
- Jul. 13, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 209-223.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20233085cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20233085
• Review Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
FENG Yuan1,2,3,4,*( ), QIU Suhao1,2,3, YAN Fuhua4, YANG Guang-Zhong1,2,3
), QIU Suhao1,2,3, YAN Fuhua4, YANG Guang-Zhong1,2,3
Received:2023-10-07
Published:2024-06-05
Online:2023-11-21
Contact:
*Tel: 18625085336, E-mail: fengyuan@sjtu.edu.cn.
CLC Number:
FENG Yuan, QIU Suhao, YAN Fuhua, YANG Guang-Zhong. Magnetic Resonance Elastography and Its Application in Brain Diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 209-223.
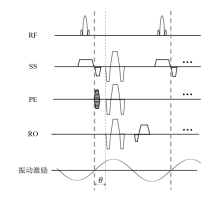
Fig. 1
A typical MRE sequence based on gradient-echo imaging. Motion-encoding gradients can be applied to either SS, PE, or RO directions based on conventional gradient-echo sequence. SS: slice selection; PE: phase encoding; RO: readout; θ: phase offset between the motion encoding gradient and the harmonic motion
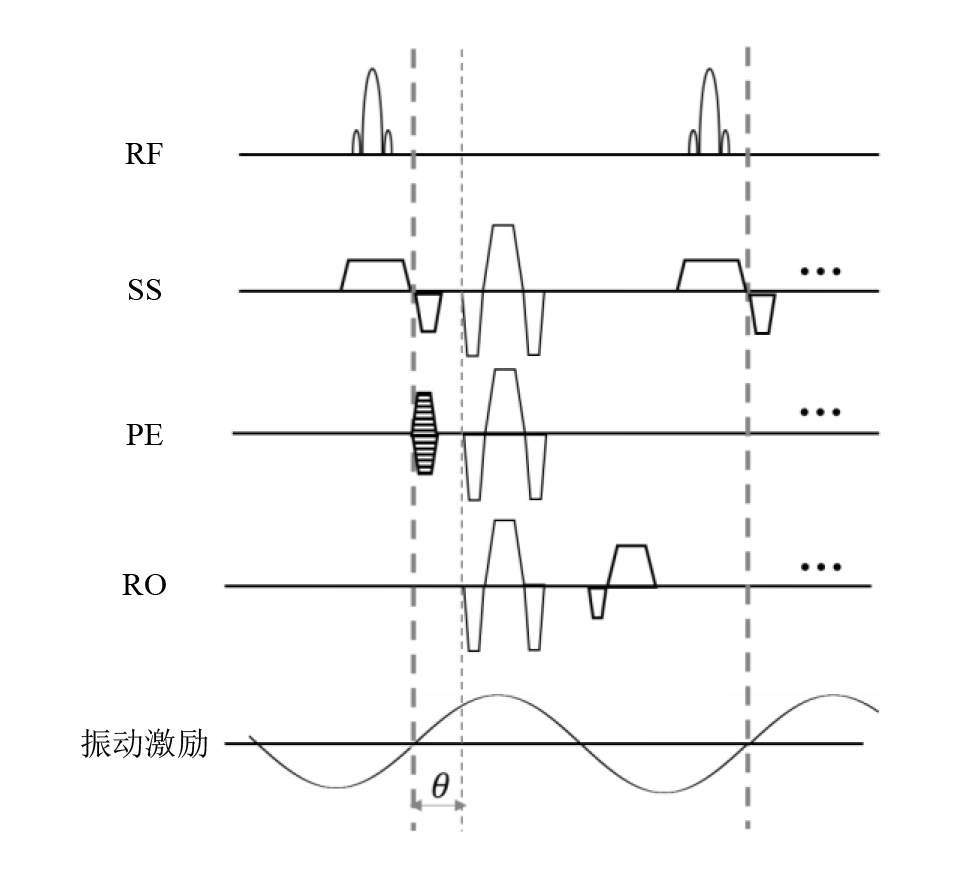
Fig. 2
Procedures of brain MRE. The wave actuation includes generating, amplifying, and transmitting shear waves to brain. The recording of waves include using MRE sequence implemented in the MR scanner for displacement encoding. The image processing steps include image reconstruction and inversion of biomechanical properties
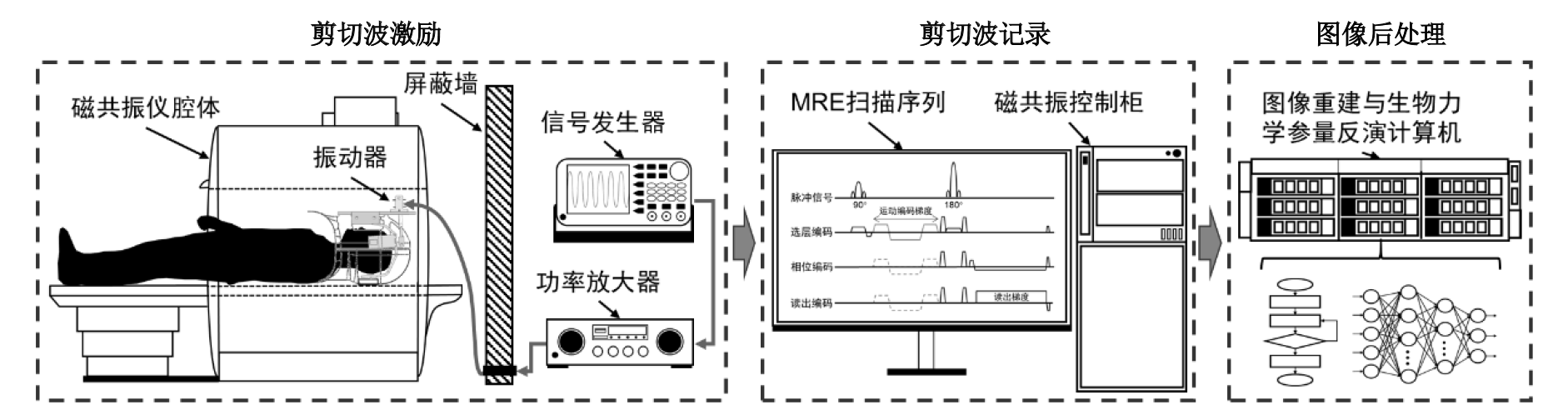
Table 1
A summary of MRE studies of brain tumor. All the measurements were carried out in 3 T scanners
| 文献 | 肿瘤类型 | 患者总数(分布) | 驱动器/序列 | 分辨率/mm3 | 反演算法 | 测量结果/kPa* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | 脑膜瘤(4)、血管外皮细胞瘤(1)、神经鞘瘤(1) | 6(2男/4女, 16~63岁) | 电磁式驱动 咬棒/GRE | 1.875×1.875×5 | - | 肿瘤组织剪切模量幅值与手术直观判断相符 | |
| [ | 脑膜瘤(13) | 13 | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 4×4×4 | DI | 肿瘤组织剪切模量幅值与手术直观判断相符 | |
| [ | 淋巴瘤(1)、胶质母细胞瘤(3)、间变性星形细 瘤(3)、神经胶质 瘤(4)、脑膜瘤(2)、脑转移瘤(3) | 16(5男/11女, 26~78岁) | 头部摇篮/ EPI | 3×3×3 | MDEV | |G*| = 0.893~2.131 | |
| [ | 脑膜瘤(14) | 14(4男/10女, 28~76岁) | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 肿瘤组织剪切模量幅值与手术直观判断相符 | |
| [ | 垂体大腺瘤(10) | 10(5男/5女, 22~78岁) | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 软肿瘤平均剪切模量幅值 1.38±0.36 (1.08~1.86) 硬肿瘤平均剪切模量幅值 1.94±0.26 (1.72~2.32) | |
| [ | 神经胶质瘤(18) | 18(12男/6女, 男性25~68岁, 女性28~40) | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 平均剪切模量幅值 2.2±0.7 (1.1~3.8) | |
| [ | 垂体腺瘤(38) | 38(22男/16女, 22~78岁) | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 平均剪切模量幅值 1.8 (1.1~3.7) | |
