
- Dec. 4, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 192-206.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20223027
• Review Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
HE Caiyan1,2,XIAO Yuqing1,2,LI Shenhui1,*( ),XU Jun1,DENG Feng1,#(
),XU Jun1,DENG Feng1,#( )
)
Received:2022-10-10
Published:2023-06-05
Online:2022-11-03
Contact:
LI Shenhui,DENG Feng
E-mail:lishenhui@wipm.ac.cn;dengf@wipm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
HE Caiyan,XIAO Yuqing,LI Shenhui,XU Jun,DENG Feng. Solid-state NMR Investigation of the Host-guest Interactions in Gas Adsorption and Chemical Separation Using MOFs as Adsorbents[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 192-206.
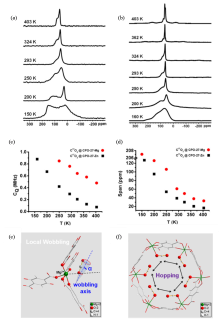
Fig. 2
Static variable temperature 17O NMR spectra of C17O2 adsorbed on (a) Mg-CPO-27 and (b) Zn-CPO-27 at temperatures ranging from 150 to 403 K. (c)~(d) Temperature-dependence of quadrupole coupling constant (CQ) and chemical shift anisotropy (CSA) span (Ω) of C17O2 adsorbed in M-CPO-27. (e)~(f) Dynamic motion of adsorbed CO2 molecules in Mg-CPO-27. Adsorbed CO2 mainly undergoes two different motions: (e) wobbling and (f) hopping[40]


Fig. 3
(a) 1H MAS NMR spectra of ethane/ethylene co-adsorbed on ZIF-8, ZIF-90 and ZIF-8-90 at 1.9 bar; (b) Ethane selectivity in ZIF-8, ZIF-90 and ZIF-8-90 determined by IAST predications and 1H MAS NMR experiments; (c) 2D 1H-1H T2-filtered spin diffusion homo-nuclear correlation NMR spectra and extracted F2 slices of ZIF-8 upon adsorption of ethane and ethylene at 1.1 bar; Density distribution contours for equi-molar mixtures of ethane (d) and ethylene (e) on ZIF-8 at 1 bar[51]

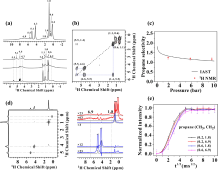
Fig. 4
(a) 1H MAS NMR spectra of propane/propylene co-adsorbed on ZIF-8 at 1.1, 1.9, 5.8 and 9.6 bar; (b) 2D 1H-1H COSY MAS NMR spectrum of propane/propylene co-adsorbed on ZIF-8 at 9.6 bar; (c) Propane selectivity in ZIF-8 determined by IAST predications and 1H MAS NMR experiments; (d) 2D 1H-1H T2-filtered spin diffusion homo-nuclear correlation NMR spectra and extracted F2 slices of ZIF-8 upon adsorption of propane and propylene at 1.1 bar; (e) Spin diffusion buildup curves for the designated polarization transfer pathway from propane CH3 and CH2-group to ZIF-8 framework[52]

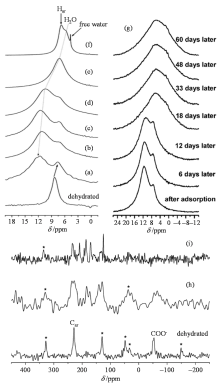
Fig. 5
(a)~(f) 1H MAS spectra of dehydrated Cu3(btc)2 and upon adsorption of (a) 0.5, (b) 0.75, (c) 1, (d) 1.5, (e) 2, and (f) 5 mole equivalents of water with respect to copper loaded on Cu3(btc)2; (g) 1H MAS NMR spectra of water (1 mole equivalents with respect to copper) loaded on Cu3(btc)2 over a period of time after adsorption; 13C direct polarization (DP) MAS spectra of (h) 1 and (i) 2 mole equivalents of water with respect to copper loaded on Cu3(btc)2 over a period of time after adsorption[57]

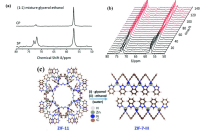
Fig. 7
(a) 13C single pulse (SP) and cross polarization (CP) NMR spectra of ZIF-11 loaded with 1 mol/L 1:1 glycerol:ethanol solution; (b) Time-dependence of 13C SP NMR spectra of ZIF-11 loaded with 1:1 glycerol:ethanol solution; (c) Structural transformation of ZIF-7-III from ZIF-11 upon the removal of guest solvents[65]

| [1] |
FURUKAWA H, CORDOVA K E, O’KEEFFE M, et al. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6149): 1230444.
