固体NMR研究MOFs吸附和分离过程中的主客体相互作用
Solid-state NMR Investigation of the Host-guest Interactions in Gas Adsorption and Chemical Separation Using MOFs as Adsorbents
固体NMR研究MOFs吸附和分离过程中的主客体相互作用 |
| 贺彩艳,肖宇情,李申慧,徐君,邓风 |
|
Solid-state NMR Investigation of the Host-guest Interactions in Gas Adsorption and Chemical Separation Using MOFs as Adsorbents |
| HE Caiyan,XIAO Yuqing,LI Shenhui,XU Jun,DENG Feng |
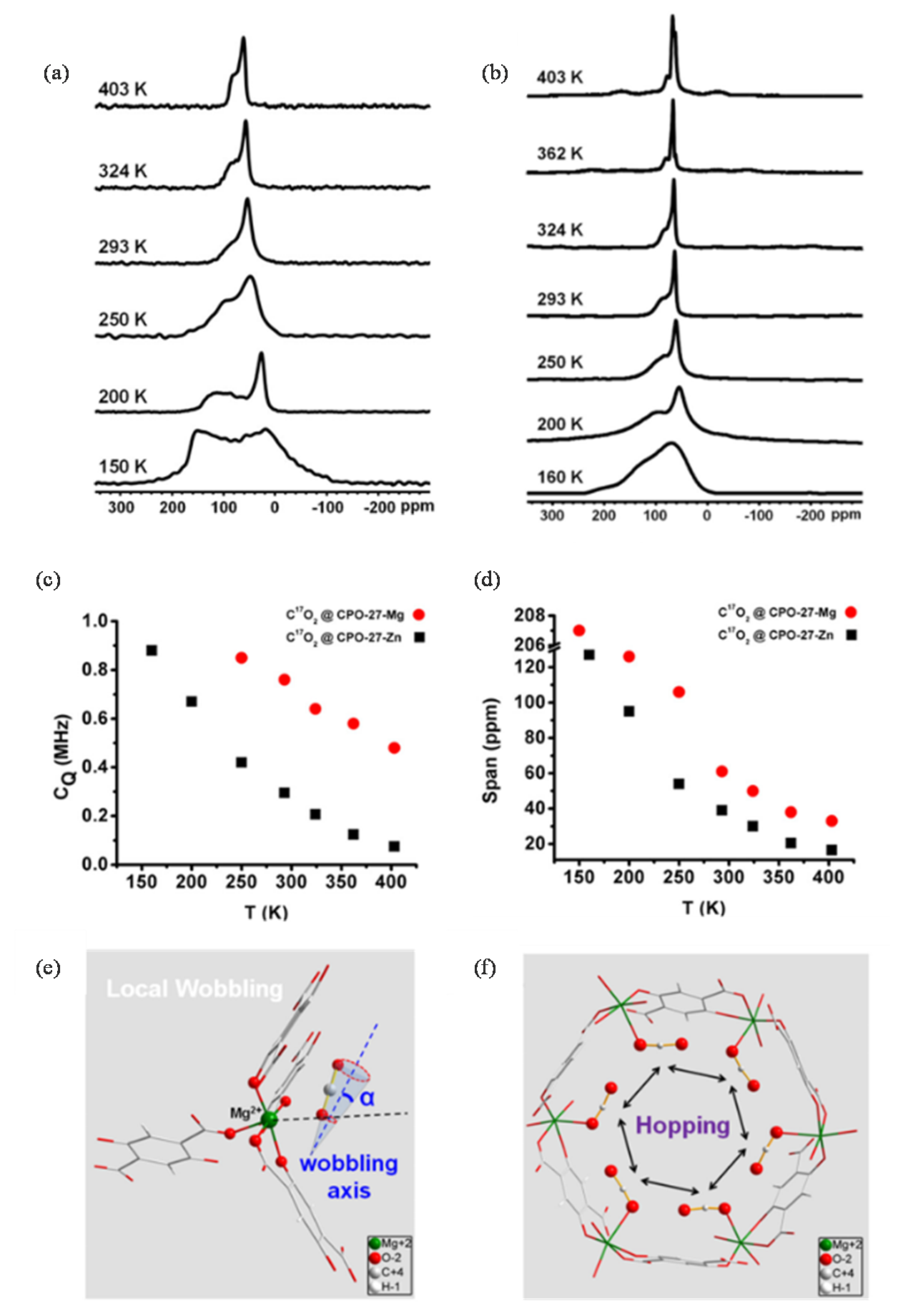
| 图2 在150~403 K温度范围内,C17O2吸附在(a) Mg-CPO-27和(b) Zn-CPO-27的变温静态17O NMR图谱;(c)~(d)吸附在M-CPO-27中的C17O2在不同温度下的四极耦合常数(CQ)和化学位移各向异性宽度(Ω);(e)~(f) Mg-CPO-27中CO2的吸附分子动力学模型,CO2主要经历两种不同的运动:(e)局域轴向转动和(f)吸附在不同金属位点上CO2的非局部跳跃[ |
| Fig. 2 Static variable temperature 17O NMR spectra of C17O2 adsorbed on (a) Mg-CPO-27 and (b) Zn-CPO-27 at temperatures ranging from 150 to 403 K. (c)~(d) Temperature-dependence of quadrupole coupling constant (CQ) and chemical shift anisotropy (CSA) span (Ω) of C17O2 adsorbed in M-CPO-27. (e)~(f) Dynamic motion of adsorbed CO2 molecules in Mg-CPO-27. Adsorbed CO2 mainly undergoes two different motions: (e) wobbling and (f) hopping[ |

|