
- Dec. 4, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 96-107.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212910
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Kai-rui HU,Xue YANG,Zhi-ming HUANG,Jia-xiang XIN,Da-xiu WEI*( ),Ye-feng YAO*(
),Ye-feng YAO*( )
)
Received:2021-04-16
Published:2022-03-05
Online:2021-06-02
Contact:
Da-xiu WEI,Ye-feng YAO
E-mail:dxwei@phy.ecnu.edu.cn;yfyao@phy.ecnu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Kai-rui HU,Xue YANG,Zhi-ming HUANG,Jia-xiang XIN,Da-xiu WEI,Ye-feng YAO. Preparing Nuclear Spin Singlet State in a Three-spin System and Its Application in 2D Spectrum[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 96-107.

Fig.2
(a) Optimal control (OC/OC′) pulse sequence for preparing and converting nuclear spin singlet state. The combination of CW and gradient field can remove spin coherent-states and retain nuclear spin singlet state. (b) The amplitude of OCI pulse versus time while OCI works; (c) The phase of OCI pulse versus time while OCI works
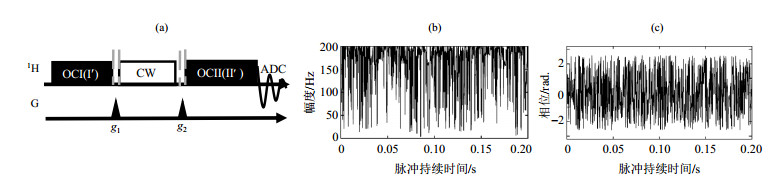
Fig.3
(a) The evolution trajectory of the spin states in a two-spin system (assume no J-coupling between Hb and Ha, Ha') operated by the pulse OCI; (b) The evolution trajectory of the spin states in an actual three-spin system operated by the pulse OCI'; (c) The evolution trajectory of the spin states in a three-spin system operated by the pulse OCI
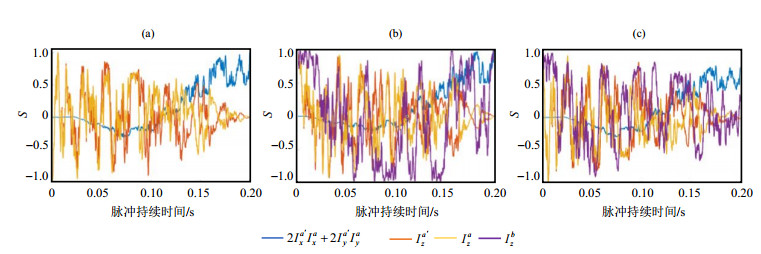
Fig.5
(a) Simulated singlet state spectra of NAA solution with pH of 2.3 obtained by (1) OC pulse sequence, (2) OC' pulse sequence, and its (3) simulated and (4) experimental single pulse 1H NMR spectra; (b) Four simulated singlet state spectra using OC' pulse sequence with offsetting the radio frequency center O1 of (1) 10 Hz, (2) 5 Hz, (3) ?5 Hz, (4) ?10 Hz, respectively; (c) Simulated (1) singlet state spectrum with OC′′ pulse and (2) single pulse 1H NMR spectrum of NAA solution with pH of 5.5
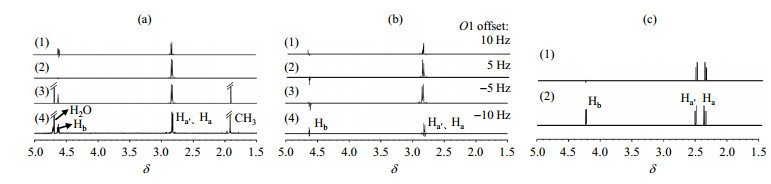
Fig.6
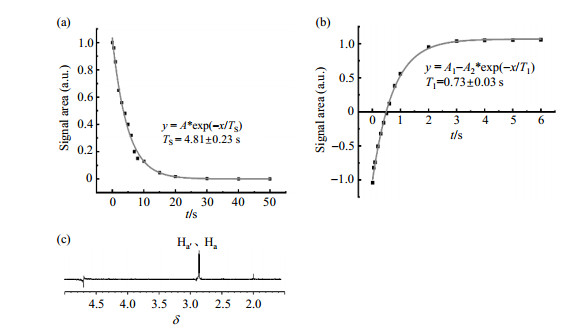
(a) The TS decay curve of the singlet state of Ha, Ha′ in NAA, TS=4.81±0.23 s; (b) The T1 decay curve of Ha、Ha′ in NAA, T1=0.73±0.03 s; (c) Experimental 1D NMR spectrum (the sample pH=2.3) of the nuclear spin singlet state. The gradient pulse and CW pulse have the effect of signal selection. The signals of Ha and Ha′ are reserved, while the other signals are suppressed
| 1 |
CARRAVETTA M , JOHANNESSEN O G , LEVITT M H . Beyond the T1 limit: singlet nuclear spin states in low magnetic fields[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 92 (15): 153003.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.153003 |
| 2 |
CARRAVETTA M , LEVITT M H . Long-lived nuclear spin states in high-field solution NMR[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126 (20): 6228- 6229.
