引言
固体核磁共振(solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance,SSNMR)技术不仅用于表征材料分子的结构和动态学行为,还可以实现多种定量信息的检测[1,2].传统SSNMR定量技术是直接激发高功率去耦(direct polarization with high power decoupling,DP)技术[3].该方法实现定量的关键是D1≥5T1(D1为弛豫等待时间,T1为检测核的自旋晶格弛豫时间).然而对于多数样品,尤其是具有刚性结构的样品,13C的T1较长且自然丰度低.定量检测时,DP实验耗时较长,往往需要花费十几个小时甚至数周的时间[4].近年来,为了实现短时间内SSNMR的定量检测,科研工作者们先后提出了数种实验技术与方法[5⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-15].在这些方法中,多次交叉极化(multiple-cross polarization,multiCP)技术由于具有较高的普适性和可行性,受到了广泛的关注.1985年,Gerstein和Dybowski[16]在交叉极化(cross polarization,CP)技术的基础上,首次提出了多次交叉极化的概念.1990年,Mehring课题组基于此技术提出了较DP方法耗时更短的SSNMR定量方法,该方法通过多次交叉极化过程,使样品体系中各种不同基团待检测核的CP效率逐步提升并趋于相同,从而实现谱图中谱峰积分的定量[17];2014年,Schmidt-Rohr课题组将该方法命名为multiCP,系统地探讨了1H射频场强度对定量结果的影响,并应用于土壤腐殖质的成分分析[13];2017年,该课题组对multiCP技术进行了优化,通过使用180˚补偿脉冲技术降低90˚脉冲共振偏置和激发脉宽不准确所导致的信号损失. 此外,Hirschinger等[18,19]基于β-甲酸钙、二茂铁和丙氨酸的multiCP实验数据,并结合理论计算,讨论了魔角旋转速率对multiCP谱图信噪比和测量结果准确性的影响.随着对multiCP方法的不断研究与推广,多个课题组相继使用该方法开展定量相关的表征与研究,从而获取多相高分子的结晶度[20]、混合物的组分含量[21,22]、分子基团的比例与结构[23⇓-25]等信息. 目前,multiCP 技术在农业[20,24]、矿物[23,25]、环境[22]等领域都表现出潜在的应用价值.
实现multiCP准确定量的关键是如何依据样品的属性合理地设置实验参数.2021年,本课题组以L-丙氨酸、L-缬氨酸和二者混合物为模型样品,深入探讨了multiCP实验的测量结果受样品属性的影响[26],发现multiCP实验参数—交叉极化接触时间(tp)的设置依赖于样品及基团的13C-1H交叉弛豫时间(TCH).对于TCH值相近的基团或体系,其获取定量结果时的实验参数设置相似.然而,对于TCH值差异较大的体系,其获取定量结果时的实验参数条件较苛刻.此外,当体系氢原子核在自旋锁定场下的自旋晶格弛豫时间(
1 实验部分
1.1 试剂与样品制备
L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸(A. R.级)粉末样品购于北京伊诺凯科技有限公司,均直接使用,未进行进一步处理.L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸混合样品的制备过程:分别以L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸摩尔比为1:1、1:3和3:1的比例称取一定质量的两种粉末样品,置于研钵中反复研磨,使两者混合均匀.
将样品填充在外径为3.2 mm的ZrO2转子中,均匀压实,进行SSNMR实验.
1.2 SSNMR实验
所有实验均在配备3.2 mm H/F/X MAS DVT三共振探头的Bruker AVANCE III HD 400 WB固体NMR波谱仪(瑞士,布鲁克公司)上进行.1H和13C的共振频率分别为400.25 MHz和100.65 MHz,魔角旋转速率为10 kHz.1H和13C的90˚脉冲宽度分别为3.2 μs和3.6 μs,所对应的射频场强度分别为78 kHz和69 kHz. 所有CP过程中1H的最大自旋锁定场强度为78 kHz,脉冲形状为功率由100%衰减至50%的ramp-CP脉冲[29],13C的自旋锁定场强度为78 kHz,采样期间使用TPPM对1H去耦[30].所有的13C NMR谱图中,13C谱峰的化学位移均以四甲基硅烷(TMS)为参比,以金刚烷作为二次标样,将分子中CH基团13C谱峰的化学位移(δC 38.484)进行定标[31,32].