| [ | 脑膜瘤(13)、垂体腺瘤(11)、前庭神经鞘瘤(6)、胶质瘤(4) | 34(11男/23女, 31~77岁) | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3.75  | DI | 平均剪切模量幅值 脑膜瘤1.9±0.8,垂体腺瘤1.2±0.3,前庭神经鞘瘤2.0±0.4,胶质瘤1.5±0.2 | |
| [ | 脑膜瘤(18) | 18(4男/14女, 62.8±15.3岁) | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 1.875×1.875×3 | DI | 平均剪切模量幅值 3.12±1.23 | |
| [ | 脑膜瘤(88) | 88(35男/53女, 22~77岁) | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 平均剪切模量幅值 3.81±1.74 (1.57~12.6) | |
| [ | 胶质母细胞瘤(22) | 22(12男/10女, 64.5±15.1岁) | 头部摇篮/ SE-EPI | 2×2×2 | MEDV | |G*| = 0.85~1.83 (1.32±0.26) | |
| [ | 胶质母细胞瘤(11)、间变性星形细胞瘤(3)、脑膜瘤(7)、脑转移瘤(5)、脑内脓肿(1) | 27(12男/15女, 49~75岁) | 头部摇篮/ SE-EPI | 2×2×2 | MEDV | |G*| = 1.43±0.33 | |
| [ | 转移瘤(1)、胶质母细胞瘤(3)、星形细胞瘤(1)、脑膜瘤(3) | 8(3男/5女, 28~76岁) | 头部摇篮/ SE-EPI | 2×2×2 | MEDV | 脑膜瘤和星形细胞瘤 |G*| = 1.52±0.20; 胶质瘤和转移瘤 |G*| = 1.28±0.14 | |
| [ | 胶质母细胞瘤(10) | 10(5男/5女, 44~74岁) | 机械转子/ GRE | 3.1×3.1×3.1 | NLI | G° = 1.15~1.62; G = 0.55~0.80 | |
Table 2
A summary of MRE studies of neurodegenerative diseases. All the measurements were carried out in 3 T scanners
| 文献 | 疾病类型 (患者数量) | 患者年龄 (岁) | 驱动器/ 序列 | 分辨率/ mm3 | 反演算法 | 测量结果/kPa* | 所测量参量显著变化 的区域 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | 遗忘型轻度认知 障碍(20) | 23~81 | 气动枕/ 3D spiral | 1.25×1.25×1.25 | NLI | 对照组:2.84±0.28 遗忘型轻度认知障碍: 2.63±0.32 | 阿蒙尼角1-2,齿状回-阿蒙尼角3 |
| [ | 阿尔茨海默症(7) | 76~94 | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 4×4×2.5 | DI | CN-: 2.37 (2.17~2.62); CN+: 2.32 (2.18~2.67); AD: 2.20 (1.96~2.29) | 全脑 |
| [ | 阿尔茨海默症(8) | - | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 对照组:2.51±0.09 疾病组:2.40±0.09 | 额叶,颞叶以及一个复合区域(额叶、顶叶和颞叶,不包括中央前回和中央后回) |
| [ | 阿尔茨海默症(8) 路易体痴呆(13) 额颞叶痴呆(5) | 78~88 55~79 54~65 | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | NLI | 对照组:2.81±0.22 阿尔茨海默症:2.35±0.26 路易体痴呆:2.84±0.30 额颞叶痴呆:2.30±0.20 | 阿尔茨海默症:额叶、颞叶、扣带回、辅助运动区、楔前叶和眶前区 路易体痴呆:楔前叶 额颞叶痴呆:顶叶、额叶、颞叶、中央前叶、枕盖、岛叶、楔前叶、眶前叶、初级视觉区、扣带回和枕叶 |
| [ | 阿尔茨海默症(21) | 67~80 | 头部摇篮/ SE-EPI | 1.9×1.9×1.9 | MDEV | 对照组:1.54±0.13 阿尔茨海默症:1.39±0.16 | 海马区 |
| [ | 阿尔茨海默症(12) | 70~87 | 气动枕/ 3D spiral | 1.6×1.6×1.6 | NLI | 对照组:2.50±0.05 阿尔茨海默症:2.25±0.05 | 白质、皮质灰质(颞中上回和楔前叶) |
| [ | 帕金森症(17) 进行性核上性麻痹 (20) | 49~78 62~82 | 头部摇篮/ SE-EPI | 2×2×2 | MDEV | 对照组:1.04±0.08 帕金森症:0.96±0.065 进行性核上性麻痹: 0.95±0.078 | 帕金森症:额叶和中脑区域 进行性核上性麻痹:额叶和中脑区域 |
| [ | 肌萎缩侧索硬化 症(14) | 57±12 | 头部摇篮/ SE-EPI | 2×2×2 | TI | C33: 27.63±2.05 (50 Hz), 40.39±3.68 (60 Hz); C44: 4.21±0.06 (50 Hz), 4.68±0.07 (60 Hz); C66: 4.89±0.09 (50 Hz), 5.35±0.13 (60 Hz) | 皮质脊髓束 |
| [ | 行为性额颞叶痴呆 (5) | 55~66 | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 对照组:2.77(中位数) 疾病组:2.57(中位数) | 额叶和颞叶 |
