428.
doi: 10.1038/srep33428 pmid: 27641997 |
| [12] |
POTENTE M, GERHARDT H, CARMELIET P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis[J]. Cell, 2011, 146(6): 873-887.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.039 pmid: 21925313 |
| [13] | LI X, LI M, TIAN L, et al. Reactive astrogliosis: implications in spinal cord injury progression and therapy[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 9494352. |
| [14] |
SHIMAMURA M, SATO N, SATA M, et al. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met after spinal cord injury in rats[J]. Brain Res, 2007, 1151: 188-194.
pmid: 17425951 |
| [15] |
NAKAMURA T, MIZUNO S. The discovery of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its significance for cell biology, life sciences and clinical medicine[J]. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, 2010, 86(6): 588-610.
doi: 10.2183/pjab.86.588 |
| [16] |
KITAMURA K, IWANAMI A, NAKAMURA M, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes endogenous repair and functional recovery after spinal cord injury[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2007, 85(11): 2332-2342.
pmid: 17549731 |
| [17] |
CHRISTOFORIDIS G A, YANG M, KONTZIALIS M S, et al. High resolution ultra high field magnetic resonance imaging of glioma microvascularity and hypoxia using ultra-small particles of iron oxide[J]. Invest Radiol, 2009, 44(7): 375-383.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181a8afea pmid: 19448552 |
| [18] |
XU C, SCHMIDT W U, VILLRINGER K, et al. Vessel size imaging reveals pathological changes of microvessel density and size in acute ischemia[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2011, 31(8): 1687-1695.
doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.38 |
| [19] | XU X, MENG T, WEN Q, et al. Dynamic changes in vascular size and density in transgenic mice with Alzheimer's disease[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12(17): 17224-17234. |
| [20] | JIANG J J, ZHAO L Y, WANG C Y, et al. Initial application of magnetic resonance vessel size imaging in cerebral glioma and meningioma[J]. Radiol Practic, 2014, 29(7): 770-773. |
| 江晶晶, 赵凌云, 王承缘, 等. 磁共振血管大小成像在脑胶质瘤和脑膜瘤中的初步应用[J]. 放射学实践, 2014, 29(7): 770-773. | |
| [21] |
IELACQUA G D, SCHLEGEL F, FüCHTEMEIER M, et al. Magnetic resonance Q mapping reveals a decrease in microvessel density in the arcAβ mouse model of cerebral amyloidosis[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2015, 7: 241.
doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00241 pmid: 26834622 |
| [22] |
LEMASSON B, VALABLE S, FARION R, et al. In vivo imaging of vessel diameter, size, and density: a comparative study between MRI and histology[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 69(1): 18-26.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24218 pmid: 22431289 |
| [23] |
HOL E M, PEKNY M. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and the astrocyte intermediate filament system in diseases of the central nervous system[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2015, 32: 121-130.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.02.004 pmid: 25726916 |
| [24] | RAZAVI S M, YAHYAABADI R. Comparative study of correlation between angiogenesis markers (CD31) and Ki67 marker with behavior of aggressive and nonaggressive central giant cell granuloma with immunohistochemistry technique[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2018, 19(8): 2279-2283. |
| [25] |
RAMU J, BOCKHORST K H, MOGATADAKALA K V, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging in rodents: Methodology and application to spinal cord injury[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2006, 84(6): 1235-1244.
pmid: 16941500 |
| [26] | SHEN Y M, ZHENG W L, CHENG Y-C N, et al. USPIO high resolution neurovascular imaging in a rat stroke model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2014, 31(1): 20-31. |
| 沈伊民, 郑伟丽, CHENG Y-C N, 等. 大鼠中风模型的超小氧化铁粒子神经血管成像[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2014, 31(1): 20-31. | |
| [27] |
JIRJIS M B, VEDANTAM A, BUDDE M D, et al. Severity of spinal cord injury influences diffusion tensor imaging of the brain[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2016, 43(1): 63-74.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.24964 pmid: 26094789 |
| [28] |
LIDDELOW S A, BARRES B A. Reactive astrocytes: production, function, and therapeutic potential[J]. Immunity, 2017, 46(6): 957-967.
doi: S1074-7613(17)30234-0 pmid: 28636962 |
| [29] |
SOFRONIEW M V. Reactive astrocytes in neural repair and protection[J]. Neuroscientist, 2005, 11(5): 400-407.
doi: 10.1177/1073858405278321 pmid: 16151042 |
| [30] |
OKADA S, HARA M, KOBAYAKAWA K, et al. Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury[J]. Neurosci Res, 2018, 126: 39-43.