doi: 10.1126/science.1230444 |
| [2] |
ZHOU H C, LONG J R, YAGHI O M. Introduction to metal-organic frameworks[J]. Chem Rev, 2012, 112(2): 673-674.
doi: 10.1021/cr300014x |
| [3] |
QI G D, WANG Q, XU J, et al. Solid-state NMR studies of internuclear correlations for characterizing catalytic materials[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2021, 50(15): 8382-8399.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS01130D |
| [4] |
MARCHETTI A, CHEN J, PANG Z, et al. Understanding surface and interfacial chemistry in functional nanomaterials via solid-state NMR[J]. Adv Mater, 2017, 29(14): 1605895.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.14 |
| [5] | FAN B H, XU S T, WEI Y X, et al. Progresses of hyperpolarized 129Xe NMR application in porous materials and catalysis[J]. Magn Reson Lett, 2021, 1(1): 11-27. |
| [6] | YANG W J, HUANG J. Analysis of local structure, acidic property and activity of solid acids by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38(4): 460-473. |
| 杨文杰, 黄骏. 基于固体核磁共振技术的固体酸结构、酸性及活性分析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(4): 460-473. | |
| [7] | XIAO Y, XIA C J, YI X F, et al. Progress in the studies on Sn-zeolites by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38(4): 571-584. |
| 肖瑶, 夏长久, 易先锋, 等. 固体核磁共振技术在锡硅分子筛表征中的应用[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(4): 571-584. | |
| [8] |
XU J, LIU Y M, LIPTON A S, et al. Amine dynamics in diamine-appended Mg2 (dobpdc) metal-organic frameworks[J]. J Phys Chem Lett, 2019, 10(22): 7044-7049.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b02883 |
| [9] | LI X, SHEN W L, SUN H. Solid-state NMR studies of sulfonated SBA-15 and the synergistic catalysis of fructose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with dimethyl sulfoxide[J]. Magn Reson Lett, 2022, 2(1): 38-47. |
| [10] | WANG C, DAI W L, WU G J, et al. Application of ammonia probe-assisted solid-state NMR technique in zeolites and catalysis[J]. Magn Reson Lett, 2022, 2(1): 28-37. |
| [11] | GAO X Z, ZHANG Y, WANG X M, et al. Structure and acidity changes in ultra-stable Y zeolites during hydrothermal aging: A solid-state NMR spectroscopy study[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37(1): 95-103. |
| 高秀枝, 张翊, 王秀梅, 等. NMR研究超稳Y分子筛水热老化过程中结构与酸性的变化[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(1): 95-103. | |
| [12] | WANG Y X, WANG Q, XU J, et al. The effects of ammonium hexafluorosilicate post-treatment on the acidity of H-ZSM-5 zeolite studied by solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38(4): 514-522. |
| 王永祥, 王强, 徐君, 等. 六氟硅酸铵后处理对H-ZSM-5分子筛酸性影响的固体NMR研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(4): 514-522. | |
| [13] |
WONG Y T A, MARTINS V, LUCIER B E, et al. Solid-state NMR spectroscopy: A powerful technique to directly study small gas molecules adsorbed in metal-organic frameworks[J]. Chem - Eur J, 2019, 25(8): 1848-1853.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v25.8 |
| [14] |
BRUNNER E, RAUCHE M. Solid-state NMR spectroscopy: an advancing tool to analyse the structure and properties of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Chem Sci, 2020, 11(17): 4297-4304.