1.3 数据分析
各基团TCH相对差异度
L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸纯净物分子基团比例的百分误差计算方法:首先对分子内各基团谱峰积分值进行归一化,
混合物中各组分含量的百分误差的计算公式为
2 结果与讨论
2.1 LGCP对体系弛豫时间的影响及multiCP方法的优化方案
图1(a)为本文提出的MLGCP-1实验脉冲序列示意图,该方法基于multiCP [脉冲序列示意图如图1(b)][13],并在最后一次CP后引入LGCP技术[27,28],使1H的磁化矢量锁定在魔角方向上.CP过程中,LG同核去耦技术削弱了氢原子核之间的偶极耦合作用,从而影响了1H→13C的CP效率.在分子体系中,非季碳受到的影响更强,TCH明显增长;而对于季碳原子,由于没有通过化学键与氢原子直接相连,TCH值大于非季碳TCH,且由于受到氢同核去耦技术的影响较小,因而TCH无明显变化.因此,LGCP技术的引入,缩小了非季碳与季碳原子核之间TCH的差异度.与此同时,由于氢原子核之间的偶极耦合被削弱,抑制了氢原子核间的自旋扩散作用,因而抑制了射频场下的氢自旋晶格弛豫作用,即
图1
图1
(a) MLGCP-1实验脉冲序列示意图,相应的相循环为:Ф1 = y, -y;Ф2 = x;Ф3 = -y, y;Ф4 = x, x, -x, -x, y, y, -y, -y;Ф5 = - y, y, y, -y, x, -x, -x, x;Ф6 = y, -y, - y, y, -x, x, x, -x;Ф7 = -y;Ф8 = y;ФRec= x, -x, -x, x, y, -y, -y, y;(b) multiCP实验脉冲序列示意图,相应的相循环为:Ф1 = y, -y;Ф2 = x;Ф3 = -y, y;Ф4 = x, x, -x, -x, y, y, -y, -y;Ф5= -y, y, y, -y, x, -x, -x, x;Ф6 = y, -y, -y, y, -x, x, x, -x;ФRec = x, -x, -x, x, y, -y, -y, y
Fig. 1
(a) The pulse sequence of MLGCP-1 method with the following phase cycles: Ф1 = y, -y; Ф2 = x; Ф3 = -y, y; Ф4 = x, x, -x, -x, y, y, -y, -y; Ф5 = - y, y, y, -y, x, -x, -x, x; Ф6 = y, -y, - y, y, -x, x, x, -x; Ф7 = -y; Ф8 = y; ФRec= x, -x, -x, x, y, -y, -y, y; (b) multiCP pulse sequence with following phase cycles: Ф1 = y, -y; Ф2 = x; Ф3 = -y, y; Ф4 = x, x, -x, -x, y, y, -y, -y; Ф5= -y, y, y, -y, x, -x, -x, x; Ф6 = y, -y, -y, y, -x, x, x, -x; ФRec = x, -x, -x, x, y, -y, -y, y
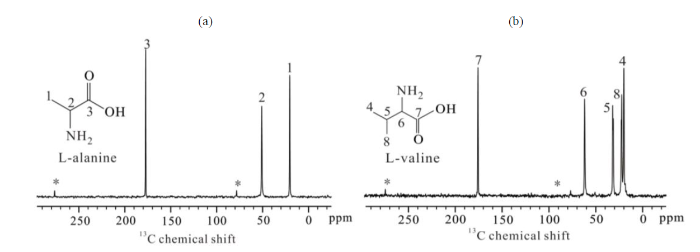
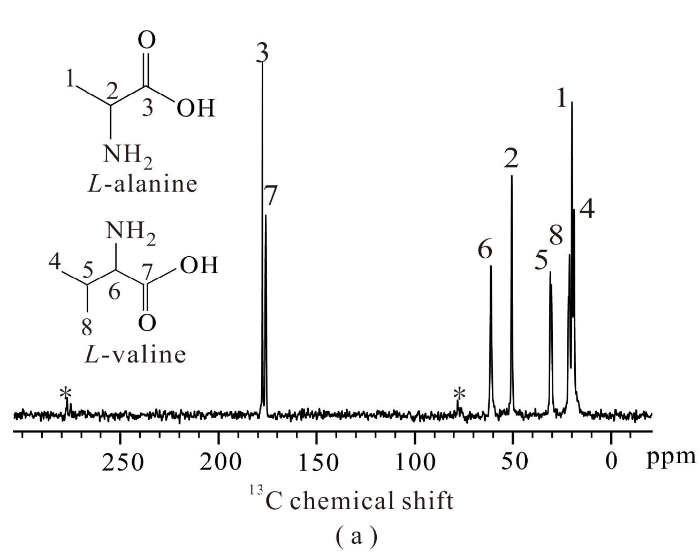
实验首先选取L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸两种固体样品,对比了绝热CP实验ramp-CP和LGCP过程中,分子各基团的TCH和
图2
图2
(a) L-丙氨酸和(b) L-缬氨酸分子化学结构示意图及13C CP NMR谱,谱峰依据结构示意图中的序号进行归属
Fig. 2
The structure schemes and 13C CP NMR spectra of (a) L-alanine and (b) L-valine. Peaks are assigned using labels with respect to the structural schemes
表1
L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸分子中各基团在ramp-CP和LGCP条件下的TCH和
Table 1
| Sample | Carbons | T1,H/ms | ramp-CP | LGCP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCH/ms | TCH/ms | ||||||
| L-alanine | 1 | 977.1 | 0.170 | 1.7 | 0.387 | 12.8 | |
| 2 | 0.042 | 0.174 | |||||
| 3 | 0.360 | 0.331 | |||||
| L-valine | 4 | 718.5 | 0.174 | 2.5 | 0.414 | 24.3 | |
| 5 | 0.036 | 0.157 | |||||
