结合局部一致性和低频振幅探究躯体症状障碍患者大脑自发性活动的改变
A Study on the Alteration of Spontaneous Brain Activity in Somatic Symptoms Disorder Combining Regional Homogeneity and Amplitude of Low-frequency Fluctuation
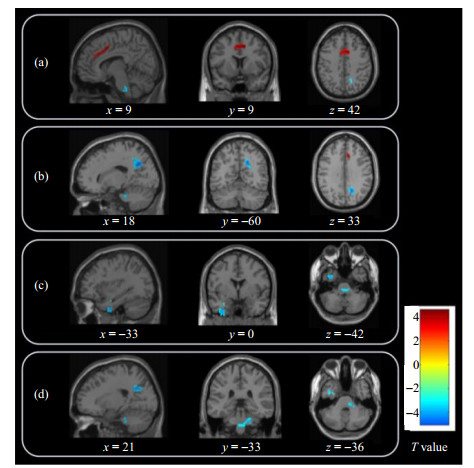
图1. 基于ReHo分析,SSD患者与健康对照组间有显著差异的脑区. 与健康对照相比,SSD患者在右侧扣带回中部[(a)图中红色标注]的ReHo值升高,在右侧楔前叶[(b)图中蓝色标注]、左侧颞下回延伸至左侧颞中回和左侧海马旁回[(c)图中蓝色标注]、右侧脑桥[(d)图中蓝色标注]的ReHo值降低
Fig.1. Significant differences in ReHo values between SSD patients and healthy controls. Compared with healthy controls, the ReHo values of SSD patients increased in the right middle cingulate gyrus [red in Fig.(a)], and decreased in the right precuneus [blue in Fig.(b)], the left inferior temporal gyrus extending to the left middle temporal gyrus and the left parahippocampal gyrus [blue in Fig.(c)], and the right pons [blue in Fig.(d)]