doi: 10.1039/d0sc00735h pmid: 34122887 |
| [15] | BERTMER M. Solid-state NMR of small molecule adsorption in metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)[M]. ATTAURRAHMAN Ed Annu Rep NMR Spectrosc, 2020: 1-64. |
| [16] |
FU Y, GUAN H X, YIN J L, et al. Probing molecular motions in metal-organic frameworks with solid-state NMR[J]. Coord Chem Rev, 2021, 427: 213563.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213563 |
| [17] |
JAEGERS N R, MUELLER K T, WANG Y, et al. Variable temperature and pressure operando MAS NMR for catalysis science and related materials[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2020, 53(3): 611-619.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00557 |
| [18] |
WITHERSPOON V J, XU J, REIMER J A. Solid-state NMR investigations of carbon dioxide gas in metal-organic frameworks: Insights into molecular motion and adsorptive behavior[J]. Chem Rev, 2018, 118(20): 10033-10048.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00695 pmid: 30288971 |
| [19] |
LUCIER B E, CHEN S S, HUANG Y N. Characterization of metal-organic frameworks: Unlocking the potential of solid-state NMR[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2018, 51(2): 319-330.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00357 |
| [20] | UR REHMAN S, XU S, XU H T, et al. The role of NMR in metal organic frameworks: deep insights into dynamics, structure and mapping of functional groups[J]. Mater Today Adv, 2022, 16: 100287. |
| [21] |
HE C Y, LI S H, XIAO Y Q, et al. Application of solid-state NMR techniques for structural characterization of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson, 2022, 117: 101772.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2022.101772 |
| [22] | LI Y X, ZHANG W L, HUANG Y N. Two open metal sites on the same metal: Dynamics of CO2 in MOF UTSA-74[J]. Magn Reson Lett, 2021, 1(2): 121-130. |
| [23] |
LI S H, LAFON O, WANG W Y, et al. Recent advances of solid-state NMR spectroscopy for microporous materials[J]. Adv Mater, 2020, 32(44): 2002879.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.44 |
| [24] |
ASHBROOK S E, DAVIS Z H, MORRIS R E, et al. O-17 NMR spectroscopy of crystalline microporous materials[J]. Chem Sci, 2021, 12(14): 5016-5036.
doi: 10.1039/D1SC00552A |
| [25] |
PAUL G, BISIO C, BRASCHI I, et al. Combined solid-state NMR, FT-IR and computational studies on layered and porous materials[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2018, 47(15): 5684-5739.
doi: 10.1039/c7cs00358g pmid: 30014075 |
| [26] |
DING S Y, DONG M, WANG Y W, et al. Thioether-based fluorescent covalent organic framework for selective detection and facile removal of mercury(II)[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2016, 138(9): 3031-3037.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b10754 |
| [27] |
COMOTTI A, BRACCO S, BEN T, et al. Molecular rotors in porous organic frameworks[J]. Angew Chem, 2014, 53(4): 1043-1047.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201309362 |
| [28] |
LUCIER B E, ZHANG Y, LEE K J, et al. Grasping hydrogen adsorption and dynamics in metal-organic frameworks using 2H solid-state NMR[J]. Chem Commun, 2016, 52(48): 7541-7544.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC03205B |
| [29] |
ZHANG Y, LUCIER B E, FISCHER M, et al. A multifaceted study of methane adsorption in metal-organic frameworks by using three complementary techniques[J]. Chem - Eur J, 2018, 24(31): 7866-7881.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.31 |
| [30] |
CHEN M S, CHEN S S, CHEN W, et al. Analyzing gas adsorption in an amide-functionalized metal organic framework: are the carbonyl or amine groups responsible?[J]. Chem Mater, 2018, 30(11): 3613-3617.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b00681 |
| [31] |
KHUDOZHITKOV A E, ARZUMANOV S S, KOLOKOLOV D I, et al. UiO-66 (Zr) MOF as a promising material for butane isomers separation: Evidence based on the analysis of the adsorbed alkanes mobility by 2H NMR and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2021, 125(24): 13391-13400.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c02849 |
| [32] |
LI J, LI S H, ZHENG A M, et al. Solid-state NMR studies of host-guest interaction between UiO-67 and light alkane at room temperature[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2017, 121(26): 14261-14268.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b04611 |
| [33] |
XIAO Y Q, CHU Y Y, LI S H, et al. Primary adsorption sites of light alkanes in multivariate UiO-66 at room temperature as revealed by solid-state NMR[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2020, 124(6): 3738-3746.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c00184 |
| [34] |
DVOYASHKINA N, FREUDE D, ARZUMANOV S S, et al. Monitoring the diffusivity of light hydrocarbons in a mixture by magic angle spinning pulsed field gradient NMR: methane/ethane/ethene in ZIF-8[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2017, 121(45): 25372-25376.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b09335 |
| [35] |
CHMELIK C, FREUDE D, BUX H, et al. Ethene/ethane mixture diffusion in the MOF sieve ZIF-8 studied by MAS PFG NMR diffusometry[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2012, 147(1): 135-141.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.06.009 |
| [36] |
BANIANI A, CHMELIK C, FORMAN E M, et al. Anomalous relationship between molecular size and diffusivity of ethane and ethylene inside crystals of zeolitic imidazolate framework-11[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2019, 123(27): 16813-16822.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b03933 |
| [37] |
FREUDE D, DVOYASHKINA N, ARZUMANOV S S, et al. NMR study of the host structure and guest dynamics investigated with alkane/alkene mixtures in metal organic frameworks ZIF-8[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2018, 123(3): 1904-1912.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b11673 |
| [38] |
WEHRING M, GASCON J, DUBBELDAM D, et al. Self-diffusion studies in CuBTC by PFG NMR and MD simulations[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2010, 114(23): 10527-10534.