| 6 | 0.033 | 0.120 | |||||
| 7 | 0.290 | 0.240 | |||||
| 8 | 0.154 | 0.374 | |||||
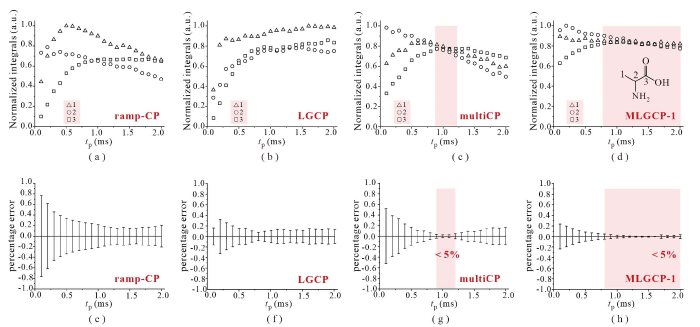
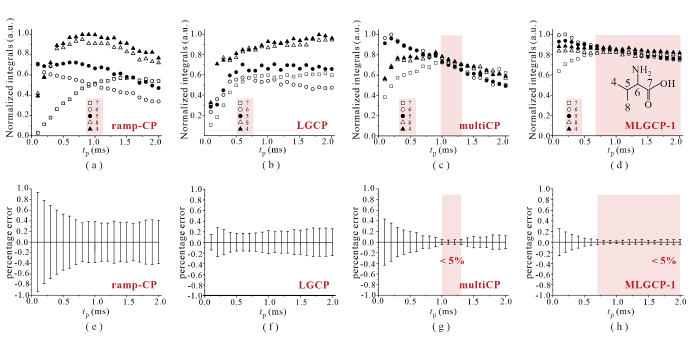
为了进一步评估MLGCP-1方法的可行性,本文仍然以L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸为模型样品,通过改变tp,绘制了的ramp-CP、LGCP、multiCP和MLGCP-1四种方法的CP动力学曲线.L-丙氨酸的CP动力学曲线如图3(a)~(d)所示.与ramp-CP、LGCP和multiCP相比,MLGCP-1所采集的L-丙氨酸各基团的归一化积分面积受tp影响更小.通过对谱峰积分值的计算,可得到归一化积分面积比值的实验值较其理论值的百分误差.L-丙氨酸的百分误差受tp的影响如图3(e)~(h)所示.ramp-CP和LGCP在所测试的tp条件下均不可定量;对于multiCP,仅当tp为0.9~1.2 ms时,对应的谱峰归一化积分面积的比值较理论值的百分误差小于5%;对于MLGCP-1,L-丙氨酸三个基团的动力学曲线在tp为0.8~2.0 ms范围内几乎重合,且实验百分误差均小于5%.L-缬氨酸实验数据表现出相同的趋势.如图4所示,随着multiCP方案中LGCP技术的引入,实验方法对tp的宽容度提升.对于L-缬氨酸,ramp-CP和LGCP无法实现定量检测;而multiCP仅当tp为1.0~1.3 ms时,定量结果的百分误差小于5%;与之相比,MLGCP-1可定量的tp范围更宽,在0.7~2.0 ms范围内实验百分误差均小于5%.由上可见,与multiCP相比,MLGCP-1可定量的实验参数tp范围更宽,该方法对tp的宽容度更高.
图3
图3
L-丙氨酸粉末样品中CH3、CH和CO三种基团的1H→13C交叉极化动力学曲线图,使用的技术分别为(a) ramp-CP、 (b) LGCP、(c) multiCP和(d) MLGCP-1;L-丙氨酸的归一化积分比例较理论值的百分误差,使用的技术分别为(e) ramp-CP、(f) LGCP、(g) multiCP和(h) MLGCP-1.红色背景区域实验百分误差小于5%
Fig. 3
The cross polarization 1H→13C dynamic curves of CH3, CH and CO groups in L-alanine by using the schemes of (a) ramp-CP, (b) LGCP, (c) multiCP and (d) MLGCP-1; The percentage errors of L-alanine were calculated according to the normalized peak integrals, by using the schemes of (e) ramp-CP, (f) LGCP, (g) multiCP and (h) MLGCP-1. The red background highlights the regions with percentage errors less than 5%
图4
图4
L-缬氨酸粉末样品中五种基团的1H→13C交叉极化动力学曲线图,使用的技术分别为(a) ramp-CP、(b) LGCP、(c) multiCP和(d) MLGCP-1.L-缬氨酸的归一化积分比例较理论值的百分误差,使用的技术分别为(e) ramp-CP、(f) LGCP、(g) multiCP和(h) MLGCP-1.红色背景区域实验百分误差小于5%
Fig. 4
The cross polarization 1H→13C dynamic curves of the five groups in L-valine by using the schemes of (a) ramp-CP, (b) LGCP, (c) multiCP and (d) MLGCP-1; The percentage errors of L-valine were calculated according to the normalized peak integrals, by using the schemes of (e) ramp-CP, (f) LGCP, (g) multiCP and (h) MLGCP-1. The red background highlights the regions with percentage errors less than 5%
2.2 实验参数的设置对MLGCP-1测量结果的影响
为了更系统地探讨MLGCP-1测试结果的准确度对弛豫恢复时间(td)、tp以及交叉极化次数(n)的依赖性,并与近期工作中multiCP的实验数据进行对比,本文采集了L-丙氨酸中CO、CH、CH3积分值随tp、td和tp、n变化的数据,以归一化积分值投影图和实验百分误差投影图方式显示,并用不同的颜色表示不同的归一化积分值或百分误差值[26].
