网络游戏障碍人群大脑功能网络rich club结构的改变
The Alteration of Rich Club in Brain Functional Network in Internet Gaming Disorder
网络游戏障碍人群大脑功能网络rich club结构的改变 |
| 邱先鑫,韩旭,汪耀,丁伟娜,孙雅文,周滟,雷皓,林富春 |
|
The Alteration of Rich Club in Brain Functional Network in Internet Gaming Disorder |
| Xian-xin QIU,Xu HAN,Yao WANG,Wei-na DING,Ya-wen SUN,Yan ZHOU,Hao LEI,Fu-chun LIN |
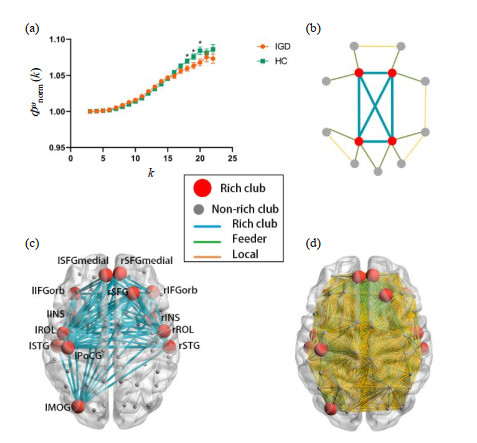
| 图1 (a)归一化的rich club加权系数(Φωnorm (k),均值±标准误)均大于1,说明rich club结构存在于网络游戏障碍(IGD)与健康对照(HC)中;IGD组的归一化的rich club加权系数在k=18, 19, 20时显著小于HC组(*,p值分别为0.04、0.03和0.03);(b) rich club连接、feeder连接和local连接的示意图;(c) HC组rich club脑区及平均rich club连接图,选择HC组平均度最高的前13个(15%)脑区为rich club脑区,本研究中的rich club脑区对应的k>9.68. 前缀l和r分别代表左侧与右侧,SFGmedial(内侧额上回),IFGorb(眶部额下回),INS(岛叶),ROL(中央沟盖),STG(颞上回),SFG(额上回),PoCG(中央后回),MOG(枕中回);(d) HC组平均的feeder连接和local连接 |
| Fig.1 (a) The normalized rich club coefficients (Φωnorm (k), mean±standard error) were lager than 1 in both IGD group and HC group. The Φωnorm (k) values in IGD group were significantly lower than that in HC group when k was 18, 19 and 20(*, p=0.04, 0.03 and 0.03); (b) A simplified example of the rich club, feeder and local connections; (c) rich club regions and rich club connections in HC group. The top 13 brain regions (15%) with the highest average degree in HC group were selected as rich club regions and the corresponding degree was k>9.68 in this study. The prefix l and r represent left and right, respectively. SFGmedial (the bilateral medial part of superior frontal gyrus), IFGorb (pars orbitalis of inferior frontal gyrus), INS (insula), ROL (Rolandic operculum), STG (superior temporal gyrus), SFG (superior frontal gyrus), PoCG (postcentral gyrus); MOG (middle occipital gyrus); (d)The feeder and local connections within group-averaged HCs |

|