doi: 10.1021/ja0490931 |
| 3 |
PILEIO G , LEVITT M H . Theory of long-lived nuclear spin states in solution nuclear magnetic resonance. Ⅱ. Singlet spin locking[J]. J Chem Phys, 2009, 130 (21): 214501.
doi: 10.1063/1.3139064 |
| 4 |
DUMEZ J N , HAKANSSON P , MAMONE S , et al. Theory of long-lived nuclear spin states in methyl groups and quantum-rotor induced polarisation[J]. J Chem Phys, 2015, 142 (4): 044506.
doi: 10.1063/1.4906273 |
| 5 |
STEVANATO G , ROY S S , HILL-COUSINS J , et al. Long-lived nuclear spin states far from magnetic equivalence[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2015, 17 (8): 5913- 5922.
doi: 10.1039/C4CP05704J |
| 6 |
LEVITT M H . Singlet nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Annu Rev Phys Chem, 2012, 63, 89- 105.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-032511-143724 |
| 7 |
TAYLER M C D , LEVITT M H . Singlet nuclear magnetic resonance of nearly-equivalent spins[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2011, 13 (13): 5556- 5560.
doi: 10.1039/c0cp02293d |
| 8 |
DEVIENCE S J , WALSWORTH R L , ROSEN M S . Preparation of nuclear spin singlet states using spin-lock induced crossing[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2013, 111 (17): 173002.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.173002 |
| 9 |
CARRAVETTA M , LEVITT M H . Theory of long-lived nuclear spin states in solution nuclear magnetic resonance. I. Singlet states in low magnetic field[J]. J Chem Phys, 2005, 122 (21): 214505.
doi: 10.1063/1.1893983 |
| 10 |
PILEIO G , CARRAVETTA M , HUGHES E , et al. The long-lived nuclear singlet state of 15N-nitrous oxide in solution[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130 (38): 12582- 12583.
doi: 10.1021/ja803601d |
| 11 |
SARKAR R , VASOS P , BODENHAUSEN G . Singlet-state exchange NMR spectroscopy for the study of very slow dynamic processes[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129 (2): 328- 334.
doi: 10.1021/ja0647396 |
| 12 |
PILEIO G , OSTROWSKA S . Accessing the long-time limit in diffusion NMR: The case of singlet assisted diffusive diffraction q-space[J]. J Magn Reson, 2017, 285, 1- 7.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2017.10.003 |
| 13 |
CAVADINI S , DITTMER J , ANTONIJEVIC S , et al. Slow diffusion by singlet state NMR spectroscopy[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127 (45): 15744- 15748.
doi: 10.1021/ja052897b |
| 14 |
PILEIO G , BOWEN S , LAUSTSEN C , et al. Recycling and imaging of nuclear singlet hyperpolarization[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135 (13): 5084- 5088.
doi: 10.1021/ja312333v |
| 15 |
KOVTUNOV K V , TRUONG M L , BARSKIY D A , et al. Long-lived spin States for low-field hyperpolarized gas MRI[J]. Chemistry, 2014, 20 (45): 14629- 14632.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201405063 |
| 16 |
SINGH M , SONI V K , MISHRA R , et al. Relaxation editing using long-lived states and coherences for analysis of mixtures[J]. Anal Chem, 2016, 88 (6): 3004- 3008.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00050 |
| 17 |
PILEIO G , CARRAVETTA M , LEVITT M H . Storage of nuclear magnetization as long-lived singlet order in low magnetic field[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107 (40): 17135- 17139.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010570107 |
| 18 |
BENGS C , SABBA M , JERSCHOW A , et al. Generalised magnetisation-to-singlet-order transfer in nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2020, 22 (17): 9703- 9712.