首先,当n = 4时,通过逐次改变MLGCP-1中tp和td两个实验参数(tp:0~2 ms;td:0.5~3 s),来研究该组参数对积分值和实验准确度的影响.与multiCP [图5(e)~(g)]相比,MLGCP-1实验结果[图5(a)~(c)]中红色区域的面积增加,说明在所选参数范围内,谱峰积分值接近最高值的MLGCP-1谱图更多.为了评估在各个实验参数条件下,使用MLGCP-1和multiCP方法获得的L-丙氨酸基团比例的准确性,实验计算了定量结果的实验百分误差,对应的误差投影图如图5(d)和5(h)所示.其中,深紫色区域的误差值小于5%.依据误差投影图的颜色信息可知,当td为0.5~1.4 s时,MLGCP-1可定量的tp范围随着td而增大;且在td > 1.4 s、tp > 0.7 ms的实验参数范围内,MLGCP-1实验误差均小于5%;与multiCP相比,紫色区域的面积大大增加.在CP实验中,足量的1H磁化矢量恢复到热力学平衡态是进行下一次CP的前提.当td过短时,为下一次CP所准备的1H初始磁化矢量过小,即使后续开展多次1H→13C CP,仍很难使13C信号达到持续增强并趋于一致;而当td满足1~2
图5
图5
使用MLGCP-1方法采集并绘制的L-丙氨酸中(a) CO、(b) CH、(c) CH3基团归一化积分值随实验参数tp、td变化的二维投影图,以及(d)相应实验参数条件下的百分误差投影图.使用multiCP方法采集并绘制的L-丙氨酸的(e) CO、(f) CH、(g) CH3基团归一化积分值随实验参数tp、td变化的二维投影图,以及(h)相应实验参数条件下实验结果的百分误差投影图
Fig. 5
The two-dimensional projection diagrams of normalized integrals of (a) CO, (b) CH, (c) CH3 in L-alanine using MLGCP-1 method, the normalized integrals was modulated by the experimental parameters tp and td. (d) The two-dimensional projection of the percentage errors under corresponding experimental parameters. multiCP method was employed for comparison. The corresponding diagrams were plotted in (e)~(h)
然后,将td固定为2 s,通过逐次改变tp和n两个实验参数,来进一步探讨MLGCP-1定量性对交叉极化次数n的依赖性,所绘制的积分值投影图及对应的误差投影图如图6所示.通过对该组数据的分析发现,MLGCP-1可定量的tp范围受n的影响规律与multiCP相似.即随着n的增大,可定量的tp范围逐渐增宽.当n ≥ 3时,MLGCP-1方法具有可用于定量的tp范围如下:n = 3时,百分误差值小于5%的tp范围为1.2~1.8 ms;n = 4时,百分误差值小于5%的tp范围为0.8~2.0 ms;n = 6时,可定量tp范围增至0.5~2.0 ms. 而对于multiCP,n = 3时,百分误差值小于5%的tp范围为1.3~1.4 ms;n = 4时,百分误差值小于5%的tp范围为0.9~1.2 ms;n = 6时,可定量tp范围为0.6~1.0 ms.
图6
图6
使用MLGCP-1方法采集并绘制的L-丙氨酸中(a) CO、(b) CH、(c) CH3基团的归一化积分值随实验参数tp、n变化的二维投影图,以及(d)相应实验参数条件下实验结果的百分误差投影图.使用multiCP方法采集并绘制的L-丙氨酸的 (e) CO、(f) CH、(g) CH3基团的归一化积分值随实验参数tp、n变化的二维投影图,以及(h)相应实验参数条件下实验结果的百分误差投影图
Fig. 6
The two-dimensional projection diagrams of normalized integrals of (a) CO, (b) CH, (c) CH3 in L-alanine using MLGCP-1 method. The normalized integrals was modulated by the experimental parameters tp and n. (d) The two-dimensional projection of the percentage errors under corresponding experimental parameters. multiCP method was employed for comparison. The corresponding diagrams were plotted in (e)~(h)
2.3 样品体系TCHT1ρH值对MLGCP-1定量结果的影响
近期的研究[26]发现,在满足td和n的设置条件下,multiCP实验参数tp的设置依赖于样品的属性参数TCH和
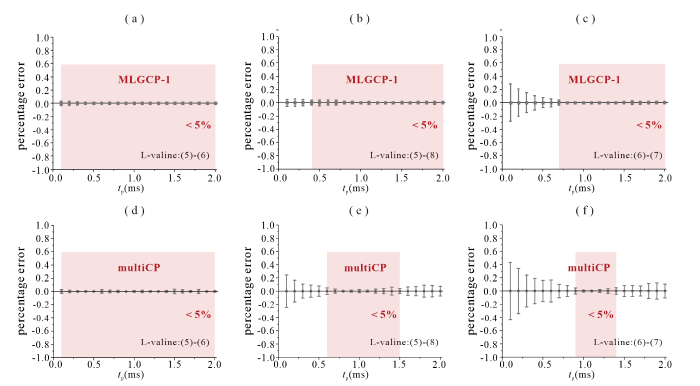
为了与multiCP方法对比,探讨MLGCP-1受样品属性的影响规律,本文选取L-缬氨酸作为模型样品,首先评估各个基团间TCH差异度对MLGCP-1实验参数tp设置的影响.L-缬氨酸分子中含有5种13C基团,如图2(b)所示.ramp-CP条件下相同种类基团之间的TCH值相近,例如同为CH基团的碳5、6;而不同种类基团之间的TCH值相差较大,例如分别为CO、CH和CH3的碳7、5和8.实验选取了三组13C进行研究,分别是5和6、5和8、6和7,ramp-CP条件下对应的TCH差异度依次为8%、76%、89%.MLGCP-1实验的百分误差如图7(a)~(c)所示,multiCP实验的百分误差如图7(d)~(f)所示.对于5和6两个基团,MLGCP-1定量结果的百分误差始终小于5%,与multiCP结果基本一致;对于TCH差异度较大的5和8、 6和7,MLGCP-1可定量的tp范围分别为0.4~2.0 ms、0.7~2.0 ms,而multiCP可定量的tp范围分别为0.6~1.5 ms、0.9~1.4 ms.可见,MLGCP-1方法中tp参数受TCH差异度的影响趋势与multiCP相同,即TCH差异度越大,tp范围越小.但对于相同的样品体系,MLGCP-1方法可定量的tp范围更宽,对样品的属性表现出更高的宽容度.