| [ | 阿尔茨海默症(8) 路易体痴呆(5) 额颞叶痴呆(5) 常压脑积水(20) | 78~87 63~76 54~65 60~86 | 气动枕/ SE-EPI | 3×3×3 | DI | 对照组:2.44±0.08 阿尔茨海默症:2.32±0.09 路易体痴呆:2.43±0.11 额颞叶痴呆:2.28±0.10 常压脑积水:2.46 ±0.08 | 阿尔茨海默症:额叶、颞叶、顶叶和运动感知区 路易体痴呆:无 额颞叶痴呆:额叶和颞叶 常压脑积水:顶叶、枕叶和运动感知区 |
| [1] | CHAUDHURI O, COOPER-WHITE J, JANMEY P A, et al. Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour[J]. Nature, 2020, 584: 535-546. |
| [2] | BUDDAY S, OVAERT T C, HOLZAPFEL G A, et al. Fifty shades of brain: a review on the mechanical testing and modeling of brain tissue[J]. Arch of Computat Methods Eng, 2020,27:1187-1230. |
| [3] | BAYLY P V. Perspective: Challenges and opportunities in computational brain mechanics research: How can we use recent experimental data to improve models of brain mechanics?[J]. Brain Multiphysics, 2023, 4:100075. |
| [4] | GONG Z, YOU R, CHANG R C-C, et al. Viscoelastic response of neural cells governed by the deposition of amyloid-β peptides (Aβ)[J]. Appl Phys, 2016, 119:214701. |
| [5] | NIA H T, LIU H, SEANO G, et al. Solid stress and elastic energy as measures of tumour mechanopathology[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2017, 1:0004. |
| [6] | BUNEVICIUS A, SCHREGEL K, SINKUS R, et al. REVIEW: MR elastography of brain tumors[J]. Neuroimage: Clin, 2020, 25:102109. |
| [7] | SACK I. Magnetic resonance elastography from fundamental soft-tissue mechanics to diagnostic imaging[J]. Nat Rev Phys, 2023, 5(1): 25-42. |
| [8] | VENKATESH S K, EHMAN R L. Magnetic resonance elastography[M]. Springer, 2014. |
| [9] |
MANDUCA A, BAYLY P J, EHMAN R L, et al. MR elastography: Principles, guidelines, and terminology[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(5): 2377-2390.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28627 pmid: 33296103 |
| [10] |
FENG Y, ZHU M, QIU S, et al. A multi-purpose electromagnetic actuator for magnetic resonance elastography[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 51:29-34.
doi: S0730-725X(18)30057-2 pmid: 29679635 |
| [11] | FENG Y, CLAYTON E H, OKAMOTO R J, et al. A longitudinal magnetic resonance elastography study of murine brain tumors following radiation therapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2016, 61(16): 6121. |
| [12] |
YIN M, GLASER K J, TALWALKAR J A, et al. Hepatic MR elastography: clinical performance in a series of 1377 consecutive examinations[J]. Radiology, 2016, 278(1): 114-124.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015142141 pmid: 26162026 |