doi: 10.1021/jp102212w |
| [39] |
KONG X Q, SCOTT E, DING W, et al. CO2 dynamics in a metal-organic framework with open metal sites[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134(35): 14341-14344.
doi: 10.1021/ja306822p |
| [40] |
WANG W D, LUCIER B E, TERSKIKH V V, et al. Wobbling and hopping: studying dynamics of CO2 adsorbed in metal-organic frameworks via 17O solid-state NMR[J]. J Phys Chem Lett, 2014, 5(19): 3360-3365.
doi: 10.1021/jz501729d |
| [41] |
LU Y J, LUCIER B E, ZHANG Y, et al. Sizable dynamics in small pores: CO2 location and motion in the α-Mg formate metal-organic framework[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2017, 19(8): 6130-6141.
doi: 10.1039/C7CP00199A |
| [42] |
ZHANG Y, LUCIER B E, HUANG Y N. Deducing CO2 motion, adsorption locations and binding strengths in a flexible metal-organic framework without open metal sites[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2016, 18(12): 8327-8341.
doi: 10.1039/C5CP04984A |
| [43] |
WU B W, WONG Y A, LUCIER B E, et al. Exploring host-guest interactions in the α-Zn3 (HCOO)6 metal-organic framework[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(2): 4000-4011.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b03623 |
| [44] |
CHEN S S, LUCIER B E, BOYLE P D, et al. Understanding the fascinating origins of CO2 adsorption and dynamics in MOFs[J]. Chem Mater, 2016, 28(16): 5829-5846.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b02239 |
| [45] |
GUL-E-NOOR F, MENDT M, MICHEL D, et al. Adsorption of small molecules on Cu3(btc)2 and Cu3-xZnx(btc)2 metal-organic frameworks (MOF) as studied by solid-state NMR[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2013, 117(15): 7703-7712.
doi: 10.1021/jp400869f |
| [46] |
DESVEAUX B E, WONG Y A, LUCIER B E, et al. CO2 behavior in a highly selective ultramicroporous framework: insights from single-crystal X-ray diffraction and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2019, 123(29): 17798-17807.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b03221 |
| [47] |
MILNER P J, SIEGELMAN R L, FORSE A C, et al. A diaminopropane-appended metal-organic framework enabling efficient CO2 capture from coal flue gas via a mixed adsorption mechanism[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139(38): 13541-13553.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b07612 |
| [48] |
FORSE A C, MILNER P J, LEE J-H, et al. Elucidating CO2 chemisorption in diamine-appended metal-organic frameworks[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140(51): 18016-18031.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b10203 |
| [49] |
SIEGELMAN R L, MILNER P J, FORSE A C, et al. Water enables efficient CO2 capture from natural gas flue emissions in an oxidation-resistant diamine-appended metal-organic framework[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2019, 141(33): 13171-13186.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b05567 |
| [50] |
DINAKAR B, FORSE A C, JIANG H Z, et al. Overcoming metastable CO2 Adsorption in a bulky diamine-appended metal-organic framework[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2021, 143(37): 15258-15270.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c06434 |
| [51] |
XIAO Y Q, CHU Y Y, LI S H, et al. Host-guest interaction in ethylene and ethane separation on zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as revealed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Chem - Eur J, 2021, 27(44): 11303-11308.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v27.44 |
| [52] |
XIAO Y Q, CHU Y Y, LI S H, et al. Preferential adsorption sites for propane/propylene separation on ZIF-8 as revealed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2022, 24(11): 6535-6543.