图7
图7
MLGCP-1和multiCP可定量的tp范围受L-缬氨酸中基团TCH差异度的影响规律.(a) MLGCP-1实验百分误差图,测量体系的TCH差异度为8%;(b) MLGCP-1实验百分误差图,测量体系的TCH差异度为76%;(c) MLGCP-1实验百分误差图,测量体系的TCH差异度为89%;(d) multiCP实验百分误差图,测量体系的TCH差异度为8%;(e) multiCP实验百分误差图,测量体系的TCH差异度为76%;(f) multiCP实验百分误差图,测量体系的TCH差异度为89%. TCH差异度均使用ramp-CP测得
Fig. 7
The impact of TCH difference in L-valine on the quantified range of tp. (a) MLGCP-1 percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 8%; (b) MLGCP-1 percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 76%; (c) MLGCP-1 percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 89%; (d) multiCP percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 8%; (e) multiCP percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 76%; (f) multiCP percentage errors, recorded on the system with TCH difference of 89%. TCH values were measured under ramp-CP condition
为了进一步探讨MLGCP-1对于共混体系组分含量测定的优势,本文选取L-缬氨酸和L-丙氨酸摩尔比分别为1:3、1:1、3:1的三种混合物作为模型样品,通过分析几组TCH差异度不同的基团的实验数据,并与multiCP方法的实验结果进行对比.如图8所示,L-缬氨酸和L-丙氨酸混合物的13C CP NMR谱图中,L-丙氨酸的C-2、3和L-缬氨酸的C-5、6所对应的谱峰没有重叠.基于此,实验选取三组基团用于计算组分含量,包括:1)L-丙氨酸的2号碳和L-缬氨酸的5号碳(记为2/5);2)L-丙氨酸的2号碳和L-缬氨酸的6号碳(记为2/6);3)L-丙氨酸的3号碳和L-缬氨酸的6号碳(记为3/6).ramp-CP条件下三组基团TCH相对差异度分别为14%、21%、91%.并通过改变tp依次采集了tp为0.5 ms、1.0 ms、1.5 ms和2.0 ms的四组数据.MLGCP-1和multiCP测试结果的实验百分误差详见表2.表中百分误差大于5%的数据用下划线标记.通过对测试结果的分析可见,对于2/5体系,由于其TCH差异度较小,仅为14%,MLGCP-1和multiCP方法均可实现定量检测.对于TCH差异度较大的碳3/6体系,仅当两样品摩尔比为1:1和3:1且tp为0.5 ms、摩尔比为1:3且tp为0.5和2.0 ms时,MLGCP-1的实验百分误差大于5%,其余数据均小于5%.而multiCP方法对于2/6和3/6体系的定量条件均比较苛刻,且随着TCH差异度的增加,其可定量的tp范围越小;当使用3/6基团进行定量表征时,1:3样品无法定量,1:1和3:1样品仅当tp为1.0 ms时,multiCP的实验百分误差小于5%.上述数据说明,在对L-缬氨酸和/L-丙氨酸混合物进行组分测定时,MLGCP-1对样品属性和tp参数的宽容度均高于multiCP,其定量结果更可靠,实验可行性较高.
图8
图8
摩尔比为1:1的L-缬氨酸/L-丙氨酸混合物的13C CP谱图.谱峰归属序号参考图中分子化学结构示意图
Fig. 8
13C CP spectrum of L-valine/L-alanine mixture with molar ratio of 1:1. Peaks are assigned with labels with respect to the structural scheme
表2 使用multiCP和MLGCP-1方法获得的三种L-丙氨酸/L-缬氨酸混合物中组分含量的实验百分误差
Table 2
| 样品组分 | tp/ms | MLGCP-1百分误差/% | multiCP百分误差/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/5 | 2/6 | 3/6 | 2/5 | 2/6 | 3/6 | |||
| 1:3 | 0.5 | 1.29 | 0.94 | 14.4 | 4.54 | 4.40 | 18.2 | |
| 1.0 | 1.80 | 4.57 | 4.53 | 0.85 | 8.35 | 10.2 | ||
| 1.5 | 4.91 | 3.88 | 4.05 | 0.22 | 12.5 | 28.5 | ||
| 2.0 | 3.63 | 1.27 | 10.1 | 0.58 | 18.7 | 51.0 | ||
| 1:1 | 0.5 | 1.24 | 1.84 | 9.67 | 0.49 | 1.31 | 20.1 | |
| 1.0 | 1.33 | 1.40 | 3.16 | 1.14 | 2.14 | 3.96 | ||
| 1.5 | 1.09 | 1.13 | 3.54 | 0.83 | 2.63 | 12.7 | ||
| 2.0 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 4.40 | 3.71 | 0.70 | 23.1 | ||
| 3:1 | 0.5 | 0.72 | 2.09 | 6.99 | 2.31 | 0.46 | 11.9 | |
| 1.0 | 2.14 | 1.76 | 2.34 | 0.68 | 4.99 | 4.09 | ||
| 1.5 | 0.06 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 0.72 | 7.29 | 9.63 | ||
| 2.0 | 0.92 | 1.48 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 9.98 | 14.2 | ||
2.4 MLGCP-1的实验效率及参数设置
通过测试对比发现,以L-丙氨酸为模型样品,采用MLGCP-1方法进行13C谱采集时,扫描512次需100 min;而在相同的采样时间内,定量单脉冲实验方法仅扫描40次.对比相同实验时间内MLGCP-1和定量DP谱图的信噪比,发现MLGCP-1谱图较DP谱图的信噪比提升了7.3倍.由此推算,对于L-丙氨酸样品在获取相同信噪比定量谱图的前提下,MLGCP-1的实验时间为DP定量实验的1/53.