doi: S0168-0102(17)30592-8 pmid: 29054466 |
| [31] |
HUSSEIN R K, MENCIO C P, KATAGIRI Y, et al. Role of chondroitin sulfation following spinal cord injury[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2020, 14: 208.
doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00208 pmid: 32848612 |
| [32] |
WANG Y, CHENG X, HE Q, et al. Astrocytes from the contused spinal cord inhibit oligodendrocyte differentiation of adult oligodendrocyte precursor cells by increasing the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins[J]. J Neurosci, 2011, 31(16): 6053-6058.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5524-09.2011 pmid: 21508230 |
| [33] |
YIU G, HE Z. Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2006, 7(8): 617-627.
doi: 10.1038/nrn1956 pmid: 16858390 |
| [34] |
YANG T, DAI Y, CHEN G, et al. Dissecting the dual role of the glial scar and scar-forming astrocytes in spinal cord injury[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2020, 14: 78.
doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00078 pmid: 32317938 |
| [35] |
OKADA S, NAKAMURA M, KATOH H, et al. Conditional ablation of Stat3 or Socs3 discloses a dual role for reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury[J]. Nat Med, 2006, 12(7): 829-834.
doi: 10.1038/nm1425 pmid: 16783372 |
| [36] |
SOFRONIEW M V. Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2015, 16(5): 249-263.
doi: 10.1038/nrn3898 pmid: 25891508 |
| [37] |
LIU D, XU G Y, PAN E, et al. Neurotoxicity of glutamate at the concentration released upon spinal cord injury[J]. Neuroscience, 1999, 93(4): 1383-1389.
doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(99)00278-x pmid: 10501463 |
| [38] |
MARAGAKIS N J, DYKES-HOBERG M, ROTHSTEIN J D. Altered expression of the glutamate transporter EAAT2b in neurological disease[J]. Ann Neurol, 2004, 55(4): 469-477.
pmid: 15048885 |
| [39] |
CASELLA G T, MARCILLO A, BUNGE M B, et al. New vascular tissue rapidly replaces neural parenchyma and vessels destroyed by a contusion injury to the rat spinal cord[J]. Exp Neurol, 2002, 173(1): 63-76.
pmid: 11771939 |
| [40] |
YAMANE K, MISAWA H, TAKIGAWA T, et al. Multipotent neurotrophic effects of hepatocyte growth factor in spinal cord injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(23) : 6078.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20236078 |
| [41] |
MENEGHINI V, PEVIANI M, LUCIANI M, et al. Delivery platforms for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing of glial cells in the central nervous system[J]. Front Genome Ed, 2021, 3: 644319.
doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2021.644319 |
| [42] |
LIBERTO C M, ALBRECHT P J, HERX L M, et al. Pro-regenerative properties of cytokine-activated astrocytes[J]. J Neurochem, 2004, 89(5): 1092-1100.
pmid: 15147501 |
| [43] |
COLLOMBET J M, FOUR E, FAUQUETTE W, et al. Soman poisoning induces delayed astrogliotic scar and angiogenesis in damaged mouse brain areas[J]. Neurotoxicology, 2007, 28(1): 38-48.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2006.07.011 |
| [44] |
BARTANUSZ V, JEZOVA D, ALAJAJIAN B, et al. The blood-spinal cord barrier: morphology and clinical implications[J]. Ann Neurol, 2011, 70(2): 194-206.
doi: 10.1002/ana.22421 pmid: 21674586 |
| [45] |
WHETSTONE W D, HSU J Y, EISENBERG M, et al. Blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury: relation to revascularization and wound healing[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2003, 74(2): 227-239.
pmid: 14515352 |
| [46] |
WAHIS J, HENNES M, ARCKENS L, et al. Star power: the emerging role of astrocytes as neuronal partners during cortical plasticity[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2021, 67: 174-182.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2020.12.001 pmid: 33360483 |
| [47] |
CHUNG W S, ALLEN N J, EROGLU C. Astrocytes control synapse formation, function, and elimination[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2015, 7(9): a020370.
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020370 |
| [48] |
WANG Y, FU A K Y, IP N Y. Instructive roles of astrocytes in hippocampal synaptic plasticity: neuronal activity-dependent regulatory mechanisms[J]. Febs J, 2022, 289(8): 2202-2218.
doi: 10.1111/febs.v289.8 |
| [1] |
.
ABNORMAL T2-WI SIGNAL IN CHRONIC EPILEPTIC RATS INDUCED BY DELIVERING REPETITIVE TETANUS INTO THE APICAL DENDRITE REGION IN EITHER CA1 OR DENTATE GYRUS [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2001, 18(3): 193-200. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 293
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 245
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||