doi: 10.1039/d1cp05931a pmid: 35258049 |
| [53] |
SIN M, KAVOOSI N, RAUCHE M, et al. In situ 13C NMR spectroscopy study of CO2/CH4 mixture adsorption by metal-organic frameworks: does flexibility influence selectivity?[J]. Langmuir, 2019, 35(8): 3162-3170.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03554 |
| [54] |
ROZTOCKI K, RAUCHE M, BON V, et al. Combining in situ techniques (XRD, IR, and 13C NMR) and gas adsorption measurements reveals CO2-induced structural transitions and high CO2/CH4 selectivity for a flexible metal-organic framework JUK-8[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13(24): 28503-28513.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c07268 |
| [55] |
LI S H, LI J, TANG J, et al. Host-guest interaction of styrene and ethylbenzene in MIL-53 studied by solid-state NMR[J]. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson, 2018, 90: 1-6.
doi: S0926-2040(17)30150-9 pmid: 29316473 |
| [56] |
XU J, TERSKIKH V V, HUANG Y N. 25Mg solid-state NMR: a sensitive probe of adsorbing guest molecules on a metal center in metal-organic framework CPO-27-Mg[J]. J Phys Chem Lett, 2013, 4(1): 7-11.
doi: 10.1021/jz301954t |
| [57] |
GUL-E-NOOR F, JEE B, PöPPL A, et al. Effects of varying water adsorption on a Cu3(BTC)2 metal-organic framework (MOF) as studied by 1H and 13C solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2011, 13(17): 7783-7788.
doi: 10.1039/c0cp02848g |
| [58] |
GIOVINE R, POURPOINT F, DUVAL S, et al. The surprising stability of Cu3(btc)2 metal-organic framework under steam flow at high temperature[J]. Cryst Growth Des, 2018, 18(11): 6681-6693.
doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00931 |
| [59] |
GUL-E-NOOR F, MICHEL D, KRAUTSCHEID H, et al. Time dependent water uptake in Cu3(btc)2 MOF: Identification of different water adsorption states by 1H MAS NMR[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2013, 180: 8-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.06.033 |
| [60] |
MCHUGH L N, MCPHERSON M J, MCCORMICK L J, et al. Hydrolytic stability in hemilabile metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nat Chem, 2018, 10(11): 1096-1102.
doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0104-x pmid: 30104722 |
| [61] |
GUL-E-NOOR F, JEE B, MENDT M, et al. Formation of mixed metal Cu3-xZnx(btc)2 frameworks with different zinc contents: Incorporation of Zn2+ into the metal-organic framework structure as studied by solid-state NMR[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2012, 116(39): 20866-20873.
doi: 10.1021/jp3054857 |
| [62] |
NANDY A, FORSE A C, WITHERSPOON V J, et al. NMR spectroscopy reveals adsorbate binding sites in the metal-organic framework UiO-66 (Zr)[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2018, 122(15): 8295-8305.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12628 |
| [63] |
TANG J, CHU Y Y, LI S H, et al. Breathing effect via solvent inclusions on the linker rotational dynamics of functionalized MIL-53[J]. Chem - Eur J, 2021, 27(59): 14711-14720.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v27.59 |
| [64] | XU J, TERSKIKH V V, CHU Y Y, et al. 13C chemical shift tensors in MOF α-Mg3(HCOO)6: Which component is more sensitive to host-guest interaction?[J]. Magn Reson Chem, 2020, 58(11): 1082-1090. |
| [65] |
HOSSAINÁ KHAN A, AMANZADEHÁ SALOUT S, SHUPLETSOV L, et al. Solid-state NMR insights into alcohol adsorption by metal-organic frameworks: adsorption state, selectivity, and adsorption-induced phase transitions[J]. Chem Commun, 2022, 58(28): 4492-4495.