| [13] | ROMANI R, TANG W J, MAO Y, et al. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging for predicting the consistency of intracranial meningiomas[J]. Acta Neurochirurgica, 2014, 156(10): 1837-1845. |
| [14] | KRUSE S A, EHMAN R L. 2D approximation of 3D wave propagation in MR elastography of the brain[C]// Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2003, 111084. |
| [15] | ARANI A, MANDUCA A, EHMAN R L, et al. Harnessing brain waves: a review of brain magnetic resonance elastography for clinicians and scientists entering the field[J]. Br J Radiol, 2021, 94(1119): 20200265. |
| [16] |
MORAN P R. A flow velocity zeugmatographic interlace for NMR imaging in humans[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 1982, 1(4): 197-203.
pmid: 6927206 |
| [17] | SAHEBJAVAHER R S, FREW S, BYLINSKII A, et al. Prostate MR elastography with transperineal electromagnetic actuation and a fast fractionally encoded steady-state gradient echo sequence[J]. NMR in Biomed, 2014, 27(7): 784-794. |
| [18] | GUENTHNER C, RUNGE J H, SINKUS R, et al. Analysis and improvement of motion encoding in magnetic resonance elastography[J]. NMR in Biomed, 2018, 31(5). |
| [19] | WANG R, CHEN Y, LI R, et al. Fast magnetic resonance elastography with multiphase radial encoding and harmonic motion sparsity based reconstruction[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2022, 67(2): 25007. |
| [20] |
OLIPHANT T E, MANDUCA A, EHMAN R L, et al. Complex-valued stiffness reconstruction for magnetic resonance elastography by algebraic inversion of the differential equation[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2001, 45(2): 299-310.
pmid: 11180438 |
| [21] | ROMANO A J, SHIRRON J J, BUCARO J A. On the noninvasive determination of material parameters from a knowledge of elastic displacements theory and numerical simulation[J]. IEEE Trans Ultrason, Ferroelectr Freq Control, 1998, 45(3): 751-759. |
| [22] | PAPAZOGLOU S, HAMHABER U, BRAUN J, et al. Algebraic Helmholtz inversion in planar magnetic resonance elastography[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2008, 53(12): 3147. |
| [23] |
SINKUS R, TANTER M, XYDEAS T, et al. Viscoelastic shear properties of in vivo breast lesions measured by MR elastography[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2005, 23(2): 159-165.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2004.11.060 pmid: 15833607 |
| [24] |
VAN HOUTEN E E W, PAULSEN K D, MIGA M I, et al. An overlapping subzone technique for MR-based elastic property reconstruction[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1999, 42(4): 779-786.