依据本工作研究,在应用MLGCP-1进行刚性体系的定量检测时,无须测量TCH和
3 结论
本工作对multiCP脉冲序列进行了改进,结合LGCP技术,提出了一种新型的MLGCP-1定量检测方法.通过对L-丙氨酸和L-缬氨酸的检测,发现LGCP可以延长样品体系的
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Advanced solid-state NMR spectroscopy of natural organic matter
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.11.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Morphology and phase characteristics of high-density polyethylene probed by NMR spin diffusion and second moment analysis
[J].DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3935 URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative determination of phase content in multiphase polymers by combining spin-diffusion and CP-MAS NMR
[J].DOI:10.1021/ma0707786 URL [本文引用: 1]
Accurate quantitative and maximum cross polarization via multiple ramped contacts
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2017.05.009 URL [本文引用: 1]
Relaxation compensated and intensity recovered dynamics of cross polarization in the frame of reciprocity relation
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2011.06.037 URL [本文引用: 1]
Breaking the T-1 constraint for quantitative measurement in magic angle spinning solid-state NMR Spectroscopy
[J].DOI:10.1021/ja909550f URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative cross-polarization NMR spectroscopy in uniformly C-13-labeled solids
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2006.01.105 URL [本文引用: 1]
Time-saving and highly applicable quantitative method based on solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
[J].
DOI:10.1002/cjoc.v39.2
URL
[本文引用: 1]

设计了rCDPz脉冲序列, 结合使用ramp CP技术, 提出了rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>定量检测方法. 与QCP/QCP<sub>RC</sub>方法相比, rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>更适用于高速魔角旋转条件及较长的样品体系. 为了评估rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>方法的准确性, 选取丙氨酸、 组氨酸及二者的混合物作为检测样品, 分别测定了样品分子基团的相对比例及混合物的组分含量. 通过对DP, CP和rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>法测定结果进行比较发现, 与CP方法相比, rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>检测结果的准确度显著提高, 且准确度与传统的DP定量方法相当, 但实验时间大大缩减.
耗时短、通用性强的固体核磁共振交叉极化定量检测方法
[J].
DOI:10.1002/cjoc.v39.2
URL
[本文引用: 1]

设计了rCDPz脉冲序列, 结合使用ramp CP技术, 提出了rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>定量检测方法. 与QCP/QCP<sub>RC</sub>方法相比, rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>更适用于高速魔角旋转条件及较长的样品体系. 为了评估rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>方法的准确性, 选取丙氨酸、 组氨酸及二者的混合物作为检测样品, 分别测定了样品分子基团的相对比例及混合物的组分含量. 通过对DP, CP和rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>法测定结果进行比较发现, 与CP方法相比, rQCPz/rQCPz<sup>RC</sup>检测结果的准确度显著提高, 且准确度与传统的DP定量方法相当, 但实验时间大大缩减.
Quantification of cross polarization with relaxation compensated reciprocity relation in NMR
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2008.07.026 URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative solid-state C-13 NMR with signal enhancement by multiple cross polarization
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2013.11.009 URL [本文引用: 3]
Composite-pulse and partially dipolar dephased multiCP for improved quantitative solid-state C-13 NMR
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2017.10.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
Towards uniform enhancement in solid-state cross polarization magic angle spinning NMR: A scheme incorporating cross polarization with rotational resonance
[J].DOI:10.1063/1.2206787 URL [本文引用: 1]
Successive polarization under mismatched Hartmann-Hahn condition
[J].DOI:10.1016/0009-2614(90)87056-W URL [本文引用: 1]
Chemical shift powder spectra enhanced by multiple-contact cross-polarization under slow magic-angle spinning
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2012.12.006
PMID:23314257
[本文引用: 1]

A simple multiple-contact cross-polarization (CP) scheme is applied to a powder sample of ferrocene and β-calcium formate under static and magic-angle spinning (MAS) conditions. The method is described analytically through the density matrix formalism. We show that multiple equilibrations-re-equilibrations with the proton spin bath improves the polarization transfer efficiency at short contact times and provides higher signal enhancements than state-of-the art techniques such as adiabatic passage through the Hartmann-Hahn condition CP (APHH-CP) when MAS is applied. The resulting chemical shift powder spectra then are identical to the ones obtained by using ROtor-Directed Exchange of Orientations CP (APHH-RODEO-CP) with intensity gains of a factor 1.1-1.3.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Sensitivity enhancement by multiple-contact cross-polarization under magic-angle spinning
[J].