doi: 10.1039/D2CC00638C |
| [66] |
XU X H, LI S H, LIU Q, et al. Isolated π-interaction sites in mesoporous MOF backbone for repetitive and reversible dynamics in water[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 11(1): 973-981.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b19211 |
| [67] |
WITTMANN T, MONDAL A, TSCHENSE C B, et al. Probing interactions of N-donor molecules with open metal sites within paramagnetic Cr-MIL-101: a solid-state NMR spectroscopic and density functional theory study[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140(6): 2135-2144.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b10148 pmid: 29316398 |
| [68] |
VENEL F, VOLKRINGER C, LAFON O, et al. Probing adsorption of water and DMF in UiO-66 (Zr) using solid-state NMR[J]. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson, 2022, 120: 101797-101797.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2022.101797 |
| [69] |
BAE J, CHOI J S, HWANG S, et al. Multiple coordination exchanges for room-temperature activation of open-metal sites in metal-organic frameworks[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9(29): 24743-24752.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b07299 |
| [1] | SHEN Xueyuan, WANG Ruichen, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Design of in situ Solid-State NMR Rotor Inserts and Their Application to Catalytic Reactions [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 13-21. |
| [2] | CHEN Yang, ZHOU Meng, LI Yong, YANG Haijun. Independent Development of Sample Preparation Tools for Solid-state NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 77-86. |
| [3] | Chao-wei SHI,Pan SHI,Chang-lin TIAN. NMR Studies of Large Protein Dynamics Using Unnatural Amino Acids [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 523-532. |
| [4] | ZHANG Zhi-jie, LI Duan-xiu, LUO Chun, QIU Ru-chen, DENG Zong-wu, ZHANG Hai-lu. 13C Chemical Shift Assignment of Solid 2-Picolinic Acid by DFT/Crystallography Integrated Approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 67-75. |
| [5] | GAO Xiu-zhi, ZHANG Yi, WANG Xiu-mei, ZHANG Zhi-hua, XU Guang-tong. Structure and Acidity Changes in Ultra-Stable Y Zeolites During Hydrothermal Aging: A Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy Study [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 95-103. |
| [6] | FENG Zong-jing, DU Ya-ping, LUO Feng, XU Jun. An Ultrawide-Line 139La Solid-State NMR Investigation of Layered La(OH)2NO3 [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 76-85. |
| [7] | WANG Yang, YANG Chang-ju, WEN Yu-jie, CHEN Jun-chao, DU Jia-huan, PENG Lu-ming. Analysis of the Concentrations of Surface Ni Ions in Ni/CeO2 With 17O Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 52-60. |
| [8] | XU Guang-yong, DONG Man-yuan, MA Jian-feng, ZHANG Li-min. Molecular Dynamics of Semi-Crystalline Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) Studies by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2019, 36(4): 544-554. |
| [9] | XU Xiao-jun, WANG Shen-lin. Probing Membrane Protein Interactions by 19F Solid-State NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2019, 36(2): 238-251. |
| [10] | GE Yu-wei, LIU Mai-li, GAN Zhe-hong, LI Cong-gang. Measurements of Proton Chemical Shift Anisotropy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2018, 35(2): 255-267. |
| [11] | JIANG Ting-ting, FU Xiao-bin, WU Jin-ze, WANG Jia-chen, YAO Ye-feng, ZHOU Bing. Structure and Dynamics of Polymer-Ceramic Interface in Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5P3O12/Polyether Solid Electrolyte:A Solid-State NMR Study [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2017, 34(4): 429-438. |
| [12] | SUN Yi, CHEN Yan-ke, LI Jian-ping, ZHAO Yong-xiang, YANG Jun. Efficiency of Double Cross Polarization in Magic-Angle Spinning Solid-State NMR Studies on Membrane Proteins [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2017, 34(3): 257-265. |
| [13] | LI Dong-bei, XU Shuai, YU Zhi-wu. Application of Solid-State NMR to Bone and Bone Biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2017, 34(1): 115-129. |
| [14] | PENG Yong-jin, SUN Ping-chuan, LI Bao-hui. Dynamic Evolution in PVPh/PEO Blend Studied by Solid-State NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2016, 33(2): 188-197. |
| [15] | HAN Ming-yue,ZHENG Hui,HU Bing-wen*,YANG Guang*. Compressed Sensing Reconstruction with Iterative Soft Thresholding for Two-Dimensional Solid-State NMR Spectra with Broad Peaks [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2015, 32(4): 551-562. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||