doi: 10.1002/(sici)1522-2594(199910)42:4<779::aid-mrm21>3.0.co;2-z pmid: 10502768 |
| [25] |
MANDUCA A, OLIPHANT T E, DRESNER M A, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography: Non-invasive mapping of tissue elasticity[J]. Med Image Anal, 2001, 5(4): 237-254.
pmid: 11731304 |
| [26] | KNUTSSON H, WESTIN C F, GRANLUND G. Local multiscale frequency and bandwidth estimation[C]// Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Image Processing, 1994, 31: 136-140. |
| [27] |
TZSCHÄTZSCH H, GUO J, DITTMANN F, et al. Tomoelastography by multifrequency wave number recovery from time-harmonic propagating shear waves[J]. Med Image Anal, 2016, 30: 1-10.
doi: S1361-8415(16)00002-5 pmid: 26845371 |
| [28] | MCGARRY M D J, VAN HOUTEN E, GUERTLER C, et al. A heterogenous, time harmonic, nearly incompressible transverse isotropic finite element brain simulation platform for MR elastography[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2021, 66(5): 055029. |
| [29] | HOU Z, OKAMOTO R J, BAYLY P V. Shear wave propagation and estimation of material parameters in a nonlinear, fibrous material[J]. J Biomech Eng, 2020, 142(5): 051010. |
| [30] |
SCHMIDT J L, TWETEN D J, BENEGAL A N, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography of slow and fast shear waves illuminates differences in shear and tensile moduli in anisotropic tissue[J]. J Biomech, 2016, 49(7): 1042-1049.
doi: S0021-9290(16)30159-2 pmid: 26920505 |
| [31] |
HISCOX L V, JOHNSON C L, MCGARRY M D J, et al. High-resolution magnetic resonance elastography reveals differences in subcortical gray matter viscoelasticity between young and healthy older adults[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2018, 65: 158-167.
doi: S0197-4580(18)30018-6 pmid: 29494862 |
| [32] |
MCGARRY M D J, VAN HOUTEN E E W. Use of a Rayleigh damping model in elastography[J]. Med Biol Eng Comput, 2008, 46(8): 759-766.
doi: 10.1007/s11517-008-0356-5 pmid: 18521645 |
| [33] |
SCOTT J M, PAVULURI K, TRZASKO J D, et al. Impact of material homogeneity assumption on cortical stiffness estimates by MR elastography[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 88(2): 916-929.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29226 pmid: 35381121 |
| [34] | QIU S, HE Z, WANG R, et al. An electromagnetic actuator for brain magnetic resonance elastography with high frequency accuracy[J]. NMR Biomed, 2021, 34(12): e4592. |
| [35] | STREITBERGER K-J, LILAJ L, SCHRANK F, et al. How tissue fluidity influences brain tumor progression[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2020, 117(1): 128-134. |
| [36] | YEUNG J, JUGÉ L, HATT A, et al. Paediatric brain tissue properties measured with magnetic resonance elastography[J]. Biomech Model Mechanobiol, 2019, 18(5): 1497-1505. |
| [37] |
SVENSSON S F, DE ARCOS J, DARWISH O I, et al. Robustness of MR elastography in the healthy brain: repeatability, reliability, and effect of different reconstruction methods[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2021, 53(5): 1510-1521.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.27475 pmid: 33403750 |
| [38] |
YIN Z, LU X, COHEN COHEN S, et al. A new method for quantification and 3D visualization of brain tumor adhesion using slip interface imaging in patients with meningiomas[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31:5554-5564.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07918-6 pmid: 33852045 |
| [39] |
MURPHY M C, HUSTON III J, JACK JR C R, et al. Decreased brain stiffness in Alzheimer's disease determined by magnetic resonance elastography[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2011, 34(3): 494-498.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.22707 pmid: 21751286 |
| [40] |
SACK I, BEIERBACH B, HAMHABER U, et al. Non-invasive measurement of brain viscoelasticity using magnetic resonance elastography[J]. NMR Biomed, 2008, 21(3): 265-271.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.1189 pmid: 17614101 |
| [41] |
FEHLNER A, PAPAZOGLOU S, MCGARRY M D, et al. Cerebral multifrequency MR elastography by remote excitation of intracranial shear waves[J]. NMR Biomed, 2015, 28(11): 1426-1432.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3388 pmid: 26373228 |
| [42] | HISCOX L V, JOHNSON C L, BARNHILL E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of the human brain: technique, findings and clinical applications[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2016, 61(24): R401-R437. |
| [43] | FENG Y, MURPHY M C, HOJO E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography in the study of neurodegenerative diseases[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2024, 59: 82-96. |
| [44] |
JOHNSON C L, MCGARRY M D J, GHARIBANS A A, et al. Local mechanical properties of white matter structures in the human brain[J]. NeuroImage, 2013, 79: 145-152.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.089 pmid: 23644001 |
| [45] | LV H, KURT M, ZENG N, et al. MR elastography frequency-dependent and independent parameters demonstrate accelerated decrease of brain stiffness in elder subjects[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(12): 6614-6623. |
| [46] |
XU L, LIN Y, HAN J C, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography of brain tumors: Preliminary results[J]. Acta Radiol, 2007, 48(3): 327-330.