doi: 10.1039/D0CP00935K |
| 19 |
PILEIO G . Singlet NMR methodology in two-spin-1/2 systems[J]. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc, 2017, 98-99, 1- 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.11.002 |
| 20 |
DEVIENCE S J , WALSWORTH R L , ROSEN M S . Nuclear spin singlet states as a contrast mechanism for NMR spectroscopy[J]. NMR Biomed, 2013, 26 (10): 1204- 1212.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.2936 |
| 21 | GUO H Q , XIN J X , LIU H X , et al. Preparation of long-lived nuclear singlet states in three-spin systems[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2018, 35 (3): 345- 352. |
| 郭海清, 辛家祥, 刘慧霞, 等. 三自旋体系长寿命核自旋单重态的制备[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2018, 35 (3): 345- 352. | |
| 22 |
KHANEJA N , REISS T , KEHLET C , et al. Optimal control of coupled spin dynamics: design of NMR pulse sequences by gradient ascent algorithms[J]. J Magn Reson, 2005, 172 (2): 296- 305.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2004.11.004 |
| 23 | LI Y , XIN J X , WANG J C , et al. Comparison of preparation efficiencies of nuclear spin singlet state based on three pulse sequences[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38 (2): 227- 238. |
| 李毅, 辛家祥, 王嘉琛, 等. 三种脉冲序列制备核自旋单重态效率的比较[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38 (2): 227- 238. | |
| 24 | LIU H X , XIN J X , WEI D X , et al. Preparation of nuclear spin singlet states and analysis of influencing factors on their conversion efficiency and lifetime[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37 (2): 182- 192. |
| 刘慧霞, 辛家祥, 魏达秀, 等. 核自旋单重态的制备及其转化效率和寿命的影响因素分析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37 (2): 182- 192. | |
| 25 |
WEI D X , XIN J X , HU K R , et al. Preparation of long-lived states in a multi-spin system by using an optimal control method[J]. Chemphyschem, 2020, 21 (12): 1326- 1330.
doi: 10.1002/cphc.202000038 |
| 26 |
TOŠNER Z , VOSEGAARD T , KEHLET C , et al. Optimal control in NMR spectroscopy: Numerical implementation in SIMPSON[J]. J Magn Reson, 2009, 197 (2): 120- 134.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2008.11.020 |
| 27 | В. И. 阿诺尔德著. 齐民友译. 经典力学中的数学方法(第4版)[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社. 2006. |
| [1] | KOU Xinhui, ZHANG Yubing. Study on the Enantiomeric Recognition of Chiral Ureas Containing Amino Acid Units [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 221-230. |
| [2] | DU Qunjie. Experimental Study on Accurate Determination of Shale Porosity by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 275-284. |
| [3] | SHAO Zhengze, WANG Xingle, YANG Xue, XIN Jiaxiang, WEI Daxiu, YAO Yefeng. A Spectral Editing Technique Based on Optimized Control of Nuclear Spin to Realize Lactate Signal Selection [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 1-12. |
| [4] | SHEN Zhiqiang, DENG Yabo, YANG Peiju, HU Xiaoxue, HUANG Xiaojuan, XU Chuanzhi, SONG Huanling. Design and Application of an in situ NMR Device for Light-Induced Reaction Systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 22-33. |
| [5] | ZHU Xiangwei, YANG Xue, WEI Daxiu, YAO Yefeng. In Vivo Glutathione Molecular MRS Signal Selection Based on Nuclear Spin Singlet States [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 373-381. |
| [6] | LIU Tingwei, PENG Bowen, XU Yajie, WANG Ya, WANG Feng, YU Peng, YANG Xiaodong. A Design of Active Shimming Power Supply for Magnetic Resonance Spectrometers [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 117-127. |
| [7] | LI Zhengzhe, GUO Liang, REN Xuhu. A Passive Shimming Method for Halbach Magnet Based on Numerical Optimization Algorithm [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 128-138. |
| [8] | WANG Ziwen, XIN Jiaxiang, WEI Daxiu, YAO Yefeng. Preparation Efficiency of Singlet States in Multi-spin Systems with Different Coupling Configurations [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 67-76. |
| [9] | XU Xiaojie, CHEN Yan’an, LI Xufei, ZHANG Yuncai, ZHANG Yong, ZHAN Dongkai, PAN Ting. Structural Elucidation of Hybutimibe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 43-55. |
| [10] | WANG Feng, LIU Tingwei, XU Yajie, YU Peng, WANG Ya, PENG Bowen, YANG Xiaodong. A Miniaturised NMR RF Probe Design with External Field-locking Channel [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 332-340. |
| [11] | WANG Yuanfang,WANG Xiaohua,SHU Chang,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili,ZENG Danyun. The Aggregation of ATAD2 Bromodomain in Solution [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 169-178. |
| [12] | GUO Jiangfeng,MACMILLAN Bryce,BALCOM Bruce. Insights into the Phase Structure and Dynamics of Polyurethane Rubber Using T1-T2* Relaxation Correlation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 111-121. |
| [13] | ZHAO Chang,GONG Zhou. Investigation of Dynamic Structure of Protein Encountering Complex with Paramagnetic NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 148-157. |
| [14] | DONG Hongchun,ZHANG Zhilan,WANG Ning,TANG Dandan,QIU Zihui,SHU Jie. The Improved Solid-state NMR Quantitative Method on the Bases of Multiple-cross Polarization Technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 136-147. |
| [15] | ZHAN Jianhua,HU Qin,ZHU Qinjun,JIANG Bin,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili. Track the Conformational Change of Unlabeled Yeast Cytochrome c in Cell Homogenate Using NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 22-29. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 248
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||