DOI:S1090-7807(17)30167-2
PMID:28662486
[本文引用: 1]

Multiple-contact cross-polarization (MC-CP) is applied to powder samples of ferrocene and l-alanine under magic-angle spinning (MAS) conditions. The method is described analytically through the density matrix formalism. The combination of a two-step memory function approach and the Anderson-Weiss approximation is found to be particularly useful to derive approximate analytical solutions for single-contact Hartmann-Hahn CP (HHCP) and MC-CP dynamics under MAS. We show that the MC-CP sequence requiring no pulse-shape optimization yields higher polarizations at short contact times than optimized adiabatic passage through the HH condition CP (APHH-CP) when the MAS frequency is comparable to the heteronuclear dipolar coupling, i.e., when APHH-CP through a single sideband matching condition is impossible or difficult to perform. It is also shown that the MC-CP sideband HH conditions are generally much broader than for single-contact HHCP and that efficient polarization transfer at the centerband HH condition can be reintroduced by rotor-asynchronous multiple equilibrations-re-equilibrations with the proton spin bath. Boundary conditions for the successful use of the MC-CP experiment when relying on spin-lattice relaxation for repolarization are also examined.Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Quantitative C-13 MultiCP solid-state NMR as a tool for evaluation of cellulose crystallinity index measured directly inside sugarcane biomass
[J].DOI:10.1186/s13068-014-0179-6 URL [本文引用: 2]
Quantitative C-13 solid-state NMR spectra by multiple-contact cross-polarization for drug delivery: From active principles to excipients and drug carriers
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.xphs.2016.05.025 URL [本文引用: 1]
Exploring water-soluble organic aerosols structures in urban atmosphere using advanced solid-state C-13 NMR spectroscopy
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117503 URL [本文引用: 2]
Investigation into the effect of heteroatom content on kerogen structure using advanced C-13 solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
[J].DOI:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b01909 URL [本文引用: 2]
Distinct changes in composition of soil organic matter with length of cropping time in subsoils of a Phaeozem and Chernozem
[J].DOI:10.1111/ejss.2018.69.issue-5 URL [本文引用: 2]
Molecular characterization of Dachengzi oil shale kerogen by multidimensional solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121215 URL [本文引用: 2]
Experimental set-up and application research of solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance Multiple-CP technique
[J].
DOI:10.7503/cjcu20200698
[本文引用: 4]

固体核磁共振Multiple-CP定量技术可实现对不同体系、 不同定量信息的检测. 然而, Multiple-CP对样品属性的宽容度较低, 其中有关样品属性的核磁共振参数包括氢的自旋晶格弛豫时间(T<sub>1,H</sub>)、 交叉弛豫时 间(T<sub>CH</sub>)和自旋锁定场下氢的自旋晶格弛豫时间(T1ρ?H)等. 因而需要系统地掌握Multiple-CP各种实验参数与样品上述特性参数之间的关系, 从而确定Multiple-CP技术可适用的体系范围以及最优的实验参数范围. 基于此, 首先以L-丙氨酸为模型样品, 探讨在Multiple-CP实验中弛豫恢复时间(t<sub>d</sub>)、 交叉极化接触时间(t<sub>p</sub>)和交叉极化次数(n) 3种实验参数对分子中基团比例测量结果的影响规律. 并以L-缬氨酸、 L-丙氨酸/L-缬氨酸的混合物为模型样品, 探讨样品特性参数的差异性对Multiple-CP实验参数范围的影响. 实验结果表明, t<sub>p</sub>受T<sub>CH</sub>和?T1ρ?H的影响较大. 对于纯净物或均相体系, T<sub>CH</sub>是影响t<sub>p</sub>参数设置的关键. 依据实验数据发现, 当样品中各基团T<sub>CH</sub>差异度小于8%时, 实验对t<sub>p</sub>的宽容度较高; 对于混合物体系, 需同时考虑混合物中组分?T1ρ?H?差异度的影响. 当组分?T1ρ?H?差异度为32%、 各基团T<sub>CH</sub>差异度为21%时, Multiple-CP对t<sub>p</sub>的宽容度高, 可在较宽的参数范围内实现定量检测. 而当T<sub>CH</sub>差异度较大时, 获取定量结果时t<sub>p</sub>的参数范围较小, 实验条件较苛刻. Multiple-CP定量方法更适用于T<sub>CH</sub>和?T1ρ?H?差异度较小的样品体系的定量研究. 通过研究样品T<sub>CH</sub>和?T1ρ?H?对实验参数的影响, 总结了Multiple-CP方法所适用的样品体系特征, 为使用Multiple-CP进行定量检测提供可参考的参数设置方案.
固体核磁共振Multiple-CP定量技术的参数优化与应用研究
[J].