pmid: 17453505 |
| [47] |
MURPHY M C, HUSTON J, GLASER K J, et al. Preoperative assessment of meningioma stiffness using magnetic resonance elastography[J]. J Neurosurg, 2013, 118(3): 643-648.
doi: 10.3171/2012.9.JNS12519 pmid: 23082888 |
| [48] | SIMON M, GUO J, PAPAZOGLOU S, et al. Non-invasive characterization of intracranial tumors by magnetic resonance elastography[J]. New J Phys, 2013, 15: 085024. |
| [49] |
HUGHES J D, FATTAHI N, VAN GOMPEL J, et al. Higher-resolution magnetic resonance elastography in meningiomas to determine intratumoral consistency[J]. Neurosurgery, 2015, 77(4): 653-659.
doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000892 pmid: 26197204 |
| [50] |
HUGHES J D, FATTAHI N, VAN GOMPEL J, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography detects tumoral consistency in pituitary macroadenomas[J]. Pituitary, 2016, 19(3): 286-292.
doi: 10.1007/s11102-016-0706-5 pmid: 26782836 |
| [51] | PEPIN K M, MCGEE K P, ARANI A, et al. MR elastography analysis of glioma stiffness and IDH1-mutation status[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2018, 39(1): 31-36. |
| [52] | COHEN-COHEN S, HELAL A, YIN Z, et al. Predicting pituitary adenoma consistency with preoperative magnetic resonance elastography[J]. J Neurosurg, 2022, 136(5): 1356-1363. |
| [53] |
SAKAI N, TAKEHARA Y, YAMASHITA S, et al. Shear stiffness of 4 common intracranial tumors measured using MR elastography: comparison with intraoperative consistency grading[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2016, 37(10): 1851-1859.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4832 pmid: 27339950 |
| [54] |
TAKAMURA T, MOTOSUGI U, OGIWARA M, et al. Relationship between shear stiffness measured by MR elastography and perfusion metrics measured by perfusion CT of meningiomas[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2021, 42(7): 1216-1222.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7117 pmid: 33985944 |
| [55] | SHI Y, HUO Y, PAN C, et al. Use of magnetic resonance elastography to gauge meningioma intratumoral consistency and histotype[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2022, 36: 103173. |
| [56] | STREITBERGER K J, REISS-ZIMMERMANN M, FREIMANN F B, et al. High-resolution mechanical imaging of glioblastoma by multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e110588. |
| [57] | REISS-ZIMMERMANN M, STREITBERGER K J, SACK I, et al. High resolution imaging of viscoelastic properties of intracranial tumours by multi-frequency magnetic resonance elastography[J]. Clin Neuroradiol, 2015, 25(4): 371-378. |
| [58] |
SAUER F, FRITSCH A, GROSSER S, et al. Whole tissue and single cell mechanics are correlated in human brain tumors[J]. Soft Matter, 2021, 17(47): 10744-10752.
doi: 10.1039/d1sm01291f pmid: 34787626 |
| [59] | FLøGSTAD SVENSSON S, FUSTER-GARCIA E, LATYSHEVA A, et al. Decreased tissue stiffness in glioblastoma by MR elastography is associated with increased cerebral blood flow[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2022, 147: 110136. |
| [60] |
SACK I, BEIERBACH B, WUERFEL J, et al. The impact of aging and gender on brain viscoelasticity[J]. NeuroImage, 2009, 46(3): 652-657.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.040 pmid: 19281851 |
| [61] |
ARANI A, MURPHY M C, GLASER K J, et al. Measuring the effects of aging and sex on regional brain stiffness with MR elastography in healthy older adults[J]. NeuroImage, 2015, 111: 59-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.016 pmid: 25698157 |
| [62] | DELGORIO P L, HISCOX L V, DAUGHERTY A M, et al. Effect of aging on the viscoelastic properties of hippocampal subfields assessed with high-resolution MR elastography[J]. Cerebral Cortex, 2021, 31(6): 2799-2811. |
| [63] | DELGORIO P L, HISCOX L V, MCILVAIN G, et al. Hippocampal subfield viscoelasticity in amnestic mild cognitive impairment evaluated with MR elastography[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2023, 37: 103327. |
| [64] |
MURPHY M C, HUSTON J, JACK C R, et al. Decreased brain stiffness in Alzheimer's disease determined by magnetic resonance elastography[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2011, 34(3): 494-498.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.22707 pmid: 21751286 |
| [65] | MURPHY M C, JONES D T, JACK C R, et al. Regional brain stiffness changes across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2016, 10: 283-290. |
| [66] | PAVULURI K, SCOTT J M, HUSTON J, et al. Differential effect of dementia etiology on cortical stiffness as assessed by MR elastography[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2023, 37: 103328. |
| [67] | GERISCHER L M, FEHLNER A, KÖBE T, et al. Combining viscoelasticity, diffusivity and volume of the hippocampus for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2018, 18: 485-493. |
| [68] | HISCOX L V, JOHNSON C L, MCGARRY M D J, et al. Mechanical property alterations across the cerebral cortex due to Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Brain Communications, 2020, 2(1). |
| [69] | LIPP A, SKOWRONEK C, FEHLNER A, et al. Progressive supranuclear palsy and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease are associated with local reduction of in vivo brain viscoelasticity[J]. European Radiology, 2018, 28(8): 3347-3354. |
| [70] |
ROMANO A, GUO J, PROKSCHA T, et al. In vivo waveguide elastography: Effects of neurodegeneration in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 72(6): 1755-1761.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25067 pmid: 24347290 |
| [71] |
HUSTON J 3rd, MURPHY M C, BOEVE B F, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography of frontotemporal dementia[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2016, 43(2): 474-478.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.24977 pmid: 26130216 |
| [72] |
ELSHEIKH M, ARANI A, PERRY A, et al. MR elastography demonstrates unique regional brain stiffness patterns in dementias[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2017, 209(2): 403-408.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.16.17455 pmid: 28570101 |
| [73] | LIANG Z P, LAUTERBUR P C. A generalized series approach to MR spectroscopic imaging[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 1991, 10(2): 132-137. |
| [74] | LIANG Z P, LAUTERBUR P C. An efficient method for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 1994, 13(4): 677-686. |
| [75] | LIANG Z P. Spatiotemporal Imaging with partially separable functions[C]// 2007 Joint Meeting of the 6th International Symposium on Noninvasive Functional Source Imaging of the Brain and Heart and the International Conference on Functional Biomedical Imaging, 2007: 181-182. |
| [76] |
MCILVAIN G, CERJANIC A M, CHRISTODOULOU A G, et al. OSCILLATE: A low-rank approach for accelerated magnetic resonance elastography[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 88(4): 1659-1672.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29308 pmid: 35649188 |
| [77] |
PENG X, SUI Y, TRZASKO J D, et al. Fast 3D MR elastography of the whole brain using spiral staircase: Data acquisition, image reconstruction, and joint deblurring[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 86(4): 2011-2024.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28855 pmid: 34096097 |
| [78] | SUI Y, ARANI A, TRZASKO J D, et al. TURBINE-MRE: A 3D hybrid radial-Cartesian EPI acquisition for MR elastography[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(2): 945-952. |
| [79] | LAN P S, GLASER K J, EHMAN R L, et al. Imaging brain function with simultaneous BOLD and viscoelasticity contrast: fMRI/fMRE[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 211: 116592. |
| [80] |
YIN Z, KEARNEY S P, MAGIN R L, et al. Concurrent 3D acquisition of diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance elastography displacement data (DTI-MRE): Theory and in vivo application[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2017, 77(1): 273-284.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26121 pmid: 26787007 |
| [81] | NGUYEN K D, BONNER B P, FOSTER A N, et al. Asynchronous magnetic resonance elastography: Shear wave speed reconstruction using noise correlation of incoherent waves[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 89(3): 990-1001. |
| [82] | ZORGANI A, SOUCHON R, DINH A-H, et al. Brain palpation from physiological vibrations using MRI[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2015, 112(42): 12917-12921. |
| [83] | HISCOX L V, MCGARRY M D J, SCHWARB H, et al. Standard-space atlas of the viscoelastic properties of the human brain[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2020, 41(18): 5282-5300. |
| [84] |
FENG Y, OKAMOTO R J, NAMANI R, et al. Measurements of mechanical anisotropy in brain tissue and implications for transversely isotropic material models of white matter[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2013, 23: 117-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.04.007 pmid: 23680651 |
| [85] |
FENG Y, LEE C-H, SUN L, et al. Characterizing white matter tissue in large strain via asymmetric indentation and inverse finite element modeling[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2017, 65: 490-501.