DOI:10.7503/cjcu20200698
[本文引用: 4]

固体核磁共振Multiple-CP定量技术可实现对不同体系、 不同定量信息的检测. 然而, Multiple-CP对样品属性的宽容度较低, 其中有关样品属性的核磁共振参数包括氢的自旋晶格弛豫时间(T<sub>1,H</sub>)、 交叉弛豫时 间(T<sub>CH</sub>)和自旋锁定场下氢的自旋晶格弛豫时间(T1ρ?H)等. 因而需要系统地掌握Multiple-CP各种实验参数与样品上述特性参数之间的关系, 从而确定Multiple-CP技术可适用的体系范围以及最优的实验参数范围. 基于此, 首先以L-丙氨酸为模型样品, 探讨在Multiple-CP实验中弛豫恢复时间(t<sub>d</sub>)、 交叉极化接触时间(t<sub>p</sub>)和交叉极化次数(n) 3种实验参数对分子中基团比例测量结果的影响规律. 并以L-缬氨酸、 L-丙氨酸/L-缬氨酸的混合物为模型样品, 探讨样品特性参数的差异性对Multiple-CP实验参数范围的影响. 实验结果表明, t<sub>p</sub>受T<sub>CH</sub>和?T1ρ?H的影响较大. 对于纯净物或均相体系, T<sub>CH</sub>是影响t<sub>p</sub>参数设置的关键. 依据实验数据发现, 当样品中各基团T<sub>CH</sub>差异度小于8%时, 实验对t<sub>p</sub>的宽容度较高; 对于混合物体系, 需同时考虑混合物中组分?T1ρ?H?差异度的影响. 当组分?T1ρ?H?差异度为32%、 各基团T<sub>CH</sub>差异度为21%时, Multiple-CP对t<sub>p</sub>的宽容度高, 可在较宽的参数范围内实现定量检测. 而当T<sub>CH</sub>差异度较大时, 获取定量结果时t<sub>p</sub>的参数范围较小, 实验条件较苛刻. Multiple-CP定量方法更适用于T<sub>CH</sub>和?T1ρ?H?差异度较小的样品体系的定量研究. 通过研究样品T<sub>CH</sub>和?T1ρ?H?对实验参数的影响, 总结了Multiple-CP方法所适用的样品体系特征, 为使用Multiple-CP进行定量检测提供可参考的参数设置方案.
Nuclear magnetic resonance line narrowing by a rotating RF field
[J].DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.11.255 URL [本文引用: 2]
Nuclear-magnetic-resonance line narrowing by a Rotating RF field
[J].
Rotational resonance NMR of biological membranes
[J].DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0534 URL [本文引用: 1]
Heteronuclear decoupling in rotating solids
[J].DOI:10.1063/1.470372 URL [本文引用: 1]
Chemical shift referencing in MAS solid state NMR
[J].Solid state 13C magic angle spinning (MAS) NMR spectra are typically referenced externally using a probe which does not incorporate a field frequency lock. Solution NMR shifts on the other hand are more often determined with respect to an internal reference and using a deuterium based field frequency lock. Further differences arise in solution NMR of proteins and nucleic acids where both 13C and 1H shifts are referenced by recording the frequency of the 1H resonance of DSS (sodium salt of 2,2-dimethyl-2-silapentane-5-sulphonic acid) instead of TMS (tetramethylsilane). In this note we investigate the difficulties in relating shifts measured relative to TMS and DSS by these various approaches in solution and solids NMR, and calibrate adamantane as an external 13C standard for solids NMR. We find that external chemical shift referencing of magic angle spinning spectra is typically quite reproducible and accurate, with better than +/-0.03 ppm accuracy being straight forward to achieve. Solid state and liquid phase NMR shifts obtained by magic angle spinning with external referencing agree with those measured using typical solution NMR hardware with the sample tube aligned with the applied field as long as magnetic susceptibility corrections and solvent shifts are taken into account. The DSS and TMS reference scales for 13C and 1H are related accurately using MAS NMR. Large solvent shifts for the 13C resonance in TMS in either deuterochloroform or methanol are observed, being +0.71 ppm and -0.74 ppm from external TMS, respectively. The ratio of the 13C resonance frequencies for the two carbons in solid adamantane to the 1H resonance of TMS is reported.
Polarization transfer dynamics in Lee-Goldburg cross polarization nuclear magnetic resonance experiments on rotating solids
[J].DOI:10.1063/1.481281 URL [本文引用: 1]
Towards quantitative measurements in solid-state CPMAS NMR: A Lee-Goldburg frequency modulated cross-polarization scheme
[J].A new scheme combining a Lee-Goldburg (LG) sequence with frequency modulation is proposed for cross-polarization (LG-FMCP) in solid-state magic-angle-spinning nuclear magnetic resonance. During the CP contact time, the (1)H magnetization is spin-locked along the magic angle by the LG sequence and the irradiation offset of the S spins (e.g., (15)N) is modulated sinusoidally with a constant RF amplitude. It is shown experimentally that the LG sequence significantly lengthens the proton spin-lattice relaxation time in the tilted rotating frame and that the frequency modulation shortens the cross-polarization time for non-protonated S spins. As a result of substantially increasing the difference in these relaxation rates, the non-protonated and protonated S spins can be more efficiently and more uniformly polarized with a relatively long CP contact time, making quantitative CP measurements possible. A sample of (15)N-delta 1-L-histidine lyophilized from a solution of pH 6.3 and a (15)N-delta 1-L-His labeled transmembrane helical peptide in hydrated lipid bilayers were used to illustrate the advantages of this scheme.
Quantitative solid-state 13C NMR with signal enhancement by multiple cross polarization
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2013.11.009 URL [本文引用: 1]