doi: S1751-6161(16)30326-5 pmid: 27665084 |
| [86] | JAMAL A, BERNARDINI A, DINI D. Microscale characterisation of the time-dependent mechanical behaviour of brain white matter[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2022, 125: 104917. |
| [87] |
MURPHY M C, COGSWELL P M, TRZASKO J D, et al. Identification of normal pressure hydrocephalus by disease-specific patterns of brain stiffness and damping ratio[J]. Invest Radiol, 2020, 55(4): 200-208.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000630 pmid: 32058331 |
| [88] |
SINKUS R, TANTER M, CATHELINE S, et al. Imaging anisotropic and viscous properties of breast tissue by magnetic resonance-elastography[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 53(2): 372-387.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.20355 pmid: 15678538 |
| [89] |
ROMANO A, SCHEEL M, HIRSCH S, et al. In vivo waveguide elastography of white matter tracts in the human brain[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012, 68(5): 1410-1422.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24141 pmid: 22252792 |
| [90] | MCGARRY M, VAN HOUTEN E, SOWINSKI D, et al. Mapping heterogenous anisotropic tissue mechanical properties with transverse isotropic nonlinear inversion MR elastography[J]. Med Image Anal, 2022, 78: 102432. |
| [91] | JYOTI D, MCGARRY M, CABAN-RIVERA D A, et al. Transversely-isotropic brain in vivo MR elastography with anisotropic damping[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2023, 141: 105744. |
| [92] | BABAEI B, FOVARGUE D, LLOYD R A, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography reconstruction for anisotropic tissues[J]. Med Image Anal, 2021, 74: 102212. |
| [93] |
KALRA P, RATERMAN B, MO X, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography of brain: Comparison between anisotropic and isotropic stiffness and its correlation to age[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 82(2): 671-679.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27757 pmid: 30957304 |
| [94] | HOU Z X, GUERTLER C A, OKAMOTO R J, et al. Estimation of the mechanical properties of a transversely isotropic material from shear wave fields via artificial neural networks[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2022, 126: 105046. |
| [95] |
LE BIHAN D, ICHIKAWA S, MOTOSUGI U. Diffusion and intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging-based virtual elastography: A hypothesis-generating study in the liver[J]. Radiology, 2017, 285(2): 609-619.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017170025 pmid: 28604279 |
| [96] | KROMREY M-L, LE BIHAN D, ICHIKAWA S, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI-based virtual elastography for the assessment of liver fibrosis[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(1): 127-135. |
| [97] |
LAGERSTRAND K, GAEDES N, ERIKSSON S, et al. Virtual magnetic resonance elastography has the feasibility to evaluate preoperative pituitary adenoma consistency[J]. Pituitary, 2021, 24(4): 530-541.
doi: 10.1007/s11102-021-01129-4 pmid: 33555485 |
| [98] | HU J, CHEN S, HUANG D, et al. Global mapping of live cell mechanical features using PeakForce QNM AFM[J]. Biophys Rep, 2020, 6: 9-18. |
| [99] | SHEN P, MA S Y, XU H Y, et al. A study of diagnostic performance of MR elastography in liver fibrosis with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Radidol, 2019, 53(8): 710-714. |
| 沈萍, 马盛元, 许华宇, 等. MR弹性成像对慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化的诊断价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2019, 53(8): 710-714. | |
| [100] | YUAN J, ZHAN S H. Application and research progress of magnetic resonance elastography in cancer[J]. Int J Radiat Med Nucl Med, 2010, 43(2): 171-175. |
| 袁杰, 詹松华. 磁共振弹性成像技术在肿瘤中的应用及研究进展[J]. 国际放射医学核医学杂志, 2019, 43(2): 171-175. | |
| [101] | YANG J, SUI S F, LIU Z. Brain structure and structural basis of neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Biophys Rep, 2022, 8(3): 170-181. |
| [102] | LONG H, ZENG S, LI D. Cellular and animal models to investigate pathogenesis of amyloid aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Biophys Rep, 2022, 8(1): 14-28. |
| [1] | MA Yun, GUO Hong, WANG Qiu-shi, ZHANG Wei-guo, WU Hao. Correlations Between Morphological Characteristics and Expression Levels of Specific Molecular Biomarkers in Glioblastoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2018, 35(1): 22-30. |
| [2] | ZHOU Jin-yuan1,2*, HONG Xiao-hua1,3. Molecular Imaging Using Endogenous Cellular Proteins [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2013, 30(3): 307-321. |
| [3] | Lindon J C, Holmes E, Nicholson J K. Recent Developments and Applications of NMR-Based Metabonomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2006, 23(1): 101-127. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 158
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 151
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||